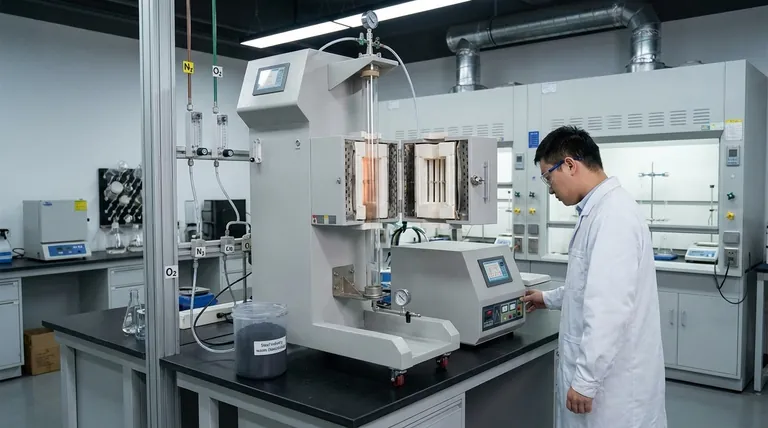
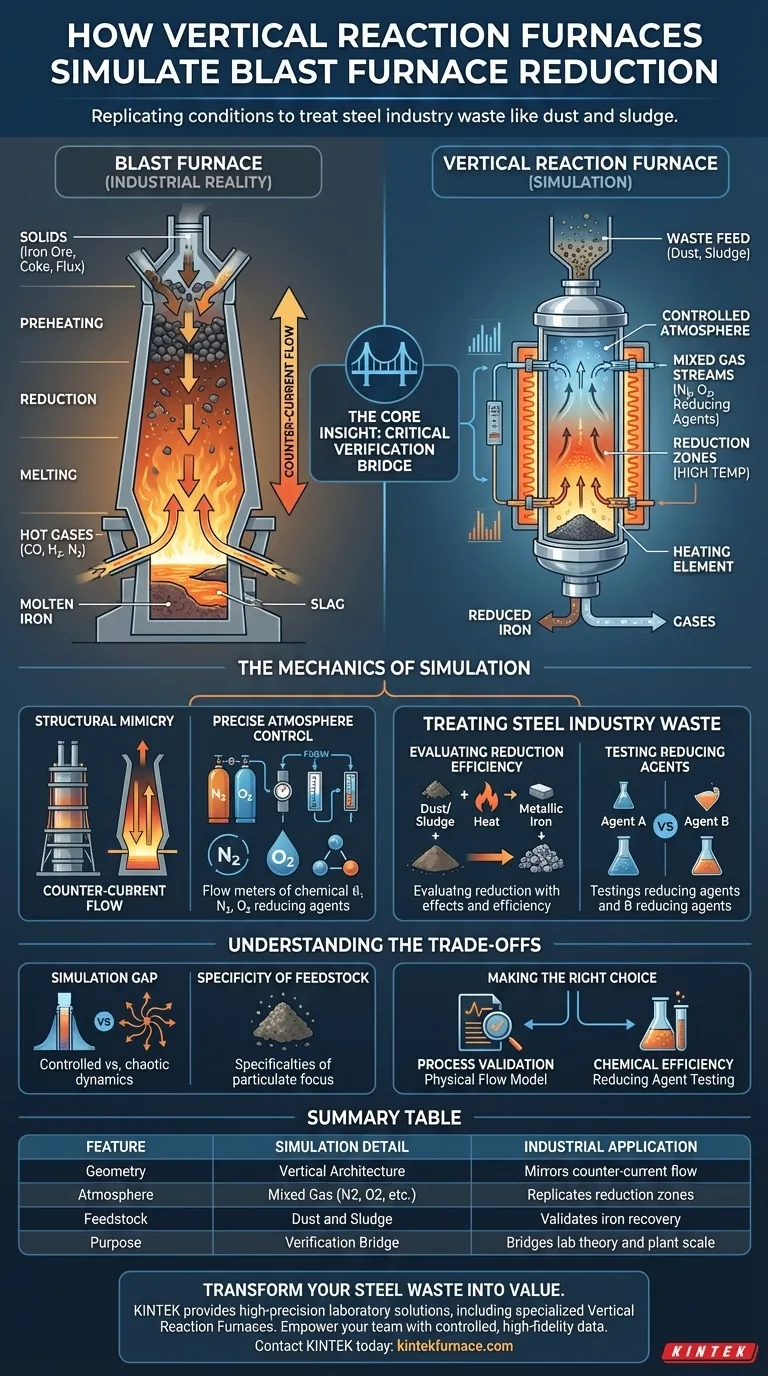
Vertical reaction furnaces replicate the complex internal conditions of a blast furnace by combining a specialized vertical architecture with precise atmospheric controls. These systems utilize mixed gas streams at high temperatures to test how effectively different reducing agents can recover iron from steel industry waste products, such as dust and sludge. By mimicking these specific reduction zones, engineers can evaluate treatment processes without interrupting actual plant operations.
The Core Insight: Vertical reaction furnaces act as the critical verification bridge between laboratory theories and industrial reality. They provide a controlled, high-fidelity environment to validate the efficiency of converting waste into raw materials before scaling up to full blast furnace operations.

The Mechanics of Simulation
Structural Mimicry
The physical design of the furnace is strictly vertical to mirror the geometry of an industrial blast furnace. This allows researchers to replicate the counter-current flow, where solid materials descend while hot gases ascend through the stack.
Precise Atmosphere Control
To simulate specific reduction zones, operators can generate exact mixed gas streams. The system allows for the introduction of gases such as nitrogen and oxygen, creating a controlled environment that mimics the chemical conditions found inside a working furnace.
Treating Steel Industry Waste
Evaluating Reduction Efficiency
The primary application of this technology is testing the recovery of iron from industrial byproducts. The furnace measures how efficiently iron-containing dust and sludge can be reduced back into metallic iron under high heat.
Testing Reducing Agents
Researchers use this setup to compare the performance of various reducing agents. This comparative testing helps identify the most effective chemical agents for treating waste before they are procured for large-scale use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Simulation Gap
While these furnaces are a "critical bridge," they remain simulations. A vertical reaction furnace offers a highly controlled environment, which may not perfectly capture the chaotic physical dynamics or uneven load distributions of a massive, operating blast furnace.
Specificity of Feedstock
The system described is specifically optimized for particulate matter like dust and sludge. While highly effective for waste treatment analysis, the results may not directly translate to the behavior of bulkier raw materials or large iron ore pellets without further correlation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of vertical reaction furnace testing, align your approach with your specific operational needs:
- If your primary focus is process validation: Use the vertical structure to model the physical flow of particulates, ensuring your waste materials will not disrupt the aerodynamics of the actual blast furnace.
- If your primary focus is chemical efficiency: Leverage the precise atmosphere controls to test multiple reducing agents against your specific sludge composition to find the highest yield at the lowest cost.
By accurately simulating reduction zones, vertical reaction furnaces provide the data necessary to transform hazardous industrial waste into valuable production inputs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Simulation Detail | Industrial Application |
|---|---|---|
| Geometry | Vertical Architecture | Mirrors counter-current flow (gas up, solids down) |
| Atmosphere | Mixed Gas (N2, O2, etc.) | Replicates specific reduction zones |
| Feedstock | Dust and Sludge | Validates iron recovery from industrial waste |
| Purpose | Verification Bridge | Bridges the gap between lab theory and plant scale |
Transform Your Steel Waste into Value
Ready to optimize your reduction processes? KINTEK provides high-precision laboratory solutions designed to bridge the gap between testing and industrial reality. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized Vertical Reaction Furnaces—all fully customizable to your unique waste treatment and metallurgy needs.
Empower your team with controlled, high-fidelity data to maximize iron recovery and lower costs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom thermal solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Menglan Zeng, Fawei Lin. Application of Waste Tire Carbon for Iron-Containing Dust Reduction in Industrial Processes. DOI: 10.3390/app15126504
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does thermal processing in a furnace play in phase analysis of kaolin? Optimize Your Catalyst Structure
- What are the advantages of Zr2Cu alloy over pure zirconium in RMI? Optimize Fiber Integrity at Lower Temperatures
- How does the perpendicular orientation of substrate holders benefit VTD? Maximize Efficiency and Thermal Control
- Why is niobium foil wrapped around niobium cavity flanges? Protect Your UHV Seals During Heat Treatment
- What is the purpose of performing high-temperature calcination on diatomite? Boost Reactivity for Geopolymer Prep
- Why is Water Quenching Critical for Metastable Phases in Titanium? Unlock High-Performance Alloy Strength
- What are the methods of heat transfer in furnaces? Master Heat Control for Better Results
- What is the primary function of a laboratory electric drying oven in sample prep? Ensure Pure, Grinder-Ready Powders



















