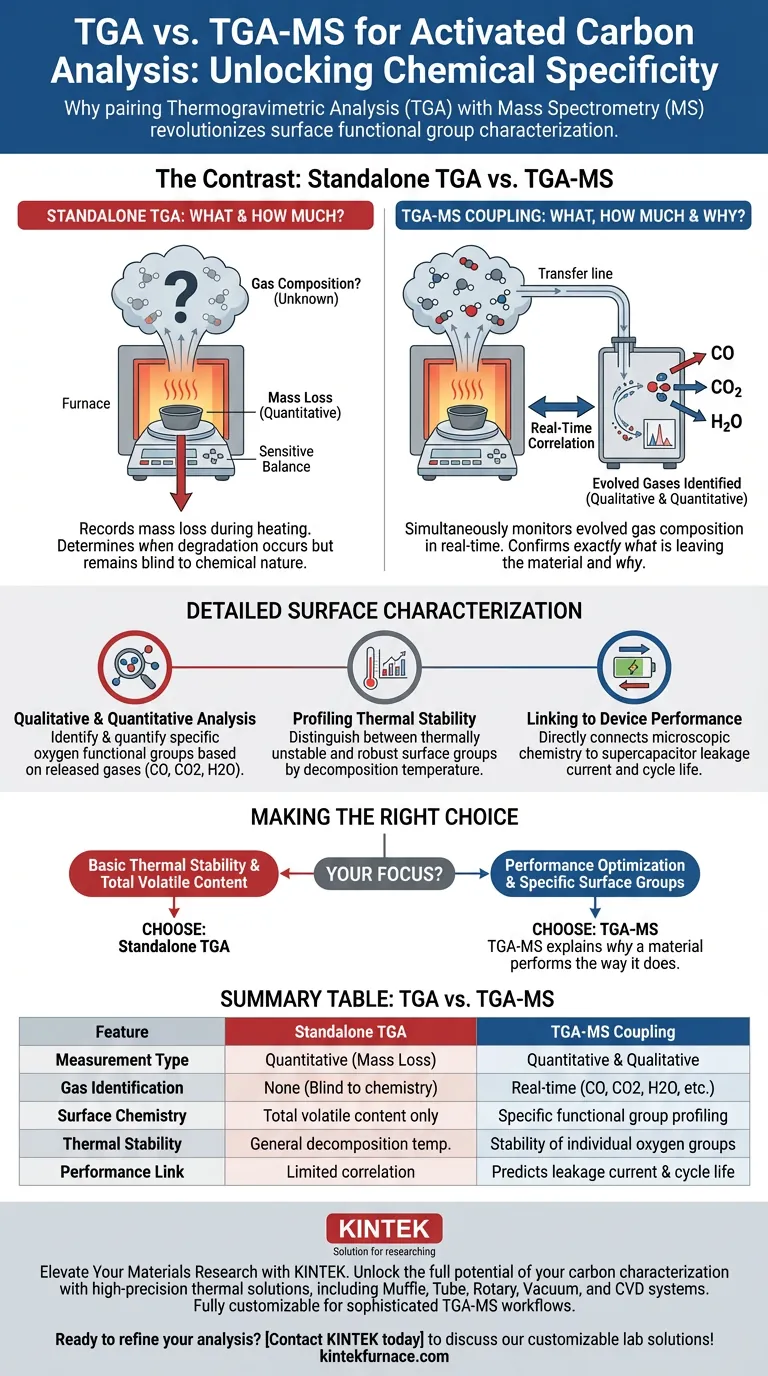
Thermogravimetric Analysis coupled with Mass Spectrometry (TGA-MS) provides a critical layer of chemical specificity that standalone TGA lacks. While standard TGA only measures how much weight a sample loses during heating, TGA-MS simultaneously identifies the specific composition of the evolved gases. This dual capability is essential for the precise characterization of oxygen-containing functional groups on activated carbon surfaces.
By correlating mass loss with specific gas emissions like CO, CO2, and H2O in real-time, TGA-MS transforms a simple weight-loss measurement into a comprehensive chemical analysis. This deeper insight connects surface chemistry directly to practical performance metrics, such as the cycle life and leakage current of supercapacitors.

Beyond Simple Mass Loss
The Limitation of Standalone TGA
Standard TGA records the mass loss of activated carbon as it is heated. While this determines when the material degrades or loses volatile components, it remains blind to the chemical nature of those components. It provides a quantitative measure of weight change but lacks qualitative identification.
The Solution via Mass Spectrometry
TGA-MS overcomes this by monitoring the composition of evolved gases in real-time. As the sample heats up, the mass spectrometer detects specific molecules released from the surface, such as CO, CO2, and H2O. This allows you to confirm exactly what is leaving the material at any given temperature.
Detailed Surface Characterization
Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis
The combination of techniques allows researchers to perform both qualitative and quantitative analysis of surface chemistry. You can identify which oxygen-containing functional groups are present based on the gases they release. Furthermore, you can quantify the abundance of these specific groups, rather than just measuring total mass loss.
Profiling Thermal Stability
Different functional groups decompose at different temperatures. TGA-MS reveals the specific thermal stabilities of these groups. By observing which gases evolve at which temperatures, you can distinguish between unstable surface groups and those that are thermally robust.
Linking Chemistry to Device Performance
Predicting Supercapacitor Efficiency
The data derived from TGA-MS has direct implications for energy storage applications. The analysis reveals how specific functional groups impact the leakage current of supercapacitors. This connects microscopic surface chemistry to macroscopic device failure modes.
Optimizing Cycle Life
Understanding the stability of surface groups also aids in predicting longevity. TGA-MS helps researchers understand how different functional groups influence the cycle life of the device. This insight allows for the engineering of carbon surfaces that maintain performance over time.
Analytical Considerations
Interpretation Complexity
While TGA-MS offers superior data, it requires correlating two distinct data streams. You must accurately map the gas evolution profiles to the mass loss steps to identify the source of the emissions.
Specificity of Detection
The value of TGA-MS relies on the ability to detect specific gases. The primary reference highlights CO, CO2, and H2O as key indicators, meaning the analysis is most effective when targeted at releasing these specific decomposition products.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine which analytical technique suits your project, consider the depth of information required:
- If your primary focus is basic thermal stability: Standalone TGA is sufficient for determining decomposition temperatures and total volatile content.
- If your primary focus is performance optimization: Use TGA-MS to identify specific oxygen functional groups that drive leakage current and affect the cycle life of supercapacitors.
The superior insight of TGA-MS lies in its ability to explain why a material performs the way it does, not just how it degrades.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standalone TGA | TGA-MS Coupling |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Type | Quantitative (Mass Loss) | Quantitative & Qualitative |
| Gas Identification | None (Blind to chemistry) | Real-time (CO, CO2, H2O, etc.) |
| Surface Chemistry | Total volatile content only | Specific functional group profiling |
| Thermal Stability | General decomposition temperature | Stability of individual oxygen groups |
| Performance Link | Limited correlation | Predicts leakage current & cycle life |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of your carbon characterization with high-precision thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of laboratory equipment including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable for your unique research needs.
Whether you are optimizing supercapacitor cycle life or engineering advanced functional materials, our high-temp furnaces provide the thermal stability and precision required for sophisticated TGA-MS workflows.
Ready to refine your analysis? Contact KINTEK today to discuss our customizable lab solutions!
Visual Guide
References
- Xiaoyang Guo, Steven T. Boles. Holistic Processing of Sawdust to Enable Sustainable Hybrid Li-Ion Capacitors. DOI: 10.1007/s11837-024-06542-1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Ultra High Vacuum Observation Window Stainless Steel Flange Sapphire Glass Sight Glass for KF
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of maintaining an inert nitrogen atmosphere during molten salt activation? Ensure Pore Purity
- Why is a specific glass slide used to cover Zinc powder? Mastering ZnO Nanostructure Precision
- Why is programmable heating equipment necessary for composite curing? Master Thermal Control for Superior Strength
- What is the function of coke and flux in lithium battery recycling? Optimize Metal Recovery and Slag Separation
- How does oxygen-enhanced alkaline thermal treatment benefit high-purity cellulose pulp? Achieve Superior Fiber Yield
- How do industrial molds and 10 MPa pressure impact PEEK quality? Unlock Superior Density & Structural Integrity
- What PPE is suggested for adjusting controls or handling equipment during furnace operation? Essential Gear for Operator Safety
- What is the main benefit of using a benchtop industrial oven? Save Space and Boost Efficiency in Your Lab





