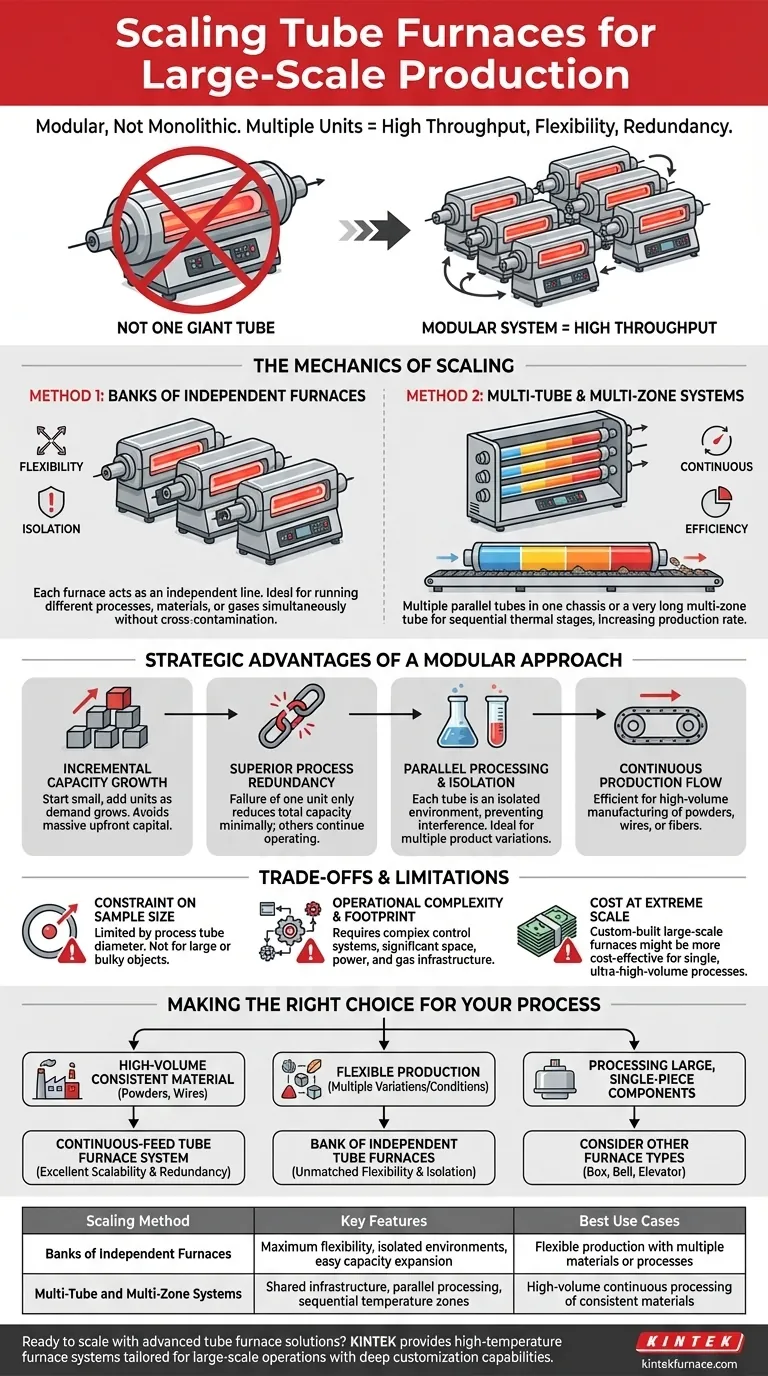
Yes, tube furnaces can be effectively scaled for large-scale production by combining multiple units into a larger, integrated system. This modular approach allows for a significant increase in throughput, making it a viable and common strategy for industrial operations that require consistent and high-volume thermal processing.
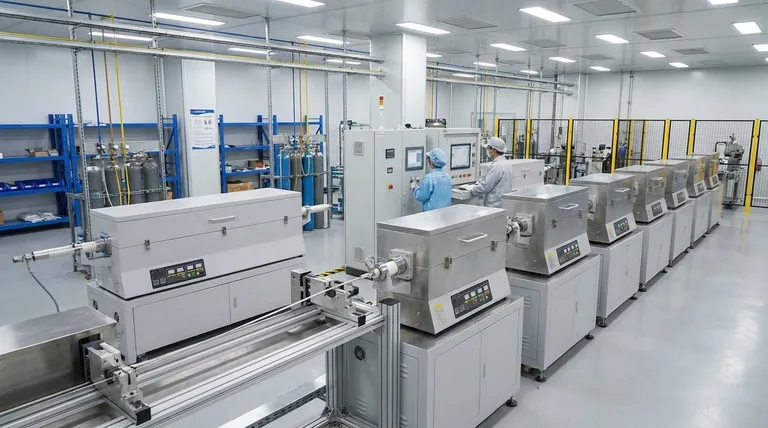
The core principle behind scaling tube furnaces is not building a single, massive tube, but creating a high-throughput system by multiplying the number of processing units. This provides unique advantages in flexibility, redundancy, and process control that a monolithic furnace cannot offer.

The Mechanics of Scaling Tube Furnaces
Scaling is achieved through two primary methods, both centered on the idea of parallel processing. The choice between them depends on your specific needs for process integration and control.
Method 1: Banks of Independent Furnaces
The most straightforward approach is to arrange multiple, separate tube furnaces side-by-side. Each furnace acts as an independent production line.
This setup is ideal for maximum flexibility. You can run different temperature profiles, use different atmospheric gases, or even process entirely different materials in adjacent furnaces simultaneously without cross-contamination.
Method 2: Multi-Tube and Multi-Zone Systems
Some manufacturers offer furnace models that contain several process tubes within a single chassis. These systems share a common casing and some control infrastructure but allow for parallel processing.
Similarly, a very long multi-zone tube furnace can sometimes be used to scale a process. By creating sequential temperature zones, you can move a product through different stages of a thermal cycle within a single tube, increasing the rate at which finished material is produced.
Key Strategic Advantages of a Modular Approach
Scaling with multiple tubes isn't just about increasing volume; it provides strategic benefits that are critical in a production environment.
Incremental Capacity Growth
You can start with one or two furnaces and add more units as demand grows. This avoids a massive upfront capital investment and allows your production capacity to scale linearly with your business needs.
Superior Process Redundancy
In a system with ten furnaces, the failure of one unit only reduces your total capacity by 10%. The other nine can continue operating. This built-in redundancy is a significant advantage over a single large furnace, where any failure can halt all production.
Parallel Processing and Isolation
A modular setup allows for true parallel processing. This is invaluable for labs scaling up a process or for manufacturing facilities that produce multiple product variations. Each tube is a perfectly isolated environment, preventing any interference between batches.
Continuous Production Flow
Tube furnaces are exceptionally well-suited for continuous processing. Materials like powders, wires, or fibers can be fed continuously through the heated tube, a method that is far more efficient for high-volume manufacturing than batch-based processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the modular scaling approach has practical considerations that must be weighed against its benefits.
Constraint on Sample Size
The primary limitation is the diameter of the process tube. Tube furnaces are ideal for processing powders, wafers, small parts, or thin films. They are not suitable for thermally treating large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects.
Operational Complexity and Footprint
Managing a large bank of individual furnaces requires more complex control and monitoring systems than a single furnace. The overall physical footprint, along with the required power and gas supply infrastructure, can also be substantial.
Cost at Extreme Scale
For a single, unchanging, high-volume process, there may be a point where a custom-built, large-scale continuous furnace (like a belt or rotary kiln furnace) becomes more cost-effective per unit of output. The trade-off is a complete loss of flexibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding if a scaled tube furnace system is right for you depends entirely on your production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing of a consistent material (powders, wires): A system of continuous-feed tube furnaces is an excellent, scalable, and redundant solution.
- If your primary focus is flexible production with multiple product variations or process conditions: A bank of independent tube furnaces provides unmatched flexibility and process isolation.
- If your primary focus is processing large, single-piece components: You should consider other furnace types, such as a box, bell, or elevator furnace, as a tube furnace is not the right tool.
By understanding this modular philosophy, you can leverage tube furnaces not just as lab instruments, but as robust and scalable engines for industrial production.
Summary Table:
| Scaling Method | Key Features | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Banks of Independent Furnaces | Maximum flexibility, isolated environments, easy capacity expansion | Flexible production with multiple materials or processes |
| Multi-Tube and Multi-Zone Systems | Shared infrastructure, parallel processing, sequential temperature zones | High-volume continuous processing of consistent materials |
Ready to scale your production with advanced tube furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored for large-scale operations. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our scalable solutions can enhance your efficiency and output!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















