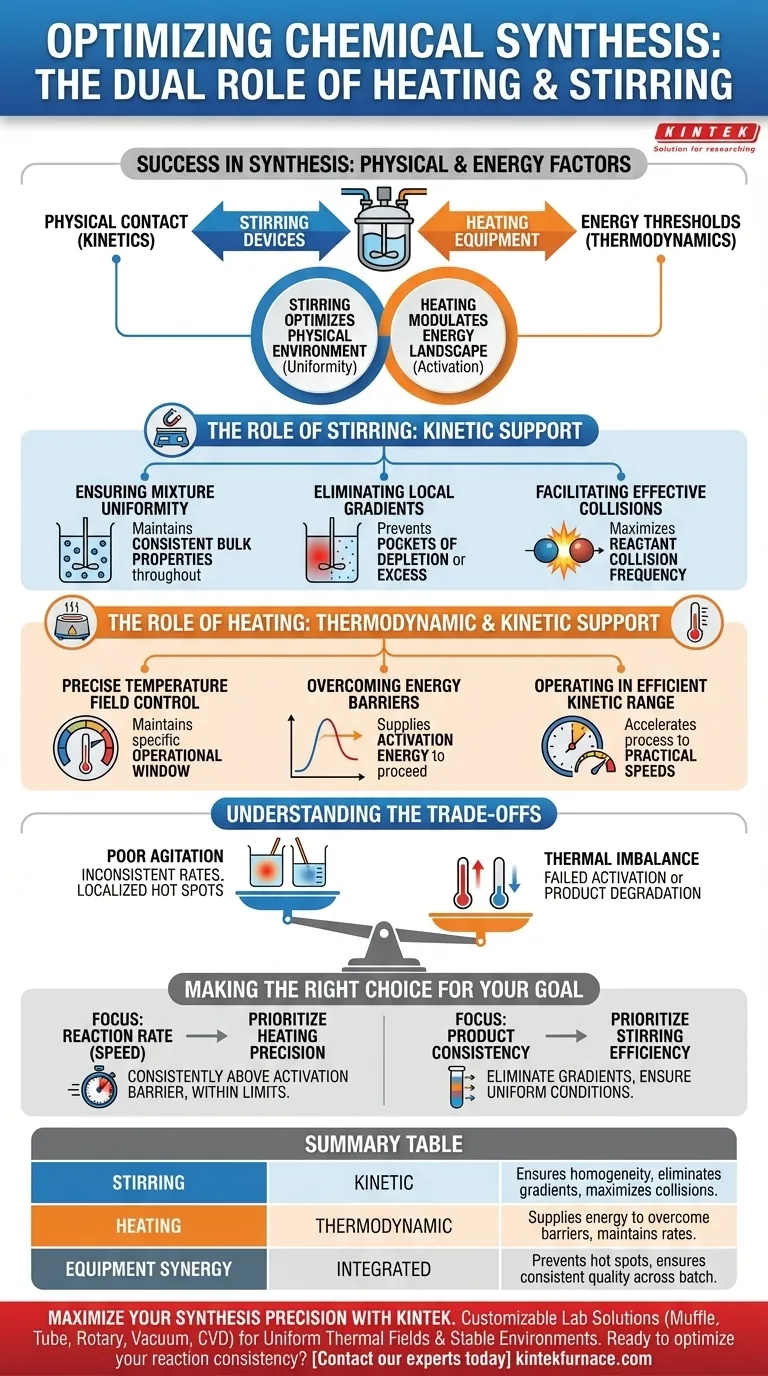
Success in chemical synthesis relies on controlling two fundamental factors: physical contact and energy thresholds. Heating equipment supplies the thermal energy required to surmount thermodynamic barriers, while stirring devices ensure the physical consistency needed for effective kinetic interactions. Together, these tools transform a static mixture into a dynamic, reacting system.
Effective synthesis requires a dual approach: Stirring optimizes the physical environment by ensuring uniform reactant distribution for maximum collision frequency, while heating modulates the energy landscape to overcome activation barriers and accelerate reaction rates.

The Role of Stirring: Kinetic Support
Stirring devices are the primary drivers of physical homogeneity within a reaction vessel. Their function is not merely to move fluid, but to maximize the probability of molecular interaction.
Ensuring Mixture Uniformity
A reaction cannot proceed efficiently if the components remain separated. Stirring equipment maintains a uniform mixture throughout the system. This ensures that the bulk fluid properties are consistent from the center of the vessel to the walls.
Eliminating Local Gradients
Without agitation, reactions often develop local concentration gradients. These are pockets where one reactant is depleted while another is in excess. Stirring actively disrupts these zones, constantly refreshing the material available for reaction.
Facilitating Effective Collisions
Kinetically, a reaction is defined by how often molecules bump into each other. By removing gradients and maintaining uniformity, stirring ensures effective reactant collisions. This physical manipulation directly supports the kinetic requirements of the synthesis.
The Role of Heating: Thermodynamic and Kinetic Support
Heating equipment provides the energy input required to initiate and sustain chemical transformations. It acts as the "accelerator" for the process.
Precise Temperature Field Control
Synthesis is rarely successful at random temperatures. Heating equipment provides precise control over the thermal environment. This stability is crucial for maintaining the reaction within a specific operational window.
Overcoming Energy Barriers
Thermodynamically, molecules must possess a minimum amount of energy to react. Heating provides the necessary energy to help reactants overcome these energy barriers (activation energy). Without this thermodynamic support, the reaction would remain stagnant regardless of how well it is mixed.
Operating in the Efficient Kinetic Range
Temperature directly influences the rate of reaction. Heating allows the system to operate within the most efficient kinetic range. This ensures the synthesis proceeds at a practical speed rather than dragging on indefinitely.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While heating and stirring are essential, they must be balanced carefully to avoid compromising the synthesis.
The Risk of Poor Agitation
If stirring is inadequate, the system will suffer from inconsistent reaction rates. Localized "hot spots" may form where heat is not distributed evenly, potentially leading to side reactions or degradation, while other areas remain unreacted due to reactant depletion.
The Danger of Thermal Imbalance
If heating is uncontrolled, the reaction may exit its efficient kinetic range. Too little heat fails to surmount the energy barrier, resulting in no product. Conversely, excessive heat can push the system beyond stable limits, overriding the thermodynamic controls and ruining the product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your synthesis process, you must tune your equipment based on the specific limiting factors of your reaction.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Rate (Speed): Prioritize heating precision to ensure the system consistently operates above the activation energy barrier without exceeding stability limits.
- If your primary focus is Product Consistency: Prioritize stirring efficiency to eliminate concentration gradients and ensure every molecule experiences the same reaction conditions.
The most successful synthesis processes view heating and stirring not as separate tasks, but as an integrated system for controlling molecular behavior.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Support Type | Primary Role in Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Stirring | Kinetic | Ensures physical homogeneity, eliminates gradients, and maximizes collision frequency. |
| Heating | Thermodynamic | Supplies energy to overcome activation barriers and maintains optimal reaction rates. |
| Equipment Synergy | Integrated | Prevents localized 'hot spots' and ensures consistent product quality across the batch. |
Maximize Your Synthesis Precision with KINTEK
Don't let inefficient heat distribution or poor agitation compromise your research results. KINTEK provides high-performance laboratory solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable to meet your specific thermodynamic and kinetic requirements. Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our high-temperature furnaces and lab equipment ensure uniform thermal fields and stable reaction environments for researchers and industrial manufacturers alike.
Ready to optimize your reaction consistency? Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Sebastian Jarczewski, Piotr Kuśtrowski. Improved Catalytic Efficiency of Pt/CeO<sub>2</sub> in Toluene Combustion by Its Incorporation in the Structure of Hydrophobic Mesoporous Carbon. DOI: 10.1002/cctc.202500204
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using TGA-MS over standalone TGA for activated carbon? Unlock Deep Chemical Insights
- What is the purpose of pre-drying SiO2 raw materials at 400 degrees Celsius? Ensure Precise Stoichiometric Synthesis
- What is the primary function of a laboratory blast drying oven? Mastering Coconut Husk Biochar Preparation
- What is the function of 0.5 mbar nitrogen in sintering? Prevent Chromium Loss for Stronger Cermets
- How does a gas evolution analysis system monitor gas release? Optimize Your Casting Integrity
- Why is industrial-grade isostatic pressing necessary for zirconia? Achieve Uniform Density & Structural Integrity
- What role does the soaking zone of a walking-beam furnace play in the final quality of heated Titanium/Steel clad plates?
- What is the purpose of introducing a pure iron interlayer between the titanium layer and the steel layer? Enhancing Bond Integrity



















