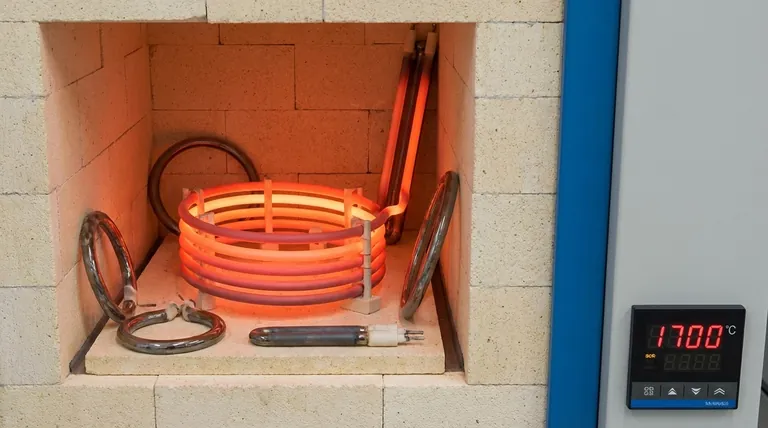
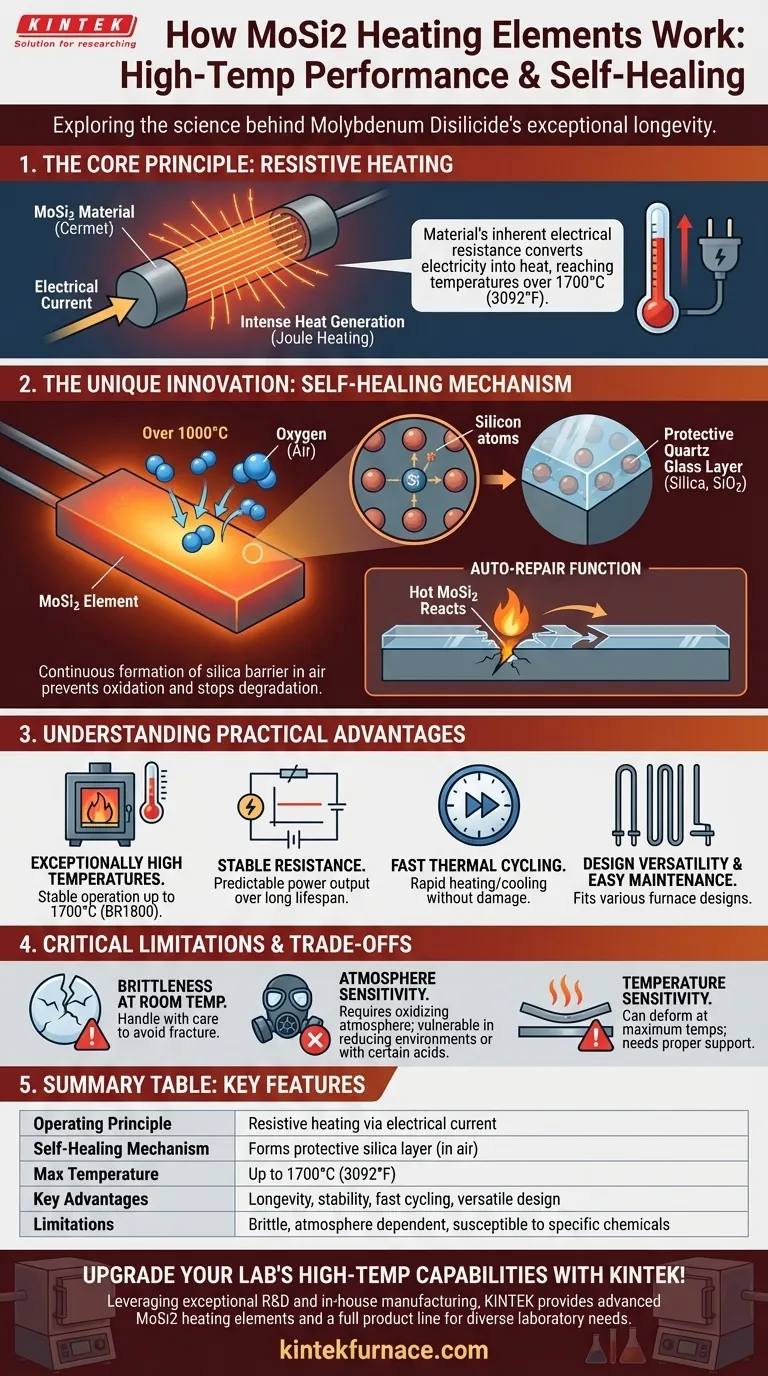
At its core, a Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating element works by passing an electrical current through its specialized ceramic-metal material. The material's inherent electrical resistance causes it to heat up intensely, converting electrical energy into thermal energy. What truly sets MoSi2 elements apart is their unique ability to form a protective, self-healing layer of glass on their surface at high temperatures, which gives them exceptional longevity and stability.
While many materials can generate heat from electricity, the defining characteristic of MoSi2 is its "self-healing" nature. This ability to continuously repair its own protective oxide layer in air allows it to operate reliably at extreme temperatures where other elements would quickly fail.

The Fundamental Principle: Resistive Heating
Resistive heating is the foundational process behind all MoSi2 elements. The concept is straightforward but its application in this material is highly advanced.
Converting Electricity to Heat
When an electric current is passed through any material, it encounters resistance. This opposition to the flow of electricity generates heat, a principle known as Joule heating. In MoSi2 elements, this effect is harnessed and amplified to produce temperatures exceeding 1700°C (3092°F).
The Role of Molybdenum Disilicide
Molybdenum Disilicide is a cermet—a composite material combining ceramic and metallic properties. It possesses high electrical resistance, which is essential for efficient heat generation, and the structural integrity to withstand extreme thermal stress.
The "Self-Healing" Mechanism: The Key to Longevity
The true innovation of MoSi2 is not just that it gets hot, but that it protects itself from the very heat and oxygen that would destroy other materials.
Oxidation as a Feature, Not a Flaw
When an MoSi2 element is heated above approximately 1000°C in an oxygen-containing atmosphere, a remarkable chemical reaction occurs. The silicon within the material oxidizes, forming a thin, non-porous layer of quartz glass (silica, SiO2) on the surface.
How the Protective Layer Works
This glassy silica layer is chemically stable and acts as a barrier. It prevents the atmosphere from reaching and further oxidizing the underlying MoSi2 material, effectively stopping degradation in its tracks.
The Auto-Repair Function
If this protective layer is scratched or damaged during operation, the newly exposed hot MoSi2 immediately reacts with the air to form new silica. This "heals" the breach, restoring the protective coating and enabling an exceptionally long and reliable service life, even with continuous use.
Understanding the Practical Advantages
This unique self-healing property translates directly into several significant operational benefits.
Exceptionally High Operating Temperatures
The stability of the silica layer allows MoSi2 elements to perform consistently at very high temperatures. Commercial models are readily available with maximum operating temperatures of 1600°C (BR1700) and 1700°C (BR1800).
Stable Resistance and Fast Cycling
Because the core material is protected from degradation, its electrical resistance remains stable over its lifespan. This ensures predictable power output and allows for rapid heating and cooling cycles without damaging the element.
Design Versatility and Easy Maintenance
MoSi2 elements can be manufactured in various shapes (U, W, L) to fit specific furnace designs. Furthermore, their stable resistance profile means new elements can be connected in series with older ones, simplifying replacement and reducing downtime.
Critical Limitations and Trade-offs
Despite their advantages, MoSi2 elements are not universally applicable. Understanding their limitations is crucial for proper selection and use.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
Like many ceramics, MoSi2 elements are brittle and fragile at room temperature. They must be handled with care during shipping, storage, and installation to avoid fractures.
Susceptibility to Atmosphere
The protective silica layer only forms in an oxidizing atmosphere (like air). In certain reducing or reactive atmospheres, the element can be attacked and degraded. They will also dissolve in the presence of hydrofluoric and nitric acids.
Temperature Sensitivity
While strong at high temperatures, MoSi2 elements become soft and subject to plastic deformation near their maximum operating temperature. They must be properly supported in a furnace to prevent them from sagging or breaking under their own weight.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element requires matching its characteristics to your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is continuous, high-temperature operation in air: MoSi2 is an ideal choice due to its self-healing protective layer and unparalleled service life.
- If your primary focus is rapid thermal cycling for processes like lab testing: The stable resistance and physical durability of MoSi2 make it highly reliable for applications requiring frequent and fast temperature changes.
- If you are working with reducing atmospheres or specific chemicals: You must verify compatibility, as MoSi2 can be degraded by environments that prevent the formation of its protective silica layer.
By understanding this unique self-healing mechanism, you can leverage MoSi2 elements for superior performance in the most demanding high-temperature environments.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Resistive heating via electrical current in MoSi2 material |
| Self-Healing Mechanism | Forms protective silica layer in oxidizing atmospheres for auto-repair |
| Max Temperature | Up to 1700°C (3092°F) |
| Key Advantages | High longevity, stable resistance, fast cycling, design versatility |
| Limitations | Brittle at room temperature, requires oxidizing atmosphere, susceptible to certain chemicals |
Upgrade your lab's high-temperature capabilities with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide MoSi2 heating elements and a full product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—tailored for diverse laboratories. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for reliable, high-performance heating. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















