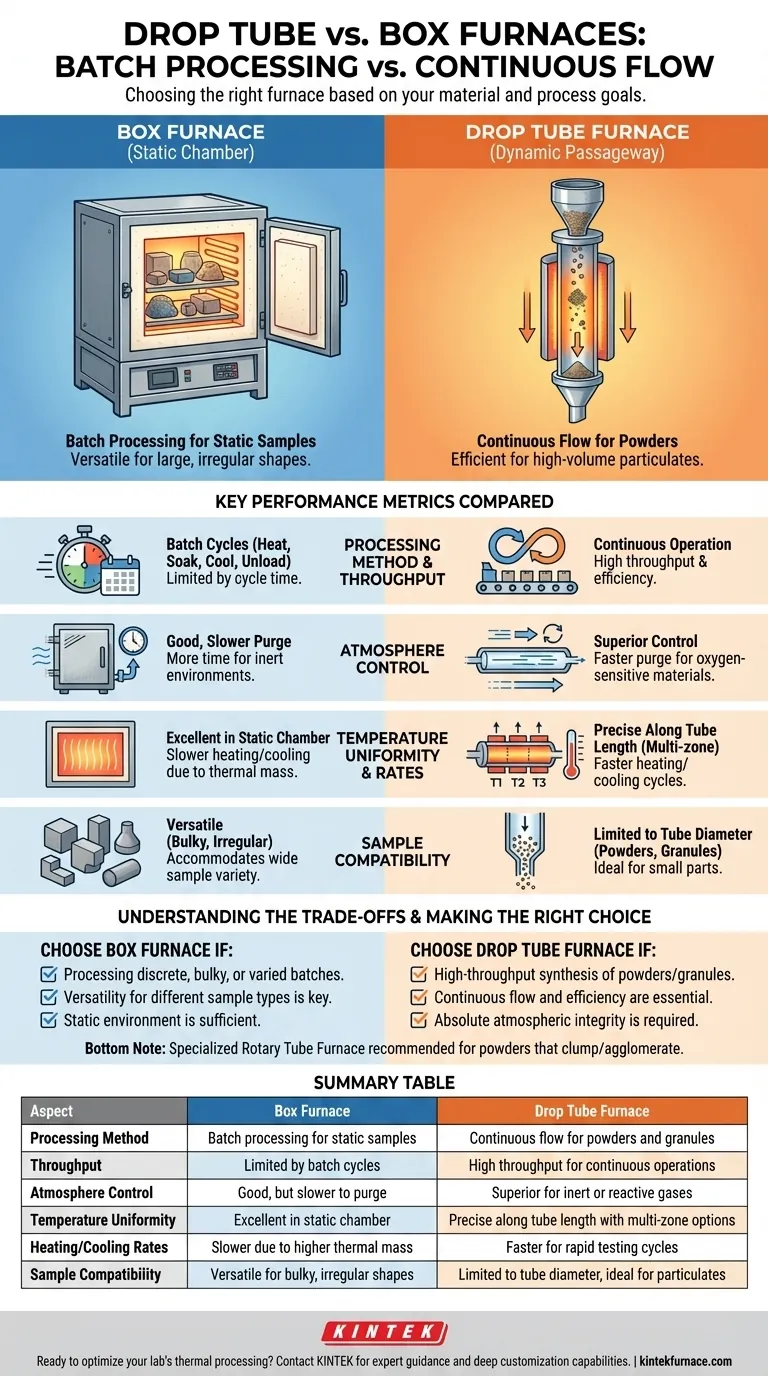
At its core, the choice is between batch processing and continuous flow. A traditional box furnace is a sealed chamber designed to heat static items in discrete batches, much like a conventional oven. In contrast, a drop tube furnace uses a vertical, heated tube through which materials fall, enabling continuous or semi-continuous processing in a highly controlled atmosphere.
The decision between a drop tube and a box furnace is not about which is superior, but which aligns with your material's form and your process goals. Box furnaces offer versatility for static, bulky samples, while drop tube furnaces provide efficiency for the continuous flow of powders and particulates.

The Fundamental Design: Batch vs. Flow
The most significant difference between these two furnace types lies in how they hold and process materials. This design philosophy dictates their ideal applications.
The Box Furnace: A Static Chamber
A box furnace, also known as a muffle furnace, operates on a simple principle: you place your sample inside a chamber, close the door, and heat it for a set duration.
This design is ideal for batch work, where you process one or more discrete items at a time. It is highly versatile, accommodating a wide variety of sample sizes, shapes, and weights.
The Tube Furnace: A Dynamic Passageway
A tube furnace processes material as it moves through a heated cylindrical tube. A drop tube furnace is a specific, vertical configuration of this design where gravity is used to move the material.
This enables continuous or semi-continuous processing. Materials, typically powders or granules, are introduced at the top and collected at the bottom after passing through the controlled heating zone.
Key Performance Metrics Compared
Understanding the design difference clarifies how each furnace performs in key areas.
Processing Method and Throughput
A box furnace is defined by its batch processing. Throughput is limited by the time it takes to heat, soak, cool, and manually unload one batch before starting the next.
A drop tube furnace is built for continuous flow. For high-volume production of specific powders, its automated, continuous nature offers far greater throughput and efficiency.
Atmosphere Control
Tube furnaces provide superior atmosphere control. The small, contained volume of the tube is much easier and faster to purge of ambient air and fill with a precise, inert, or reactive gas.
This makes them essential for working with oxygen-sensitive materials or for processes that require a specific gas environment, like the synthesis of carbon nanotubes or graphene.
Temperature Uniformity
A high-quality box furnace provides excellent temperature uniformity within its large, static chamber.
A multi-zone tube furnace offers exceptional uniformity along the length of the tube. This allows for precise temperature profiling, where a material can be exposed to different temperatures as it travels through the furnace.
Heating and Cooling Rates
Due to their lower thermal mass and smaller size, tube furnaces generally have faster heat-up and cool-down times compared to larger, more heavily insulated box furnaces. This can be a significant advantage for rapid testing cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is a universal solution. The choice involves clear trade-offs based on your specific application.
Sample Size and Geometry
The box furnace is the clear winner for flexibility. It can handle large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects that simply would not fit inside a furnace tube.
A drop tube furnace is restrictive, limited by the diameter of its tube, which typically ranges from 15 mm to 200 mm. It is only suitable for powders, granules, or very small parts.
Process Specialization
Box furnaces are general-purpose tools, jacks-of-all-trades in a lab or workshop.
Drop tube furnaces are specialists. They excel at specific tasks like calcination, pyrolysis, or synthesis of particulate materials but lack the general versatility of a box furnace.
Material Agglomeration
In a standard drop tube furnace, certain powders can stick or clump together (agglomerate), leading to uneven heating.
For these materials, a more specialized rotary tube furnace is often required. This variant rotates and tilts the tube, ensuring the material is constantly tumbling for maximum heat exposure and uniformity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be guided by your material and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is processing discrete, bulky, or varied samples in batches: A box furnace provides the necessary capacity and versatility.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput synthesis or treatment of powders and granules: A drop tube furnace delivers superior efficiency and process control.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute atmospheric integrity for sensitive materials: A tube furnace's enclosed design is more effective and economical.
- If your primary focus is processing fine powders that may clump or require agitation: A specialized rotary tube furnace is the most appropriate tool.
Choosing the correct furnace begins with a clear understanding of whether your work requires a static environment or a dynamic flow.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Box Furnace | Drop Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Method | Batch processing for static samples | Continuous flow for powders and granules |
| Throughput | Limited by batch cycles | High throughput for continuous operations |
| Atmosphere Control | Good, but slower to purge | Superior for inert or reactive gases |
| Temperature Uniformity | Excellent in static chamber | Precise along tube length with multi-zone options |
| Heating/Cooling Rates | Slower due to higher thermal mass | Faster for rapid testing cycles |
| Sample Compatibility | Versatile for bulky, irregular shapes | Limited to tube diameter, ideal for particulates |
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal processing? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether you require the versatility of Muffle or Box Furnaces for batch work or the efficiency of Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems for continuous flow, our deep customization capabilities ensure precise performance. Leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to enhance your experiments—contact us today for expert guidance and a solution that fits your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















