High-temperature muffle furnaces ensure precision by acting as a rigorously controlled thermal environment, which is the defining factor in successful manganese ore research. By enforcing specific parameters—such as a steady heating rate of 7 °C/min and maintaining a constant temperature for durations like 4 hours—the furnace drives the predictable transformation of unstable manganese phases into stable, distinct structures.
Precision in this context is not just about reaching a high temperature; it is about the control of time and thermal consistency required to convert volatile manganese-bearing phases into industrially valuable forms like hausmannite or bixbyite.

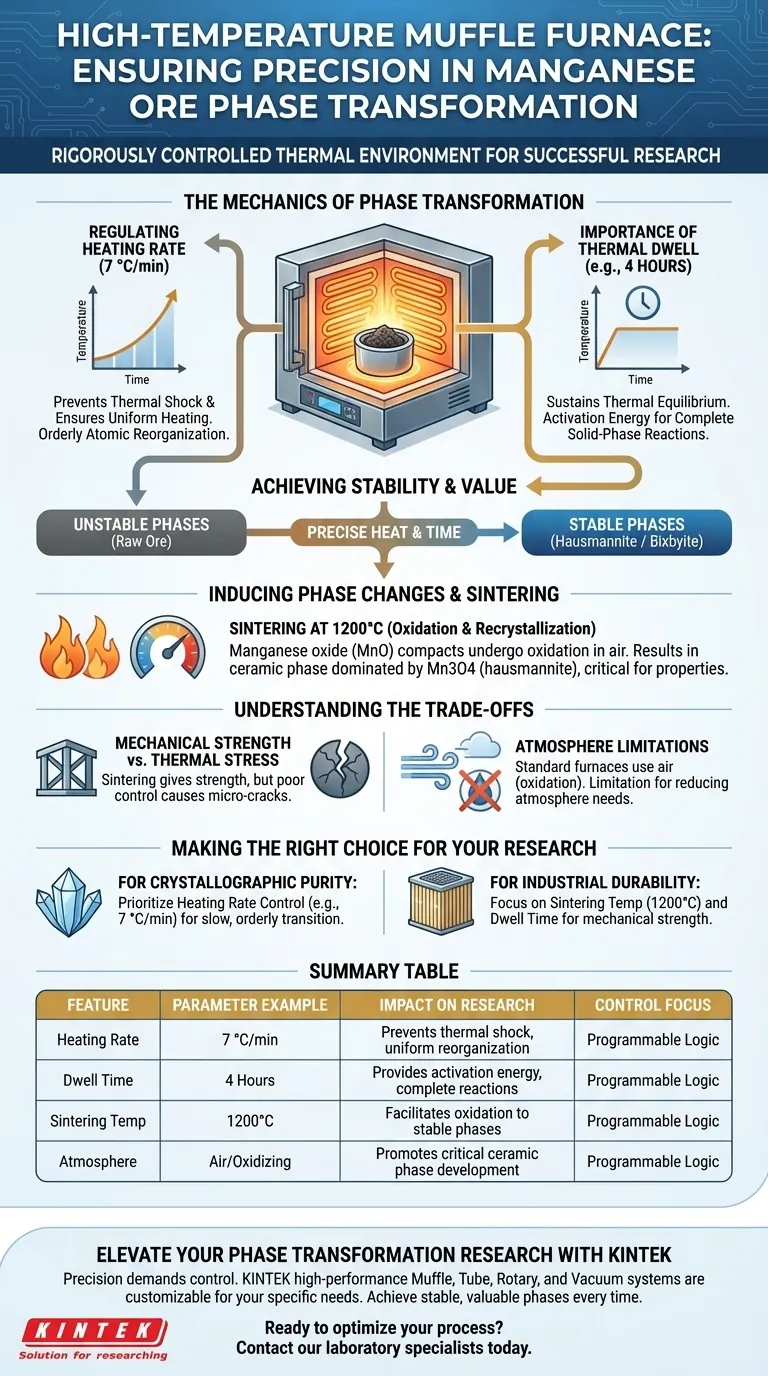
The Mechanics of Phase Transformation
Regulating the Heating Rate
The transformation of manganese ore is highly sensitive to how quickly energy is introduced to the system.
A high-quality muffle furnace allows for programmable heating rates, such as 7 °C/min.
This gradual increase prevents thermal shock and ensures that the material heats uniformly, allowing the atomic structure to reorganize systematically rather than chaotically.
The Importance of Thermal Dwell
Reaching the target temperature is only half the battle; sustaining it is where the chemistry happens.
By holding the temperature constant for extended periods, such as 4 hours, the furnace ensures the material reaches thermal equilibrium.
This "dwell time" provides the necessary activation energy for solid-phase reactions to complete, ensuring the entire sample, not just the surface, undergoes the transformation.
Achieving Chemical and Structural Stability
Inducing Phase Changes
The primary goal of this thermal processing is to stabilize the ore.
Raw manganese ore often contains unstable phases that are unsuitable for industrial use.
The precise heat of the muffle furnace facilitates the conversion of these unstable components into robust phases like hausmannite or bixbyite.
Oxidation and Recrystallization
During the sintering process, particularly around temperatures like 1200°C, significant chemical changes occur.
Manganese oxide (MnO) compacts undergo oxidation and recrystallization in the air environment of the furnace.
This results in a ceramic phase dominated by Mn3O4 (hausmannite), which is critical for the material's final properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Mechanical Strength vs. Thermal Stress
While high temperatures are necessary for sintering, they introduce physical stress to the material.
The sintering process is what gives the final product its mechanical strength, preventing it from collapsing under industrial loads (such as contact with aluminum melts).
However, if the cooling or heating rates are not precisely controlled by the furnace, the material can develop micro-cracks, compromising the very structural stability you are trying to create.
Atmosphere Limitations
Standard muffle furnaces typically operate with an air atmosphere, which promotes oxidation.
This is beneficial for creating Mn3O4, but it is a limitation if your research requires a reducing atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
You must ensure that the furnace's atmospheric conditions align with your specific phase transformation goals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
To get the most out of your manganese ore research, align your furnace settings with your specific end-goal.
- If your primary focus is crystallographic purity: Prioritize the heating rate control (e.g., 7 °C/min) to ensure a slow, orderly transition into phases like bixbyite without inducing defects.
- If your primary focus is industrial durability: Focus on the sintering temperature (up to 1200°C) and dwell time, as these factors directly dictate the mechanical strength required for filtration substrates.
True precision comes from balancing the intensity of the heat with the patience of the ramp rate.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Parameter Example | Impact on Manganese Ore Research |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | 7 °C/min | Prevents thermal shock; ensures uniform atomic reorganization. |
| Dwell Time | 4 Hours | Provides activation energy for complete solid-phase reactions. |
| Sintering Temp | 1200°C | Facilitates oxidation into stable phases like hausmannite (Mn3O4). |
| Atmosphere | Air/Oxidizing | Promotes the development of critical ceramic phases for industrial use. |
| Control Focus | Programmable Logic | Balances mechanical strength against internal thermal stress. |
Elevate Your Phase Transformation Research with KINTEK
Precision in manganese ore research demands more than just heat; it requires absolute control over thermal consistency and atmosphere. KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum systems designed to meet the rigorous standards of material science.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to your specific heating rates and dwelling requirements, ensuring you achieve stable, industrially valuable phases like bixbyite and hausmannite every time.
Ready to optimize your sintering and recrystallization processes? Contact our laboratory specialists today to find the perfect thermal solution for your unique research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Ruslan Sаfarov, L. De Los Santos Valladares. Phase Transitions and Structural Evolution of Manganese Ores During High-Temperature Treatment. DOI: 10.3390/met15010089
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why is operator training important for muffle furnace use? Ensure Safety, Accuracy, and Longevity
- What is the application of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment for Your Lab
- What conditions does a muffle furnace provide for evaluating the oxidation stability of HfOC/SiOC fiber mats?
- What design features enhance the versatility of box furnaces? Boost Your Lab's Thermal Processing Flexibility
- What key performance characteristics are required for laboratory muffle furnaces for Ti-xNb alloys? Expert Guidelines
- How does chamber size affect muffle furnace selection? Ensure Precision with the Right Fit
- What is the function of a laboratory muffle furnace for kaolinite to metakaolin? Precision Dehydroxylation Control
- What role does a laboratory muffle furnace play in the modification of mesoporous silica carriers for drug loading?



















