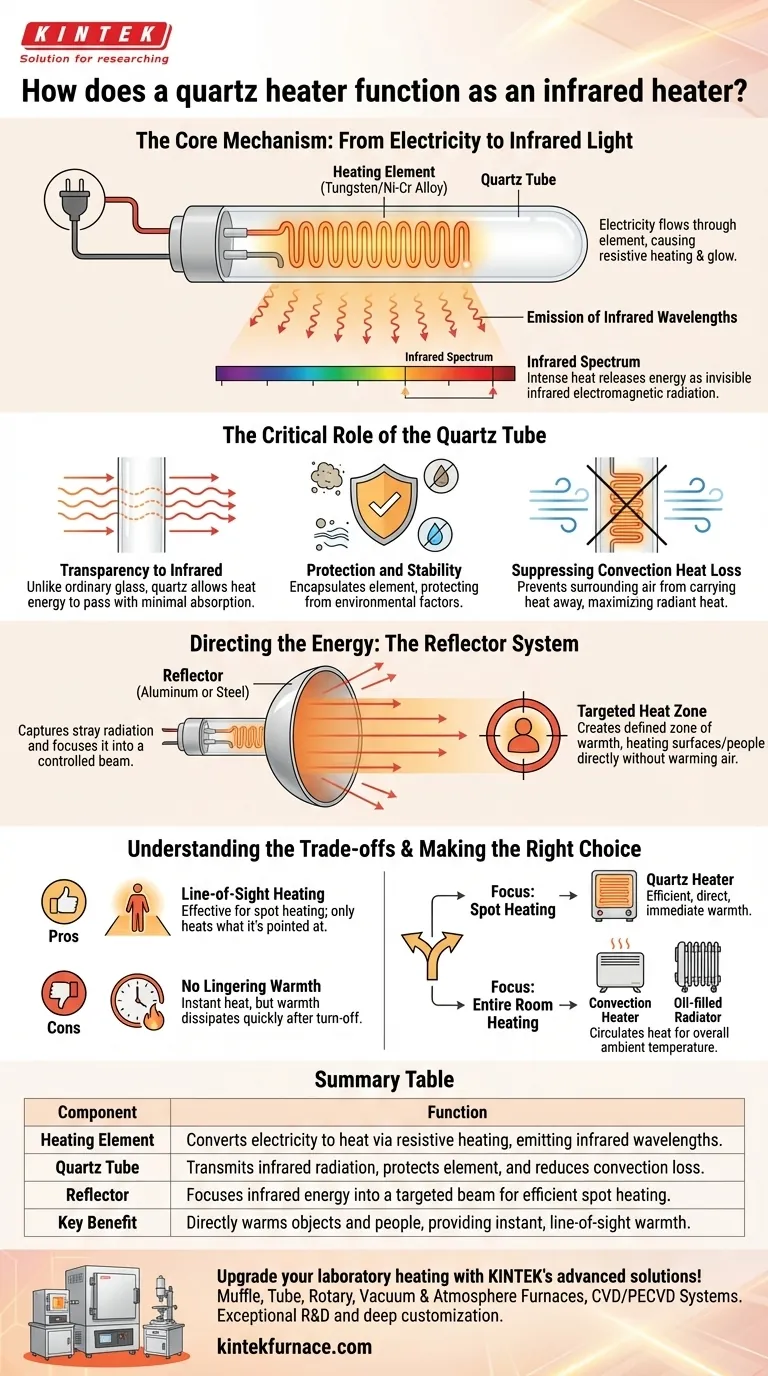
At its core, a quartz heater functions as an infrared heater by passing electricity through a resistive heating element, causing it to heat up and emit thermal radiation. This element is encased in a quartz glass tube, which is transparent to infrared energy. This design allows the invisible radiant heat to pass through and warm objects directly, while protecting the element and minimizing inefficient heat loss to the surrounding air.
A quartz heater is not designed to heat the air in a room. Instead, it converts electricity into targeted infrared radiation—a form of energy that directly warms objects and people in its path, much like the warmth of the sun.
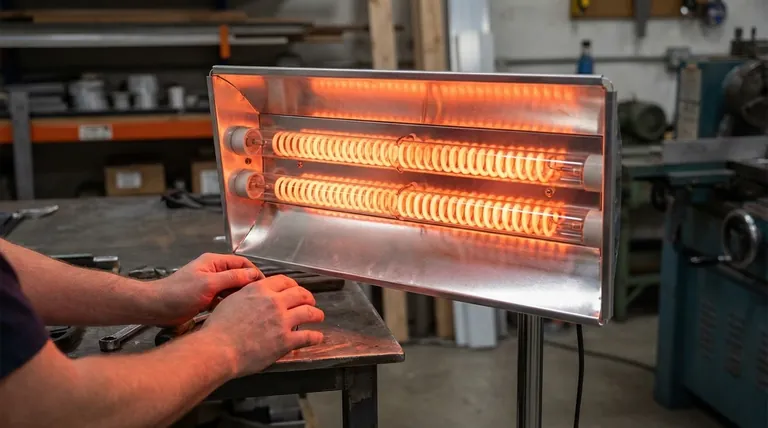

The Core Mechanism: From Electricity to Infrared Light
The Heating Element
A quartz heater's operation begins with a heating element, typically made of a resistance wire like tungsten or a nickel-chromium alloy.
When electricity flows through this element, its natural resistance causes it to get extremely hot and glow, a process known as resistive heating.
Emission of Infrared Wavelengths
This intense heat causes the element to release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. A significant portion of this energy falls within the infrared spectrum, which is invisible to the human eye but felt as heat.
The specific temperature of the element determines the exact wavelength of the infrared energy produced, which is engineered for efficient absorption by common materials, including people.
The Critical Role of the Quartz Tube
Transparency to Infrared
The key to the design is the quartz tube surrounding the element. Unlike ordinary glass, quartz is highly transparent to infrared radiation.
This property allows the heat energy to pass through the tube with minimal absorption, ensuring the maximum amount of energy is projected outward toward the target.
Protection and Stability
The quartz tube serves a vital secondary function: it protects the delicate heating element from dust, moisture, and physical contact.
This encapsulation creates a stable environment, extending the life of the element and ensuring consistent performance.
Suppressing Convection Heat Loss
By containing the element, the quartz tube prevents the surrounding air from directly touching it and carrying heat away through convection. This forces the majority of the energy to be released as radiant heat, which is the heater's intended function.
Directing the Energy: The Reflector System
The Function of the Reflector
Behind the quartz tube sits a polished, optically designed reflector, usually made of aluminum or steel. This component is just as critical as the heating element itself.
Without a reflector, the infrared energy would radiate in all directions, wasting most of it. The reflector captures stray radiation and focuses it forward in a controlled beam.
Creating a Targeted Heat Zone
This focused beam of energy is what allows a quartz heater to provide "spot heating." It creates a defined zone of warmth, directly heating surfaces, objects, and people within its line of sight without needing to warm the intervening air.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Line-of-Sight Heating
The greatest strength of a quartz heater is also its main limitation. It only heats what it is pointed at. If you move out of its path, you will no longer feel the warmth.
It is ineffective for raising the ambient temperature of an entire, poorly-insulated, or drafty room.
No Lingering Warmth
Because quartz heaters transfer energy via radiation, the heating effect is nearly instantaneous. However, once turned off, the warmth dissipates just as quickly.
They do not store thermal energy, unlike oil-filled radiators that continue to release heat after being powered down.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
A quartz heater is a specialized tool, and its effectiveness depends entirely on the heating task at hand.
- If your primary focus is spot heating a specific area: Choose a quartz heater for its efficiency in delivering direct, immediate warmth to a person, a workstation, or a small, defined zone.
- If your primary focus is evenly heating an entire room: Avoid a quartz heater. Consider a convection heater or an oil-filled radiator instead, as these are designed to circulate heat and raise the overall ambient air temperature.
Understanding that a quartz heater is a tool for radiating energy, not heating air, is the key to using it effectively.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Heating Element | Converts electricity to heat via resistive heating, emitting infrared wavelengths |
| Quartz Tube | Transmits infrared radiation, protects element, and reduces convection loss |
| Reflector | Focuses infrared energy into a targeted beam for efficient spot heating |
| Key Benefit | Directly warms objects and people, providing instant, line-of-sight warmth |
Upgrade your laboratory heating with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and performance in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance
- What are the primary applications of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements in furnaces? Achieve High-Temp Excellence
- What types of molybdenum disilicide heating elements are available? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the primary applications of MoSi2 heating elements in research? Achieve Reliable High-Temp Control for Material Synthesis
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)



















