For alloy manufacturing, induction furnaces provide unparalleled control over the final product. They achieve this through a unique combination of rapid, clean heating and inherent electromagnetic stirring. This process ensures exceptional chemical uniformity, precise temperature management, and high operational efficiency, resulting in alloys that consistently meet exact specifications.
The core value of an induction furnace in alloy production is not a single feature, but its ability to solve the fundamental challenge of the industry: achieving perfect chemical and thermal homogeneity with high repeatability, batch after batch.
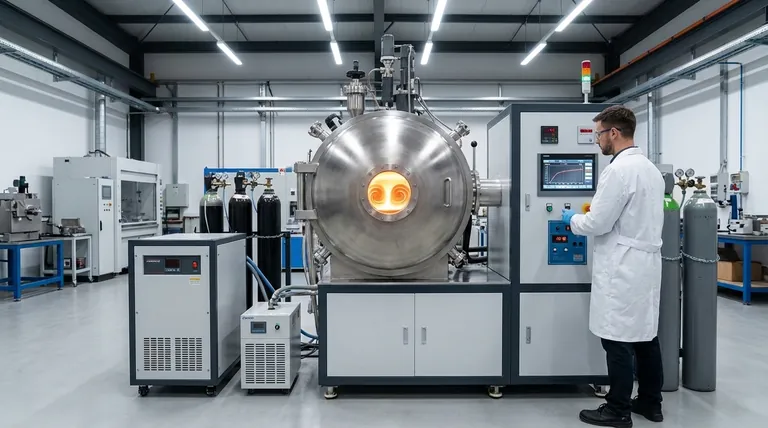

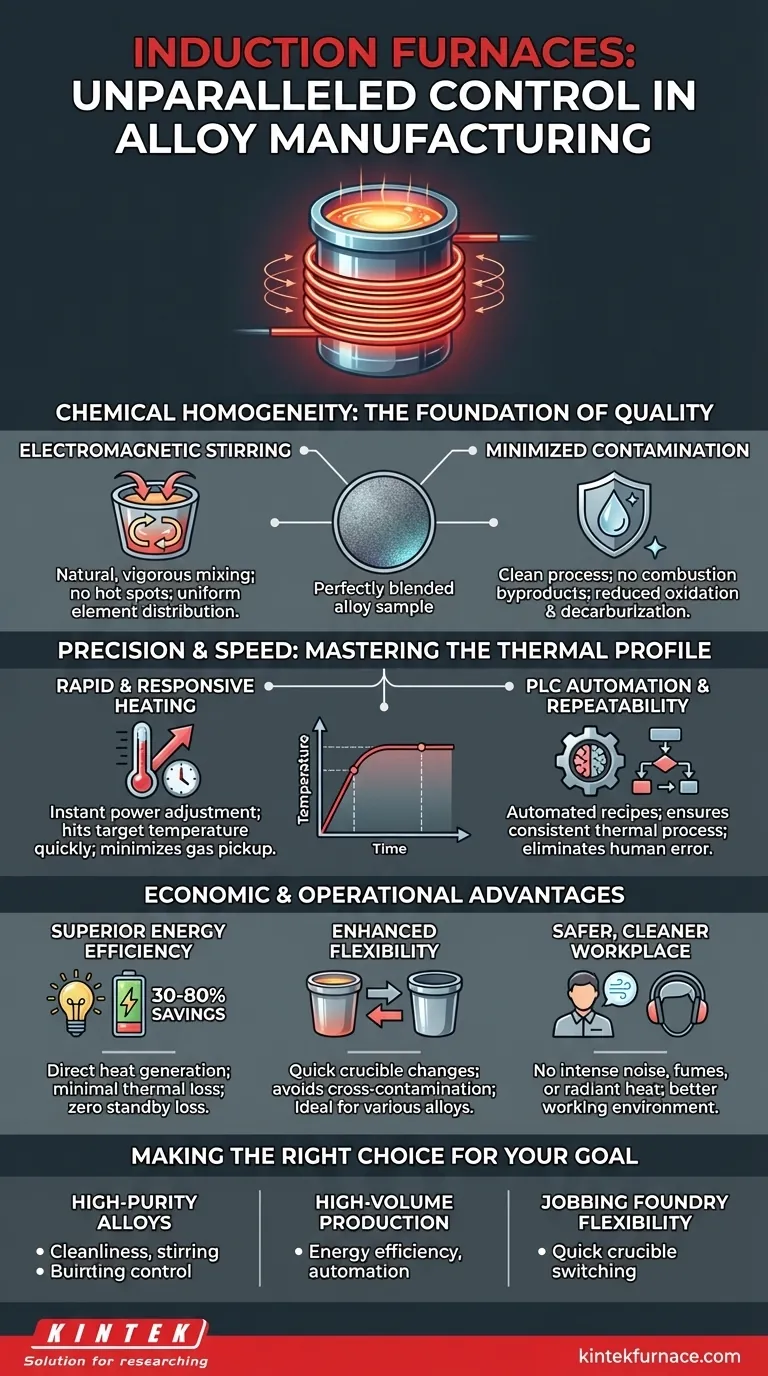
The Foundation of Quality: Achieving Chemical Homogeneity
The defining characteristic of any alloy is its precise chemical composition. Even minor deviations can drastically alter its mechanical properties. Induction furnaces are uniquely suited to guarantee this compositional integrity.
The Role of Induction Stirring
The electromagnetic field that heats the metal also creates a natural, vigorous stirring action within the molten bath. This ensures all alloying elements—from the base metal to trace additions—are distributed perfectly and evenly.
This constant, non-contact mixing eliminates hot spots and prevents elements from settling or separating, guaranteeing a completely homogenous final product without the need for mechanical stirring that could introduce impurities.
Minimizing Contamination
Induction heating is a remarkably clean process. Unlike fuel-fired furnaces, there are no combustion byproducts like carbon or sulfur to contaminate the melt.
Furthermore, because heat is generated directly within the metal, there is no need for consumable electrodes (as in an arc furnace), which can erode and alter the alloy's chemistry. This minimizes both oxidation and decarburization, which is critical for high-purity and specialty alloys.
Precision and Speed: Mastering the Thermal Profile
Controlling the temperature of the molten metal is just as important as controlling its chemistry. The thermal cycle affects everything from element retention to the final microstructure of the cast alloy.
Rapid and Responsive Heating
Induction furnaces bring metal to temperature extremely quickly. Power can be applied and adjusted almost instantaneously, allowing operators to hit precise target temperatures without overshooting.
This speed not only increases production efficiency but also minimizes the time the metal spends in a molten state, reducing the chance for gas pickup or the loss of volatile alloying elements through evaporation.
The Power of Automation
Modern induction furnaces are often integrated with PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems. This allows for the creation of specific heating and holding "recipes" for each alloy.
By automating the power input and timing, PLCs ensure that every batch undergoes the exact same thermal process. This removes the risk of human error and guarantees exceptional repeatability between melts.
Understanding the Economic and Operational Advantages
Beyond the metallurgical benefits, induction technology offers significant advantages in cost, safety, and flexibility.
Superior Energy Efficiency
Induction is one of the most energy-efficient melting methods available. Heat is generated directly inside the charge material, resulting in minimal thermal loss to the surrounding environment.
Compared to traditional methods, this can lead to energy savings of 30% to 80%. Additionally, since there is no need to keep the furnace hot between melts, standby energy losses are virtually zero.
Enhanced Operational Flexibility
Crucible-style induction furnaces are ideal for foundries that produce a wide variety of alloys. The crucibles can be switched out quickly and easily, allowing for rapid changes in material without the risk of cross-contamination.
This flexibility dramatically improves productivity for operations that require frequent material switches, reducing downtime between different production runs.
A Safer, Cleaner Workplace
Induction furnaces operate without the intense noise, combustion fumes, and massive radiant heat associated with fossil fuel or arc furnaces. This creates a significantly better and safer working environment for foundry personnel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an induction furnace should be aligned with your specific production priorities.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, complex alloys: The inherent cleanliness and precise stirring of an induction furnace are essential for meeting tight chemical specifications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of a single alloy: The energy efficiency and automated repeatability of a large induction system will significantly lower your long-term cost per part.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility for a jobbing foundry: A crucible induction furnace's ability to quickly switch between different alloy specifications is a critical competitive advantage.
Ultimately, adopting induction technology is a direct investment in process control, product quality, and operational consistency.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Homogeneity | Ensures even distribution of alloying elements through electromagnetic stirring, eliminating hot spots and contamination. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Allows rapid, responsive heating with automation via PLCs for consistent thermal profiles and repeatability. |
| Energy Efficiency | Saves 30-80% energy by generating heat directly in the metal, reducing thermal losses and standby consumption. |
| Operational Flexibility | Enables quick alloy changes with crucible systems, minimizing downtime and cross-contamination. |
| Safety and Cleanliness | Operates without noise, fumes, or radiant heat, improving workplace conditions and reducing environmental impact. |
Ready to enhance your alloy manufacturing with advanced induction furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs, delivering superior control, efficiency, and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your process and achieve consistent, high-purity results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















