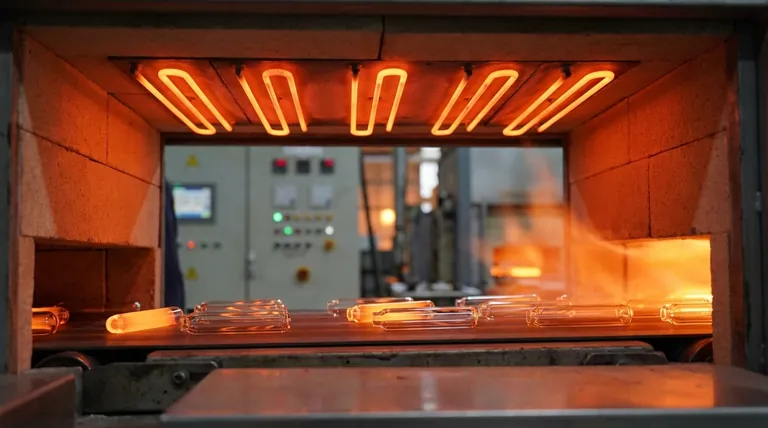
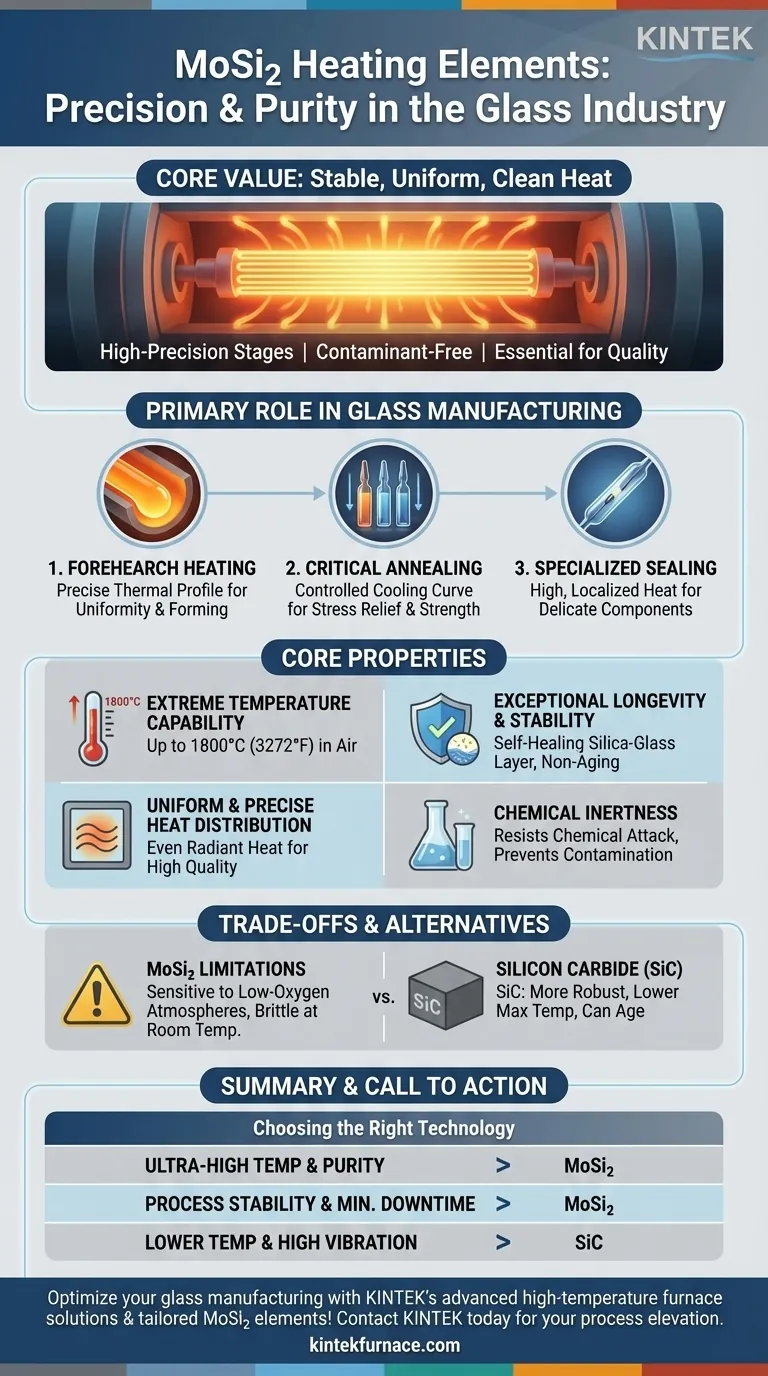
In the glass industry, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) heating elements are primarily used in the final, high-precision stages of production. They are most commonly found providing contaminant-free heat in the forehearths of melting furnaces, which is critical for processes like annealing glass ampoules and sealing electronic components such as reed switches.
The core value of MoSi₂ elements in glass manufacturing is not just their ability to reach extreme temperatures, but their capacity to deliver exceptionally stable, uniform, and clean heat. This precision is essential for ensuring the final quality, strength, and clarity of the glass product.

The Primary Role of MoSi₂ in Glass Manufacturing
MoSi₂ elements are not typically used for the initial bulk melting of raw materials, which is an extremely high-energy process. Instead, their unique properties make them indispensable for the more delicate, temperature-sensitive finishing stages.
Forehearth Heating and Conditioning
The forehearth is a critical channel that transports molten glass from the main furnace to the forming machines. Temperature control in this zone is paramount.
MoSi₂ elements provide the precise thermal profile needed to bring the glass to the exact viscosity required for forming, ensuring product uniformity and minimizing defects.
Critical Annealing Processes
Annealing is the process of slowly cooling glass to relieve internal stresses that can cause it to crack or shatter.
The uniform radiant heat from MoSi₂ elements allows for a highly controlled cooling curve. This is vital for producing strong, stable products like laboratory ampoules or other high-value glassware.
Specialized Sealing Applications
The high, localized heat from these elements is perfect for specialized tasks. A key example is the sealing of reed switches, where glass must be melted around delicate electronic components without causing damage or contamination.
Core Properties Driving Their Adoption
The preference for MoSi₂ elements in these specific glass applications is driven by a unique combination of material properties.
Extreme Temperature Capability
MoSi₂ elements can operate consistently in air at temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F). This high-temperature ceiling provides a wide operational window for processing various types of specialty glass.
Exceptional Longevity and Stability
Unlike many metallic elements, MoSi₂ elements do not "age" in the traditional sense. They develop a protective silica-glass layer on their surface that "self-heals" if damaged, preventing further oxidation and ensuring a very long and predictable service life.
Uniform and Precise Heat Distribution
These elements provide heat primarily through thermal radiation, which results in a very even temperature distribution within the furnace chamber. This uniformity is non-negotiable for high-quality annealing.
Chemical Inertness
The protective silica layer makes the element highly resistant to chemical attack and ensures it does not introduce contaminants into the furnace atmosphere. This is crucial for maintaining the purity and optical clarity of the glass.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, MoSi₂ elements are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to proper application and avoiding costly failures.
Sensitivity to Atmosphere
The maximum operating temperature of MoSi₂ elements must be lowered in low-oxygen atmospheres. The protective silica layer cannot form or be maintained without sufficient oxygen, leading to rapid degradation of the element.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
Like many ceramic materials, MoSi₂ is very brittle at low temperatures. This requires careful handling during installation and maintenance to prevent mechanical shock or fracture. They only gain ductility at very high temperatures.
Comparison with Alternatives
Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are another common choice in the glass industry. SiC is generally more robust and tolerant of mechanical stress, but it typically has a lower maximum operating temperature and can age over time, requiring more frequent monitoring and adjustment of the power supply.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Choosing the correct heating element technology requires aligning its specific strengths with your primary production goals.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature processing (>1600°C) and absolute product purity: MoSi₂ is the superior choice for its stability and non-contaminating nature.
- If your primary focus is process stability and minimizing downtime: The self-healing, non-aging characteristic of MoSi₂ provides unmatched longevity and predictable performance.
- If you are operating at lower temperatures or in an environment with high mechanical vibration: A more robust element like Silicon Carbide (SiC) may be a more practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, leveraging the right heating technology is fundamental to achieving both efficiency and quality in modern glass manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Forehearth Heating | Precise temperature control for uniform glass viscosity |
| Annealing Processes | Uniform radiant heat for stress relief and strength |
| Sealing Applications | High, localized heat for contaminant-free component sealing |
Optimize your glass manufacturing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored MoSi₂ heating elements and systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs for enhanced purity, efficiency, and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can elevate your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?



















