In short, rotary furnaces process granular and powdery materials by tumbling them inside a heated, rotating tube. This constant motion ensures every particle receives exceptionally uniform thermal exposure, which is critical for processes like calcining, drying, and sintering where consistency dictates the final product's quality and performance.
The true value of a rotary furnace is not simply heating, but the uniformity it guarantees. The mechanical rotation solves the core challenge of processing powders and granules: ensuring every particle is treated identically to achieve predictable and repeatable material properties.

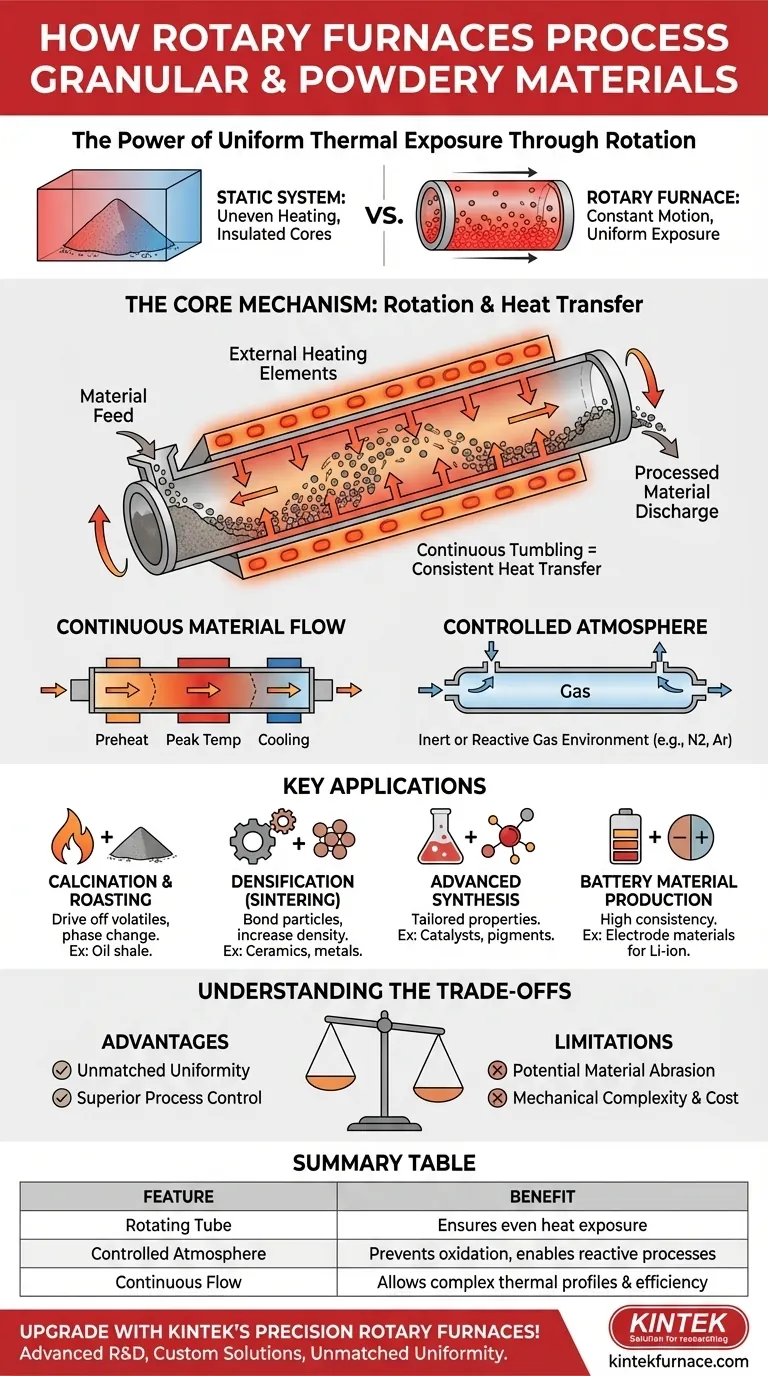
How a Rotary Furnace Achieves Uniform Processing
The design of a rotary furnace is purpose-built to overcome the challenges of heating fine materials, which tend to insulate themselves in static systems.
The Core Mechanism: Rotation and Heat Transfer
A rotary furnace consists of a cylindrical tube that rotates on its horizontal axis. The material to be processed is fed into this tube.
External heating elements, typically electric, heat the outside of the tube. As the tube rotates, the heat is transferred evenly around its circumference and then conducted into the material inside.
This tumbling action continuously exposes new surfaces of the powder or granules to the heated tube wall, ensuring consistent and efficient heat transfer throughout the entire batch.
Continuous Material Flow
Many rotary furnaces are designed for continuous processing. Material is fed into one end of the inclined, rotating tube and slowly travels to the other end.
This design allows for different thermal zones along the length of the furnace, enabling complex heating profiles where a material can be preheated, held at a peak temperature, and then cooled in a single, continuous process.
The Importance of a Controlled Atmosphere
For many advanced materials, processing must occur in a specific gaseous environment. Rotary furnaces can be sealed to operate as atmosphere furnaces.
This allows for processing in an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation, or in a reactive gas to facilitate a specific chemical change. This control is vital for producing high-purity metals, ceramics, and battery components.
Key Applications for Powders and Granules
The combination of uniform heating and atmospheric control makes rotary furnaces indispensable for several high-value industrial and research processes.
Thermal Treatment (Calcination & Roasting)
Calcination involves heating a material to drive off volatile substances or trigger a phase change. For example, oil shale is heated in a rotary furnace to release hydrocarbons.
The constant mixing ensures that the reaction proceeds evenly and completely throughout the material, maximizing yield and preventing localized overheating.
Densification and Strengthening (Sintering)
Sintering is the process of heating powders, such as ceramics or metals, to a high temperature below their melting point. This causes the particles to bond, increasing the material's density, strength, and corrosion resistance.
The uniform heating of a rotary furnace is crucial for avoiding structural defects and achieving a homogenous, densified final part.
Advanced Material Synthesis
Rotary furnaces are used to manufacture materials with highly specific characteristics. This includes producing catalysts with optimized activity and selectivity or creating pigments for paints with precise color and durability.
By carefully controlling the temperature, atmosphere, and residence time, manufacturers can tailor the final properties of the material.
Battery Material Production
The new energy sector relies heavily on rotary furnaces. They are used to process positive and negative electrode materials, such as graphitized carbon and silicon-based anodes, for lithium-ion batteries.
The extreme consistency provided by this technology is essential for the performance, longevity, and safety of the final battery cells.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their specific advantages and limitations is key to proper application.
Advantage: Unmatched Uniformity
For granular and powdered materials, no other furnace type offers this level of thermal consistency. The tumbling action is the single most important feature, directly leading to higher quality and more repeatable results.
Advantage: Superior Process Control
The ability to manage temperature profiles, rotation speed, tube incline (residence time), and atmosphere provides a high degree of control over the final material properties.
Limitation: Potential for Material Abrasion
The tumbling action that ensures uniform heating can also cause attrition. Fragile or abrasive materials may break down or wear against the tube wall, which could contaminate the product or alter particle size distribution.
Limitation: Mechanical Complexity and Cost
Compared to a static box furnace, a rotary furnace is a more complex mechanical system with a rotating seal, drive motor, and support rollers. This can result in higher initial investment and maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material consistency: A rotary furnace is ideal, as its rotation guarantees uniform heat exposure that is difficult to replicate in a static system.
- If your primary focus is producing advanced materials with tailored properties: The precise control over both temperature and atmosphere makes this technology essential for applications in batteries, catalysts, and ceramics.
- If you are processing extremely fragile or agglomerated materials: You must carefully evaluate the risk of particle breakdown from the tumbling action and consider if a static furnace might be a safer, albeit less uniform, alternative.
By understanding the interplay between mechanical rotation and thermal control, you can leverage the rotary furnace to achieve unparalleled consistency in your material processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Rotating Tube | Ensures even heat exposure for all particles |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and enables reactive processes |
| Continuous Flow | Allows for complex thermal profiles and efficient processing |
| Key Applications | Calcination, sintering, catalyst and battery material production |
Upgrade your material processing with KINTEK's precision rotary furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature solutions like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure these systems meet your unique experimental needs for granular and powdery materials, delivering unmatched uniformity and control. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















