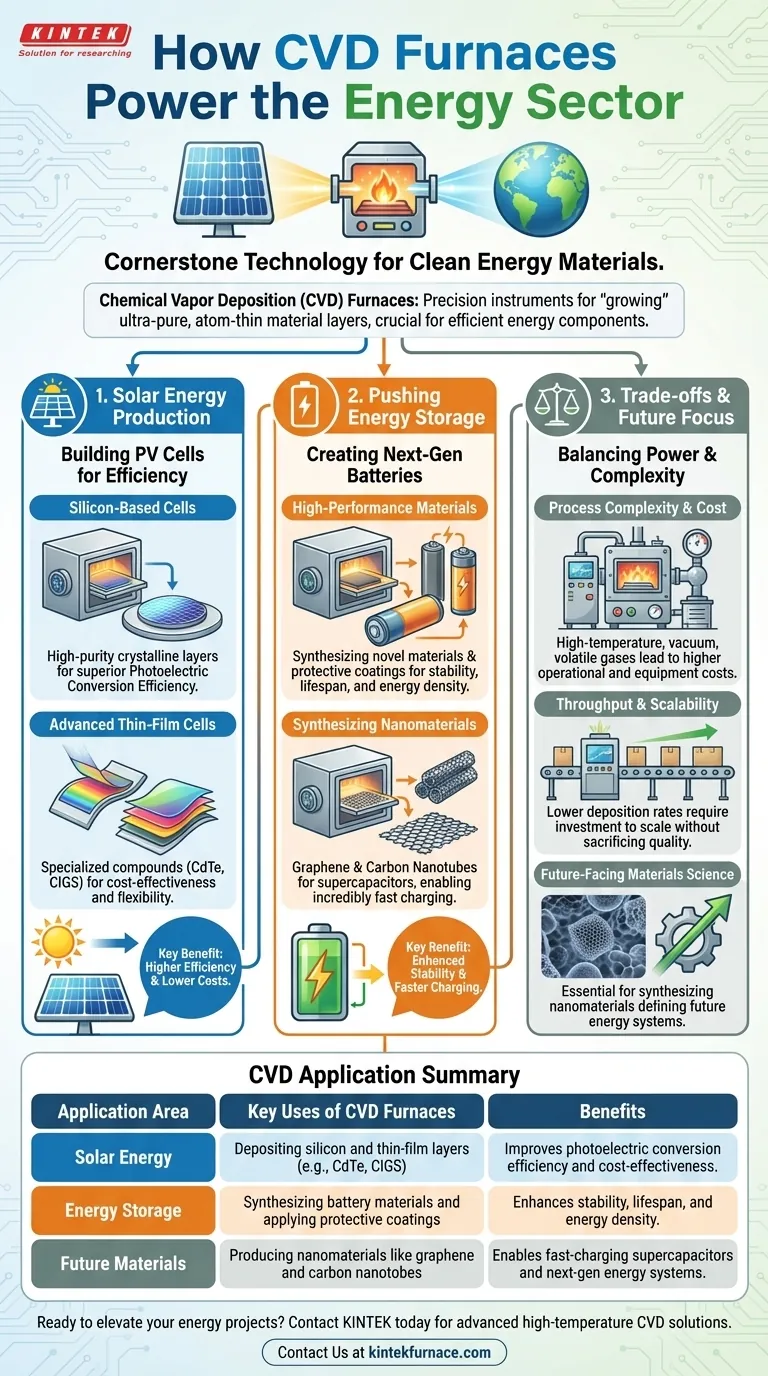
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnaces are a cornerstone technology for manufacturing the high-performance materials that power the clean energy transition. They are primarily used to produce the foundational layers of modern solar cells and are increasingly critical for developing advanced materials for next-generation batteries.
A CVD furnace isn't just a high-temperature oven; it's a precision instrument. Its unique ability to "grow" ultra-pure, atom-thin layers of material onto a surface is what makes it indispensable for creating the efficient and cost-effective components demanded by the energy sector.
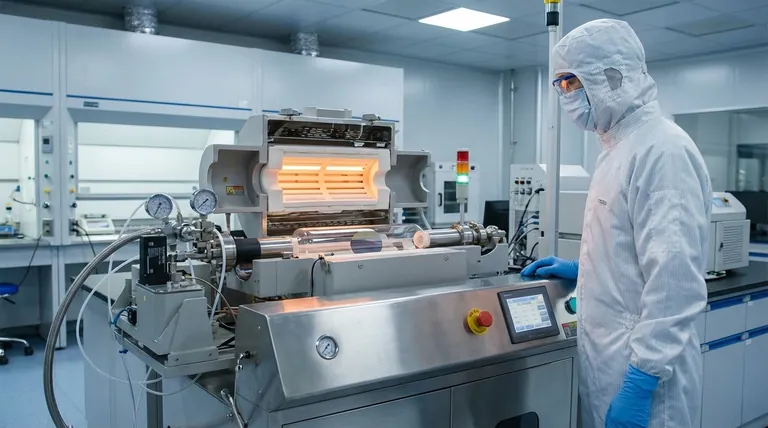

The Role of CVD in Solar Energy Production
The most significant impact of CVD furnaces in the energy sector is in the manufacturing of photovoltaic (PV) cells, commonly known as solar cells. The process is essential for creating the semiconductor layers that convert sunlight into electricity.
Building Silicon-Based Solar Cells
Most solar panels today are built on a silicon foundation. CVD furnaces are used to deposit extremely pure, crystalline layers of silicon onto a substrate.
This precise control over film thickness and purity is directly linked to the panel's photoelectric conversion efficiency—its ability to turn light into usable power.
Fabricating Advanced Thin-Film Cells
CVD is also critical for manufacturing newer types of thin-film solar cells. This technology allows for the deposition of specialized compounds with excellent solar properties.
Materials like Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) and Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS) can be deposited using CVD. These thin-film cells often offer advantages in cost-effectiveness and can be applied to flexible surfaces.
Pushing the Boundaries of Energy Storage
Beyond generation, energy storage is a critical challenge. CVD technology is being used to create the advanced materials needed for better, more powerful batteries and other storage devices.
Creating High-Performance Battery Materials
The performance of a battery is heavily dependent on the materials used in its electrodes and electrolytes. CVD furnaces are used to synthesize novel materials and apply protective coatings.
These ultra-thin coatings can improve a battery's stability, increase its lifespan, and boost its energy density, meeting the intense demands of the new energy industry.
Synthesizing Nanomaterials for Future Tech
CVD is one of the primary methods for producing advanced nanomaterials like graphene and carbon nanotubes.
These materials have extraordinary electrical and physical properties, making them ideal candidates for next-generation energy storage like supercapacitors, which promise incredibly fast charging and discharging cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is not a universal solution. It is a complex and often expensive process that requires significant expertise and capital investment.
Process Complexity and Cost
CVD furnaces operate under tightly controlled conditions, often involving high temperatures, vacuum environments, and volatile precursor gases. This complexity translates to higher operational and equipment costs compared to simpler coating methods.
Throughput and Scalability
While ideal for creating high-purity, uniform films, some CVD processes can have lower deposition rates than other industrial methods. Scaling production to meet massive demand requires significant engineering and investment to optimize throughput without sacrificing quality.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your interest in CVD's role in the energy sector depends on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is solar energy generation: Recognize that CVD is the key enabling technology behind the efficiency and falling costs of both traditional silicon and modern thin-film solar cells.
- If your primary focus is energy storage and batteries: View CVD as a critical R&D and manufacturing tool for creating the advanced materials and coatings that will unlock the next level of battery performance.
- If your primary focus is future-facing materials science: Look to CVD as the essential process for synthesizing the nanomaterials, like graphene, that will define future generations of energy systems.
Ultimately, the CVD furnace is a fundamental building block for creating the materials that make a sustainable energy future possible.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses of CVD Furnaces | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Energy | Depositing silicon and thin-film layers (e.g., CdTe, CIGS) for photovoltaic cells | Improves photoelectric conversion efficiency and cost-effectiveness |
| Energy Storage | Synthesizing battery materials and applying protective coatings | Enhances stability, lifespan, and energy density |
| Future Materials | Producing nanomaterials like graphene and carbon nanotubes | Enables fast-charging supercapacitors and next-gen energy systems |
Ready to elevate your energy projects with precision-engineered CVD solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for the energy sector. Our product line, including CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Whether you're developing solar cells, battery materials, or nanomaterials, we can help you achieve superior performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision



















