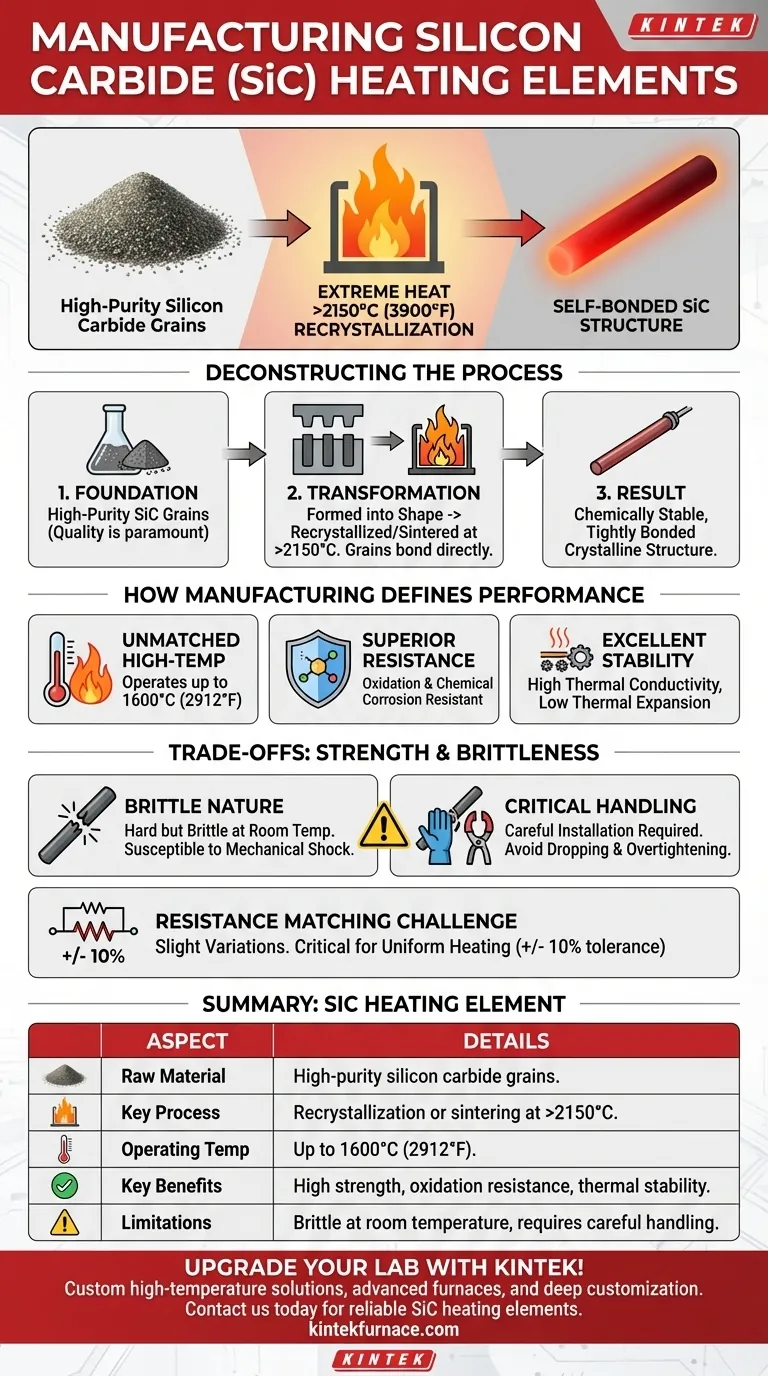
At its core, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are manufactured by taking high-purity silicon carbide grains and fusing them into a solid, self-bonded structure. This is accomplished through a process called recrystallization or reaction-bonding, which occurs at extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 2150°C (3900°F), creating a material uniquely suited for high-temperature applications.
The manufacturing process for SiC elements is designed to create a material with exceptional strength and stability at extreme temperatures. However, this same process results in a hard but brittle material at room temperature, making careful handling a critical factor for successful operation.

Deconstructing the Manufacturing Process
The creation of a SiC heating element is a feat of material science, turning a granular powder into a robust, high-performance component.
The Foundation: High-Purity Silicon Carbide
The process begins with high-purity silicon carbide grains. The quality of this raw material is paramount, as impurities can create weak points and negatively impact the element's electrical properties and lifespan at high temperatures.
The Transformation: Recrystallization
These SiC grains are formed into the desired shape, typically a rod or tube. They are then heated to extreme temperatures in a specialized furnace.
At these temperatures, the individual grains bond directly to each other, a process known as recrystallization or sintering. This fuses the powder into a single, dense, and structurally solid piece of silicon carbide without the need for any binding agent.
The Result: A Chemically Stable Structure
This high-temperature fusion creates a chemically stable material with a tightly bonded crystalline structure. This structure is the key to the element's remarkable performance characteristics.
How Manufacturing Defines Element Performance
The way a SiC element is made directly dictates its capabilities and limitations. The recrystallization process is not just for creating a shape; it's for engineering specific material properties.
Unmatched High-Temperature Capability
The self-bonded structure is incredibly strong, allowing SiC elements to operate at surface temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F). This far exceeds the capabilities of traditional metallic heating elements.
Superior Chemical and Oxidation Resistance
The tightly bonded SiC material is highly resistant to oxidation and chemical corrosion. This makes it ideal for use in harsh industrial atmospheres where other elements would quickly degrade.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity and Stability
The manufacturing process results in a material with excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to transfer heat efficiently. It also has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it won't deform or warp even under rapid temperature changes.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength and Brittleness
While the manufacturing process creates a component that is incredibly strong at high temperatures, it also introduces a critical trade-off.
The Brittle Nature of Silicon Carbide
At room temperature, SiC elements are hard but brittle. The same rigid, crystalline structure that provides high-temperature strength makes them susceptible to fracture from mechanical shock or impact.
Critical Implications for Installation
This brittleness demands careful handling during installation. The elements must be protected from being dropped or struck.
Clamps and electrical connection straps must be tightened firmly but carefully to ensure good contact without creating stress points that could cause a fracture.
The Challenge of Resistance Matching
The manufacturing process can result in slight variations in electrical resistance from one element to the next. For uniform heating in a furnace, it is critical that all elements in a set have resistance values within a tight tolerance, typically +/- 10% of each other.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding how SiC elements are made is crucial for leveraging their unique advantages in your specific application.
- If your primary focus is maximum operating temperature: SiC's recrystallized manufacturing process makes it one of the best choices available, capable of reliably reaching 1600°C.
- If your primary focus is durability in harsh environments: The chemically stable structure created during manufacturing provides superior resistance to both oxidation and chemical attack.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability: Acknowledge that the element's inherent brittleness requires meticulous handling and proper installation to prevent premature failure and ensure a long service life.
By appreciating the link between its creation and its characteristics, you can effectively deploy silicon carbide for demanding high-temperature processes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Raw Material | High-purity silicon carbide grains |
| Key Process | Recrystallization or sintering at >2150°C |
| Operating Temp | Up to 1600°C (2912°F) |
| Key Benefits | High strength, oxidation resistance, thermal stability |
| Limitations | Brittle at room temperature, requires careful handling |
Upgrade your lab with custom high-temperature solutions from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable, durable SiC heating elements tailored for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















