In industrial heating, the material you choose for a heating element is the single most important factor determining its lifespan and reliability. Environmental factors, including invisible chemical contaminants and atmospheric conditions, can attack and degrade even high-quality alloys, leading to premature failure. Selecting the right material is not about finding the "best" alloy, but the one best suited to survive its specific operating environment.
The core principle is simple: the environment dictates the material. An alloy perfectly suitable for a clean, dry furnace can fail in a matter of hours in the presence of specific chemical contaminants. Understanding the threats present in your application is the first and most critical step in heater specification.

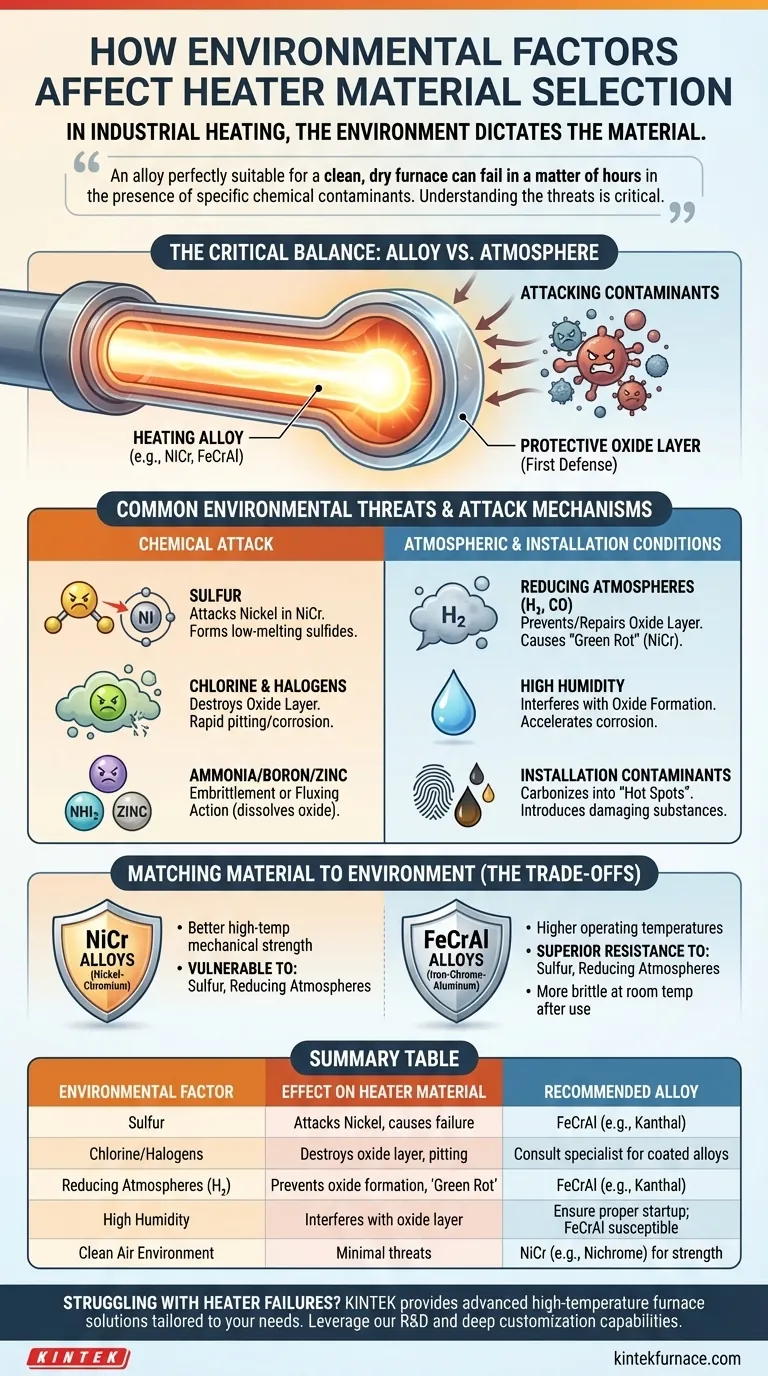
Why the Operating Environment is Critical
A heating element's survival depends on a delicate balance between the alloy and the atmosphere around it. When this balance is disrupted by external factors, rapid degradation begins.
The Protective Oxide Layer: A Heater's First Defense
Most high-temperature heating alloys, like Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) or Iron-Chrome-Aluminum (FeCrAl), don't operate as bare metal. When first heated, they form a thin, stable, and non-conductive oxide layer on their surface.
This layer acts as a protective shield, preventing oxygen from reaching the underlying metal and causing further oxidation or burnout. The integrity of this layer is paramount to the heater's longevity.
How Contaminants Breach This Defense
Environmental contaminants attack the heating element by chemically compromising this protective oxide layer. Once breached, the contaminant can directly attack the alloy, leading to rapid corrosion, embrittlement, and failure.
Common Environmental Threats to Heater Alloys
Different contaminants and conditions pose unique threats. The key is to identify which threats are present in your process and select an alloy known to resist them.
Chemical Attack from Contaminants
Certain chemicals are exceptionally destructive to common heater alloys.
- Sulfur: Sulfur aggressively attacks nickel, which is a primary component of NiCr alloys. This leads to the formation of low-melting-point nickel sulfide, causing catastrophic failure at temperatures far below the alloy's normal rating.
- Chlorine and Halogens: Chlorine, fluorine, and other halogens can destroy the protective oxide layer, leading to rapid, localized pitting and corrosion on both NiCr and FeCrAl alloys.
- Ammonia: In high-temperature applications, "cracked" ammonia can introduce nitrogen into the alloy, causing embrittlement through the formation of nitrides.
- Boron and Zinc: Compounds containing boron or zinc can create a low-melting-point "glassy" phase on the element's surface. This fluxing action dissolves the protective oxide layer, exposing the raw alloy to attack.
Atmospheric Conditions
The gas composition of the environment is also a critical factor.
- Reducing Atmospheres: Atmospheres rich in hydrogen or carbon monoxide can prevent the formation or repair of the essential oxide layer. This condition, known as "green rot," primarily affects NiCr alloys by selectively oxidizing the chromium, leading to severe embrittlement.
- High Humidity: Water vapor can interfere with the formation of a stable oxide layer, particularly on FeCrAl alloys during initial heat-up. It can also accelerate corrosion when other contaminants are present.
Contamination During Installation
Even the installation process can introduce damaging substances. Oils, greases, or fingerprints left on the element can carbonize when heated, creating localized "hot spots" or introducing contaminants that attack the alloy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single alloy is immune to all threats. The selection process involves balancing performance characteristics against the specific environmental challenges.
Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) vs. Iron-Chrome-Aluminum (FeCrAl)
These two families of alloys represent a common trade-off. NiCr alloys (like Nichrome) generally have better mechanical strength at high temperatures but are extremely vulnerable to sulfur and reducing atmospheres.
FeCrAl alloys (like Kanthal) can often operate at higher temperatures and have superior resistance to sulfur. However, they can be more brittle at room temperature after use and may be more susceptible to damage from water vapor during initial startup.
Cost vs. Longevity
Highly specialized alloys that resist a wide range of chemical attacks are available, but they often come at a significant cost premium. In many cases, a standard, well-matched alloy will provide excellent service life if the environment is properly understood and controlled. Investing in a more expensive material is only logical if a specific, known threat justifies it.
Matching the Material to Your Environment
Use your knowledge of the operating environment to guide your selection. A small investment in analysis upfront can prevent costly downtime and frequent heater replacement.
- If your environment contains sulfur: Strongly prefer an FeCrAl (Iron-Chrome-Aluminum) alloy over a NiCr (Nickel-Chromium) alloy.
- If you operate in a reducing atmosphere (e.g., hydrogen): Choose an FeCrAl alloy, as NiCr alloys are highly susceptible to green rot.
- If your primary concern is high-temperature mechanical strength in a clean air environment: A NiCr alloy is often an excellent and reliable choice.
- If halogens like chlorine are present: Consult a material specialist, as both standard alloy families can be compromised. A specialized or coated element may be necessary.
- If your process is new or the environment is unknown: Consider running a test with a small sample of the proposed alloy to observe its performance before committing to a full-scale installation.
Ultimately, designing for reliability means looking beyond the heater itself and scrutinizing the world in which it will operate.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Factor | Effect on Heater Material | Recommended Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfur | Attacks nickel in NiCr alloys, causing failure | FeCrAl (e.g., Kanthal) |
| Chlorine/Halogens | Destroys oxide layer, leading to pitting and corrosion | Consult specialist for coated or specialized alloys |
| Reducing Atmospheres (e.g., Hydrogen) | Prevents oxide layer formation, causes green rot in NiCr | FeCrAl (e.g., Kanthal) |
| High Humidity | Interferes with oxide layer, accelerates corrosion | Ensure proper startup; FeCrAl may be more susceptible |
| Clean Air Environment | Minimal threats, focuses on mechanical strength | NiCr (e.g., Nichrome) |
Struggling with heater failures due to harsh environments? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your lab's unique needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely match your experimental requirements. Don't let environmental factors compromise your results—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your heating system's reliability and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















