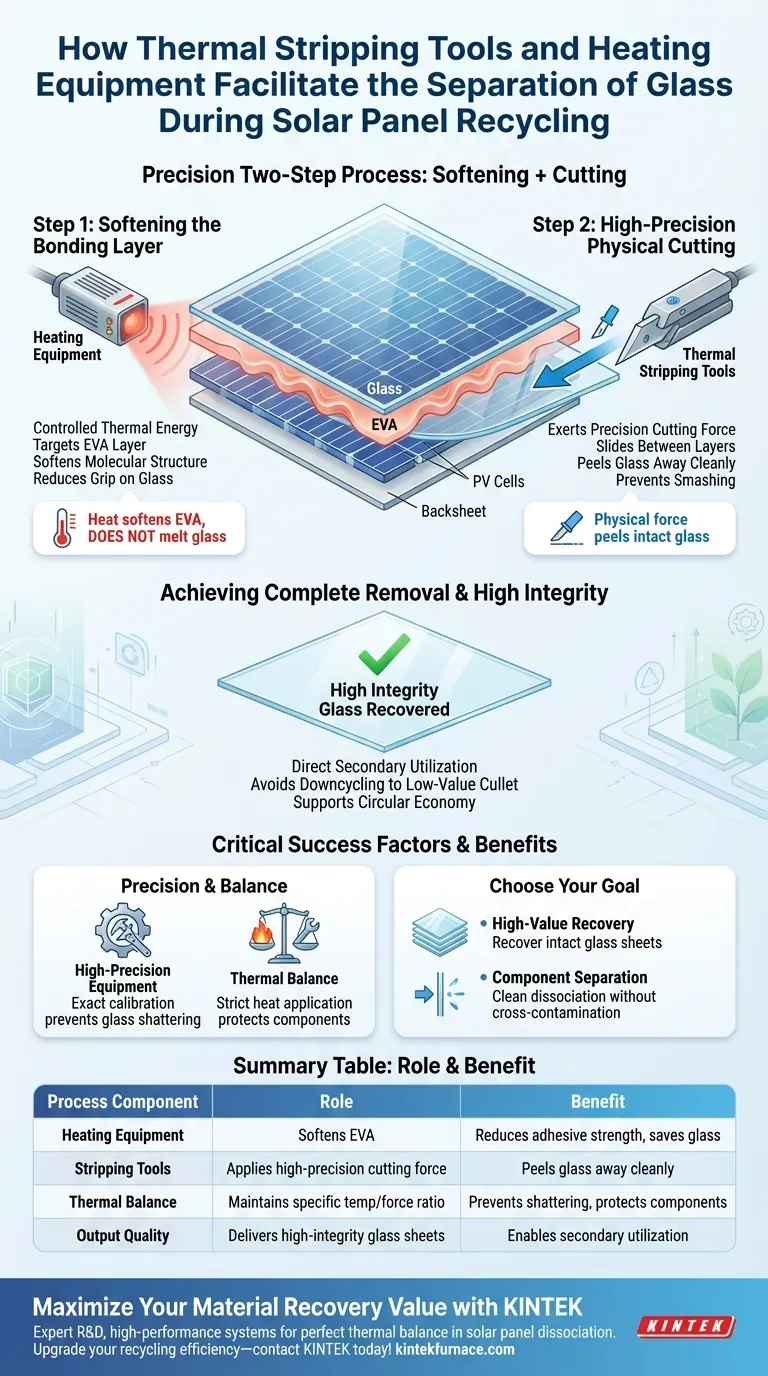
Thermal stripping utilizes a precise, two-step interaction between temperature and physical force. This process begins by using heating equipment to soften the Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) layer that bonds the solar panel components together. Once the adhesive is pliable, high-precision stripping tools apply a specific cutting force to completely peel away the glass layer.
By softening the bonding material before applying mechanical force, this method ensures the glass is recovered with high integrity, enabling its direct secondary utilization rather than reducing it to crushed scrap.

The Mechanics of Separation
Softening the Bonding Layer
The primary challenge in solar panel recycling is the strong adhesion provided by the Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) layer. Heating equipment addresses this by applying controlled thermal energy to the panel. This heat does not melt the glass but specifically targets the EVA, softening its molecular structure to reduce its grip on the glass surface.
High-Precision Physical Cutting
Once the EVA is softened, the process relies on thermal stripping tools. These tools exert a high-precision physical cutting force. Instead of smashing the panel, the tool slides between the layers or grips the surface to peel the glass away from the underlying photovoltaic cells.
Achieving Complete Removal
The synergy between the heat and the cutting tool allows for the complete removal of the glass layer. Because the bond has been thermally weakened, the physical tool can separate the materials cleanly. This prevents the residue of EVA or silicon cells from remaining stuck to the glass.
Why Integrity Matters
Enabling Secondary Utilization
The most distinct advantage of this method is the quality of the output. The process ensures that the glass is recovered with high integrity.
Avoiding Downcycling
Traditional crushing methods often turn solar glass into low-value dust or cullet. By keeping the glass intact through precision stripping, the material retains its value. This allows for direct secondary utilization, supporting a more efficient circular economy for solar materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Dependence on Precision
Success in this method relies heavily on high-precision equipment. If the stripping tools lack exact calibration, the physical force could shatter the glass despite the heating.
The Necessity of Thermal Balance
The process requires a strict balance of heat. The heating equipment must sufficiently soften the EVA without damaging other recoverable components. It is not a brute-force method; it requires the correct conjunction of thermal application and mechanical force to work effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
This technology is specifically designed for recyclers who prioritize material value over simple volume reduction.
- If your primary focus is High-Value Recovery: Utilize this method to recover intact glass sheets suitable for direct secondary utilization.
- If your primary focus is Component Separation: Rely on the combination of heat and precision cutting to cleanly dissociate the EVA from the glass without cross-contamination.
Thermal stripping transforms solar recycling from a destructive crushing process into a precision recovery operation.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role in Separation | Benefit to Recycling |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Equipment | Softens Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) layer | Reduces adhesive strength without melting glass |
| Stripping Tools | Applies high-precision physical cutting force | Peels glass away cleanly from PV cells |
| Thermal Balance | Maintains specific temperature/force ratio | Prevents glass shattering and protects components |
| Output Quality | Delivers high-integrity glass sheets | Enables direct secondary utilization & circular economy |
Maximize Your Material Recovery Value with KINTEK
Is your recycling process losing value to crushed scrap? KINTEK empowers recyclers to transition from destructive crushing to precision recovery. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable lab high-temperature furnaces designed to achieve the perfect thermal balance for solar panel dissociation.
Whether you need to refine your EVA softening process or require a bespoke thermal solution for component separation, our team is ready to help you achieve high-integrity material recovery.
Upgrade your recycling efficiency—contact KINTEK today!
Visual Guide
References
- Yuxuan Sun. Methods and Improvement Measures Based on Solar Panel Recycling. DOI: 10.54254/2755-2721/2025.gl24086
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is MgO used as a hard template for waste PET to carbon conversion? Unlock 3D Porous Structures
- How does first-order Padé approximation address technical challenges in electric furnace temperature regulation models?
- What is a horizontal furnace? A space-saving heating solution for attics and crawl spaces
- Why is the vacuum drying process essential for the synthesis of phthalonitrile-modified titanium dioxide? Expert Guide
- What are the advantages of using a microwave activation system? Unlock Superior Porosity and 90% Faster Activation
- How does a resistance heating furnace contribute to Al/Cu bimetallic interface preparation? Expert Thermal Solutions
- What is the function of a laboratory hot air drying oven in TiO2 treatment? Ensure Uniform Nanoparticle Quality
- What is the purpose of using an industrial oven for low-temperature drying? Expert Glass Processing Guide



















