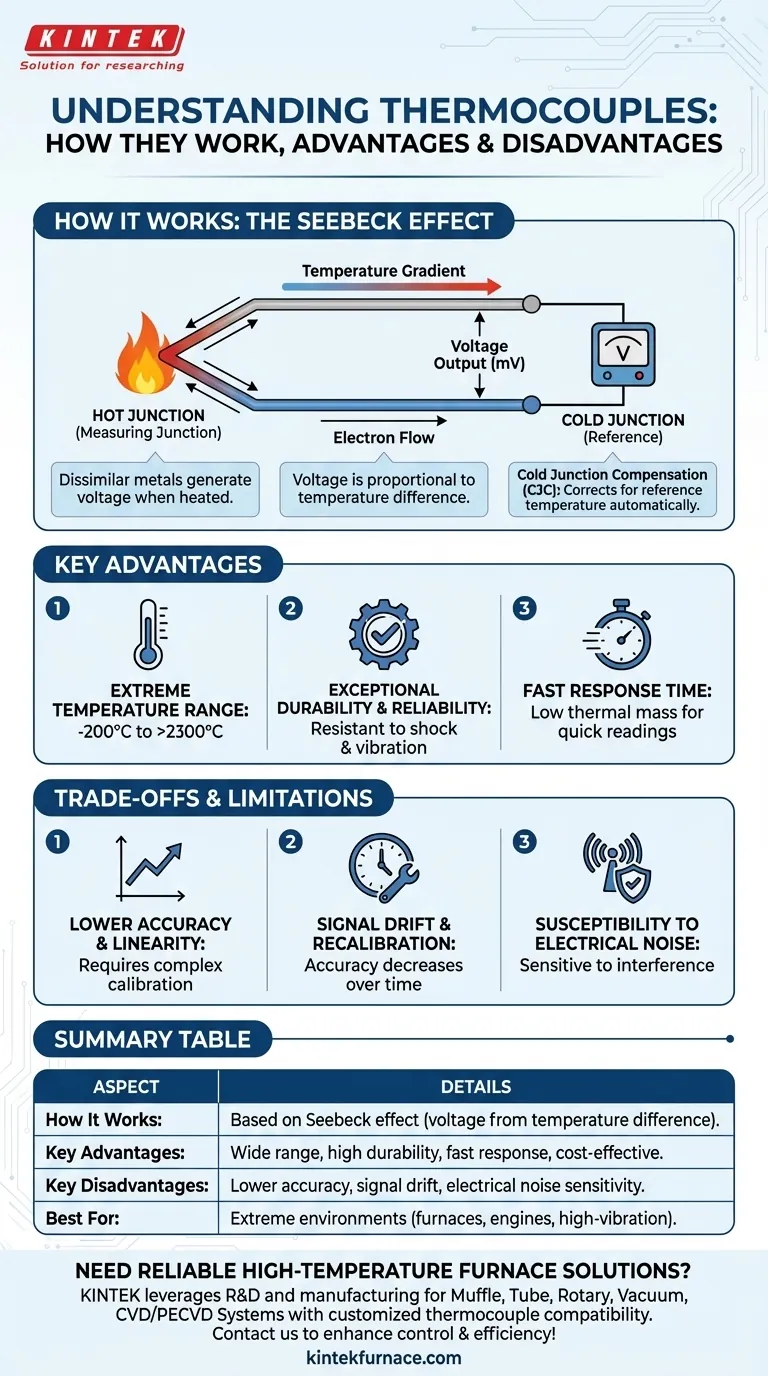
Thermocouples operate on a fundamental principle of physics known as the Seebeck effect. When two different types of metal wires are joined together at one end, a small, predictable voltage is produced when that junction is heated or cooled. This voltage is directly proportional to the temperature, allowing the thermocouple to function as a simple, robust, and versatile temperature sensor.
While they appear simple, the true value of a thermocouple is not just in its construction but in its application. They are the go-to solution for extreme environments where durability and a wide temperature range are far more critical than pinpoint accuracy.
The Seebeck Effect: How a Thermocouple Generates Voltage
At the heart of every thermocouple is a physical phenomenon that connects temperature directly to electricity. Understanding this principle is key to using them correctly.
The Junction of Dissimilar Metals
A thermocouple is created by welding two specific, dissimilar metal wires together at a point. This is known as the measuring junction or "hot junction." Different pairings of metals (like Type K's Chromel and Alumel) produce different voltage characteristics and are suited for different temperature ranges.
The Role of the Temperature Gradient
When the measuring junction is heated, electrons begin to move from the hotter metal to the colder metal, creating a tiny but measurable voltage, typically in the millivolt (mV) range. The greater the temperature difference between the measuring junction and the other end of the wires, the greater the voltage produced.
The Importance of the "Cold Junction"
The voltage a thermocouple produces is only proportional to the difference in temperature between its two ends. To find the absolute temperature at the measuring junction, you must also know the temperature at the other end, where the wires connect to your voltmeter or controller. This reference point is called the cold junction. Modern instruments perform this Cold Junction Compensation (CJC) automatically by using a separate, built-in sensor to measure the terminal temperature and add it to the calculated differential.
Key Advantages of Thermocouples
Thermocouples are one of the most widely used temperature sensors for several compelling reasons.
Extreme Temperature Range
This is their primary advantage. Certain thermocouple types can measure temperatures from cryogenic lows (-200°C) up to over 2300°C, far exceeding the capabilities of other common sensors like RTDs and thermistors.
Exceptional Durability and Reliability
A thermocouple is essentially just two welded wires, often protected by a metal sheath. This simple, solid-state construction makes them incredibly resistant to mechanical shock and vibration, which is why they are standard in engines, industrial furnaces, and heavy machinery.
Fast Response Time
Because the measuring junction can be made very small, it has a low thermal mass. This allows it to react to changes in temperature very quickly, which is critical for process control and safety applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No sensor is perfect. The strengths of the thermocouple come with inherent trade-offs that are critical to understand.
Lower Accuracy and Linearity
Compared to a sensor like an RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector), a thermocouple is less accurate. Its voltage output is also not perfectly linear with temperature, requiring the use of complex polynomial equations or lookup tables in the measurement device to provide an accurate reading.
Signal Drift and Recalibration
Over time, especially when used at the extremes of their temperature range, the chemical properties of the metal wires can change. This "drift" causes a loss of accuracy and means that thermocouples in critical applications must be periodically recalibrated or replaced.
Susceptibility to Electrical Noise
The output signal from a thermocouple is very small (millivolts). This makes it highly susceptible to electrical interference or "noise" from nearby power cables, motors, or other electromagnetic sources. Proper grounding and the use of shielded extension wire are essential for a stable reading.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct temperature sensor depends entirely on the demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures or durability: The thermocouple is the definitive choice for furnaces, exhaust gas monitoring, or high-vibration environments.
- If your primary focus is high accuracy and stability: An RTD is the superior option for laboratory work, food processing, or any application below ~600°C where precision is paramount.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in a narrow range: A thermistor provides excellent sensitivity and a low price point for consumer electronics or HVAC systems operating near ambient temperatures.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently select and implement the ideal temperature sensing solution for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| How It Works | Based on Seebeck effect: voltage generated by temperature difference between hot and cold junctions of dissimilar metals. |
| Key Advantages | Wide temperature range (-200°C to 2300°C), high durability, fast response time, cost-effective. |
| Key Disadvantages | Lower accuracy and linearity, signal drift requiring recalibration, susceptibility to electrical noise. |
| Best For | Extreme environments like furnaces, engines, and high-vibration applications where durability and range are critical. |
Need a reliable high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise performance for your experiments. Contact us today to discuss how our thermocouple-compatible furnaces can enhance your temperature control and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- High Performance Vacuum Bellows for Efficient Connection and Stable Vacuum in Systems
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















