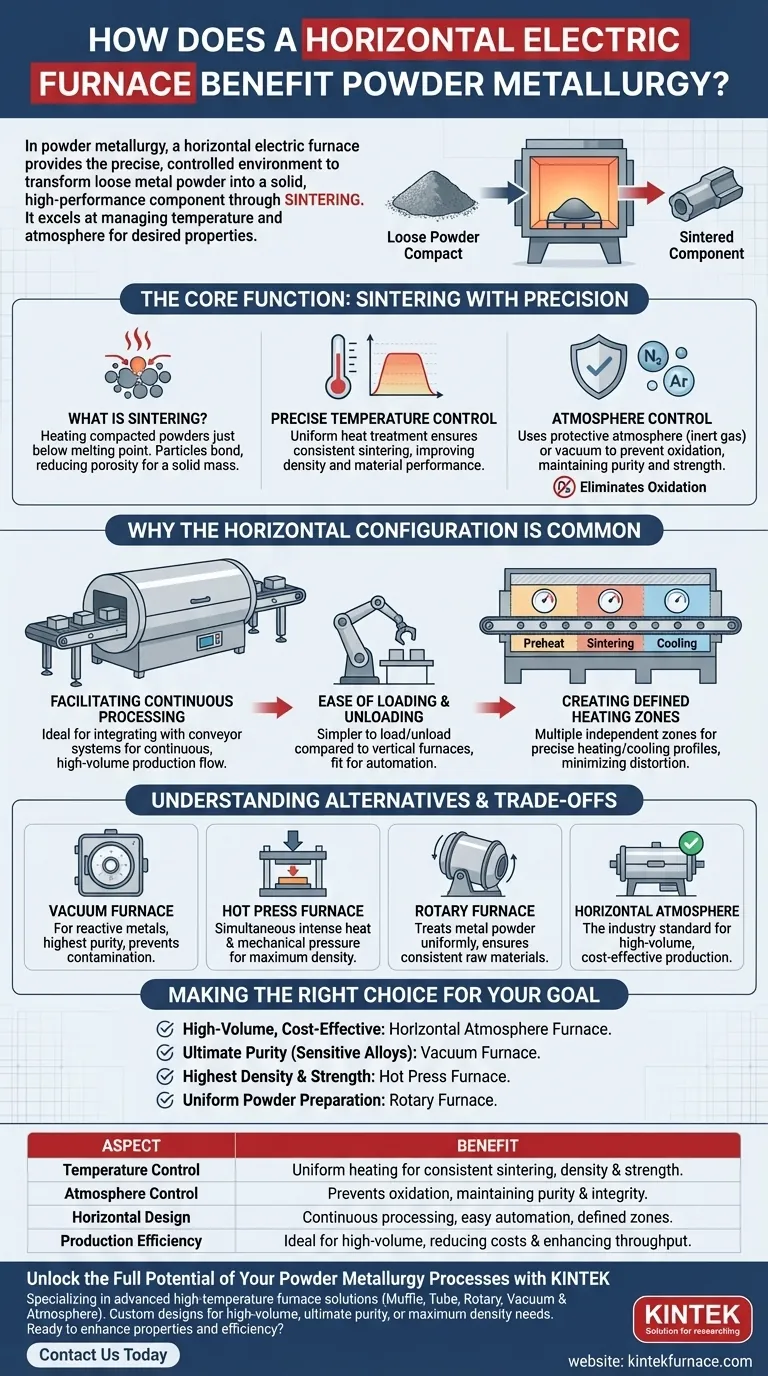
In powder metallurgy, a horizontal electric furnace provides the precise, controlled environment necessary to transform loose metal powder into a solid, high-performance component through a process called sintering. It excels at managing both temperature and atmosphere, which are the two most critical variables for achieving desired material properties like strength and density.
The fundamental benefit is not the furnace shape itself, but its ability to create a stable and repeatable heating environment. This control prevents contamination and ensures powder particles fuse together correctly, dictating the final part's density, strength, and structural integrity.

The Core Function: Sintering with Precision
What is Sintering?
Sintering is the core process in powder metallurgy where compacted metal powders are heated to a temperature just below their melting point.
Instead of melting, the heat energy causes the individual powder particles to bond and fuse together. This reduces the porosity of the initial compact and forms a solid, coherent mass.
The Role of Precise Temperature Control
The final mechanical properties of the sintered part are directly tied to the temperature and duration of the heating cycle.
An electric furnace allows for extremely uniform heat treatment, ensuring all parts of the component are sintered consistently. This precision is key to improving density and enhancing the overall performance of the material.
The Critical Need for Atmosphere Control
At high sintering temperatures, most metals will readily react with oxygen in the air, a process called oxidation.
This oxidation creates impurities that weaken the bonds between particles and severely compromise the part's integrity and strength.
Horizontal furnaces solve this by using a protective atmosphere (such as inert gases like nitrogen or argon) or a vacuum to eliminate oxygen and prevent this destructive contamination.
Why the Horizontal Configuration is Common
Facilitating Continuous Processing
The horizontal layout is ideal for integrating with conveyor systems, creating a "tunnel furnace."
This enables a continuous flow of parts through distinct heating and cooling zones, making it a highly efficient and automated solution for mass production.
Ease of Loading and Unloading
Compared to top-loading vertical furnaces, horizontal "box" or tunnel furnaces are often simpler to load and unload, both manually and with robotics.
Creating Defined Heating Zones
Long horizontal furnaces can be divided into multiple, independently controlled temperature zones. This allows for precise management of the heating and cooling profile as the component moves through the furnace, which is crucial for minimizing internal stresses and distortion.
Understanding the Alternatives and Trade-offs
While the horizontal atmosphere furnace is a workhorse, specific applications demand different technologies.
When a Vacuum Furnace is Essential
For highly reactive metals (like titanium) or applications demanding the absolute highest purity, a vacuum furnace is necessary.
By removing virtually all atmosphere, it provides the ultimate protection against contamination and ensures minimal part distortion.
Hot Press Furnaces for Maximum Density
Some applications require near-total elimination of porosity to achieve maximum strength and performance.
A hot press furnace simultaneously applies intense heat and extreme mechanical pressure to the powder, physically forcing the particles together to create exceptionally dense components.
Rotary Furnaces for Powder Treatment
When the goal is to treat the metal powder itself rather than a compacted part, a rotary furnace is often used. Its constant rotation ensures the entire batch of powder is heated uniformly, which is critical for producing consistent raw materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best furnace is dictated by the material, the desired final properties, and the required production volume.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-effective production: A continuous horizontal atmosphere furnace is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and performance for sensitive alloys: A vacuum furnace is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible density and strength: A hot press furnace is the correct tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is preparing uniform metal powders before compaction: A rotary furnace provides the necessary process consistency.
Choosing the correct furnace technology is a foundational decision that directly determines the quality and performance of the final powder metallurgy component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Ensures uniform heating for consistent sintering, improving material density and strength. |
| Atmosphere Control | Uses protective gases or vacuum to prevent oxidation, maintaining part purity and integrity. |
| Horizontal Design | Facilitates continuous processing, easy loading/unloading, and defined heating zones for automation. |
| Production Efficiency | Ideal for high-volume manufacturing, reducing costs and enhancing throughput. |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Powder Metallurgy Processes with KINTEK
Struggling to achieve precise sintering, uniform heating, or contamination-free results in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we design furnaces to meet your unique experimental requirements, whether for high-volume production, ultimate purity, or maximum density.
Ready to enhance your material properties and boost efficiency? Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can transform your powder metallurgy outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















