In the long term, induction furnaces generate significant cost savings through a powerful combination of superior energy efficiency, reduced maintenance needs, and improved material quality. Unlike traditional furnaces that waste energy heating the entire chamber, induction technology directly heats the metal itself, drastically cutting energy consumption and operational expenditures over the furnace's lifespan.
While the initial capital outlay for an induction furnace can be higher, viewing it through the lens of Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) reveals its true financial advantage. The cumulative savings in energy, maintenance, and material yield consistently outweigh the upfront investment.
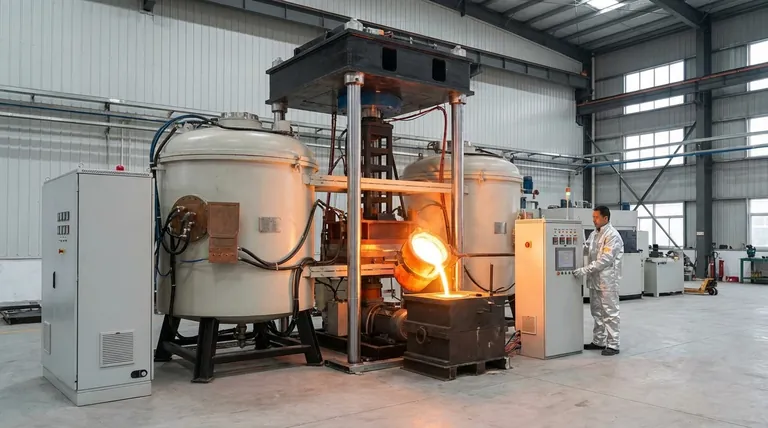

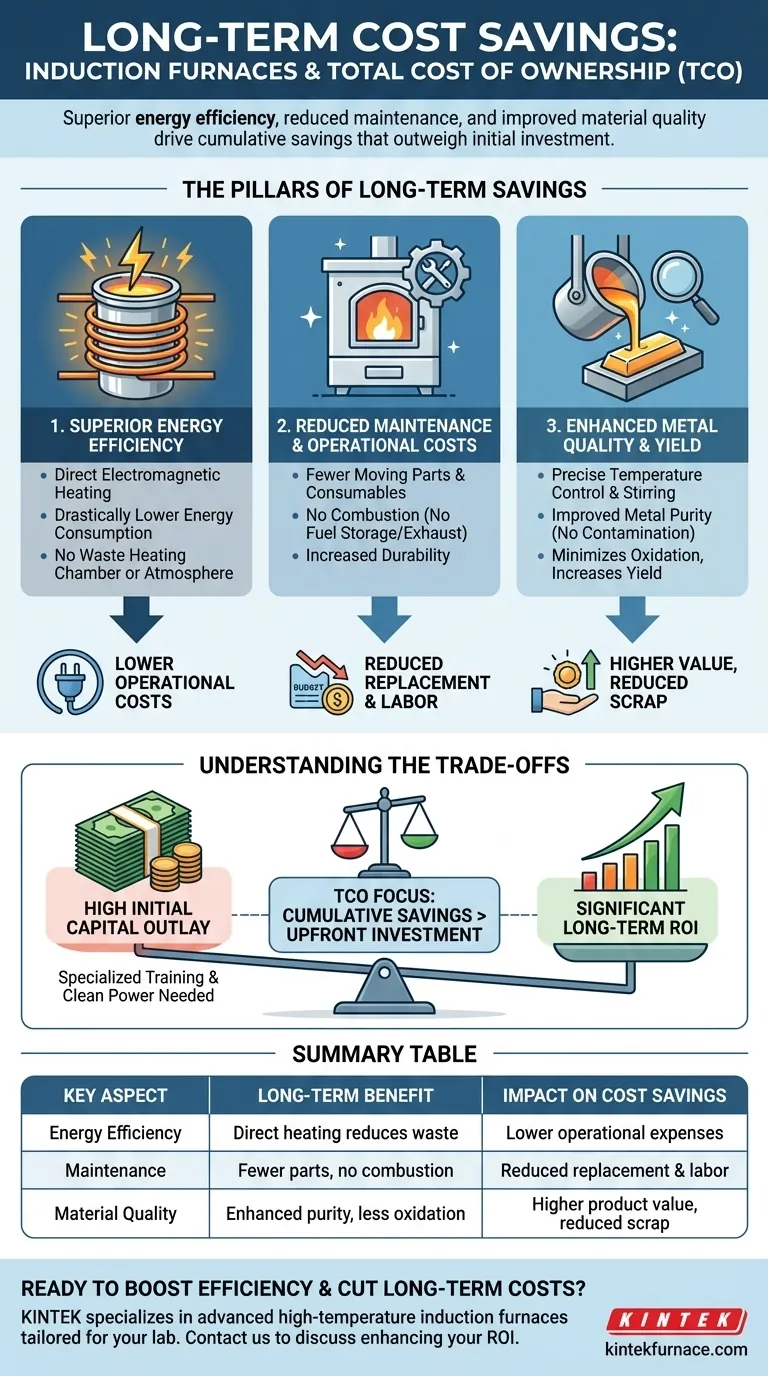
The Pillars of Long-Term Savings
The financial benefits of induction technology are not based on a single feature, but on the interplay of three core operational advantages. Understanding each is key to justifying the investment.
Pillar 1: Superior Energy Efficiency
An induction furnace functions by using an electromagnetic field to induce an electrical current directly within the metal charge. This process is inherently more efficient than combustion-based methods.
This direct heating method means energy is not wasted heating the furnace walls or the surrounding atmosphere. This leads to dramatically lower energy consumption per ton of melted metal, a primary driver of reduced operational costs.
Pillar 2: Reduced Maintenance and Operational Costs
Traditional furnaces have numerous components that wear out, such as burners, fuel lines, and extensive refractory linings that are subject to harsh chemical and thermal attack.
Induction furnaces have fewer moving parts and consumables. The absence of combustion eliminates the need for fuel storage, exhaust flues, and pollution control systems, simplifying operations and slashing the budget for replacement parts and labor. Their durability leads to lower lifetime maintenance costs.
Pillar 3: Enhanced Metal Quality and Yield
The induction process allows for precise temperature control and creates a stirring action within the molten bath. This ensures a homogenous mixture and consistent alloy quality.
Crucially, because there is no combustion, the risk of metal contamination from fuel byproducts is eliminated, leading to improved metal purity. This process also minimizes oxidation, which means less metal is lost as slag, increasing the overall material yield and reducing scrap rates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To make a fully informed decision, it's critical to acknowledge the challenges and initial requirements associated with induction technology.
High Initial Capital Outlay
The most significant barrier is the upfront purchase price. Induction furnaces represent a major capital investment compared to some traditional furnace types. The long-term ROI must be the central focus of any financial evaluation.
Requirement for Clean Power
Induction furnaces are powerful electrical devices. They require a stable, high-capacity electrical supply. For some facilities, this may necessitate an upgrade to the existing power infrastructure, adding to the initial project cost.
Specialized Operator Training
While simpler to maintain, operating an induction furnace efficiently and safely requires specific knowledge. Proper training for operators and maintenance staff is essential to maximize the furnace's benefits and ensure a long operational life.
Making the Right Investment Decision
Your specific production goals will determine how you weigh the benefits of an induction furnace.
- If your primary focus is maximizing long-term ROI: Prioritize the analysis of your energy costs and material yield, as these areas will deliver the most significant and consistent financial returns.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and a cleaner work environment: The reduction in maintenance overhead, elimination of onsite fuel storage, and lack of combustion emissions are the key advantages.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest material purity and minimizing scrap: The precise control and low-contamination environment of induction melting are unparalleled and will directly improve product quality.
Ultimately, choosing an induction furnace is an investment in predictable, efficient, and high-quality production for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Long-Term Benefit | Impact on Cost Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Direct metal heating reduces energy waste | Lower operational expenses over time |
| Maintenance | Fewer moving parts and no combustion systems | Reduced replacement and labor costs |
| Material Quality | Enhanced purity and yield with less oxidation | Higher product value and reduced scrap rates |
Ready to boost your lab's efficiency and cut long-term costs? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including induction furnaces tailored for diverse laboratories. With our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, plus deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your ROI and operational performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- What role does Vacuum Hot Press technology play in the automotive industry? Boost EV Batteries, Safety, and Efficiency
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- What are the main applications of vacuum hot pressing? Create Dense, Pure Materials for Demanding Industries
- How does induction heating ensure precision in manufacturing processes? Achieve Superior Thermal Control & Repeatability



















