A Flaw in the Void
An engineer holds a turbine blade, a marvel of metallurgy destined for the heart of a jet engine. Its shape is perfect, its alloy composition exact. But its true strength—the resilience to withstand thousands of hours of extreme heat and stress—will be forged not in a foundry, but in the silent, controlled environment of a vacuum furnace.
A temperature deviation of just a few degrees in the wrong place during heat treatment could introduce a microscopic weakness. It’s an invisible flaw that could, years later, lead to catastrophic failure.
This isn't just about heating metal. It's about managing risk at a molecular level. Choosing the right vacuum furnace is not a matter of picking the biggest or hottest model. It's a disciplined engineering decision, a process of aligning the machine's capabilities with a specific, critical outcome.
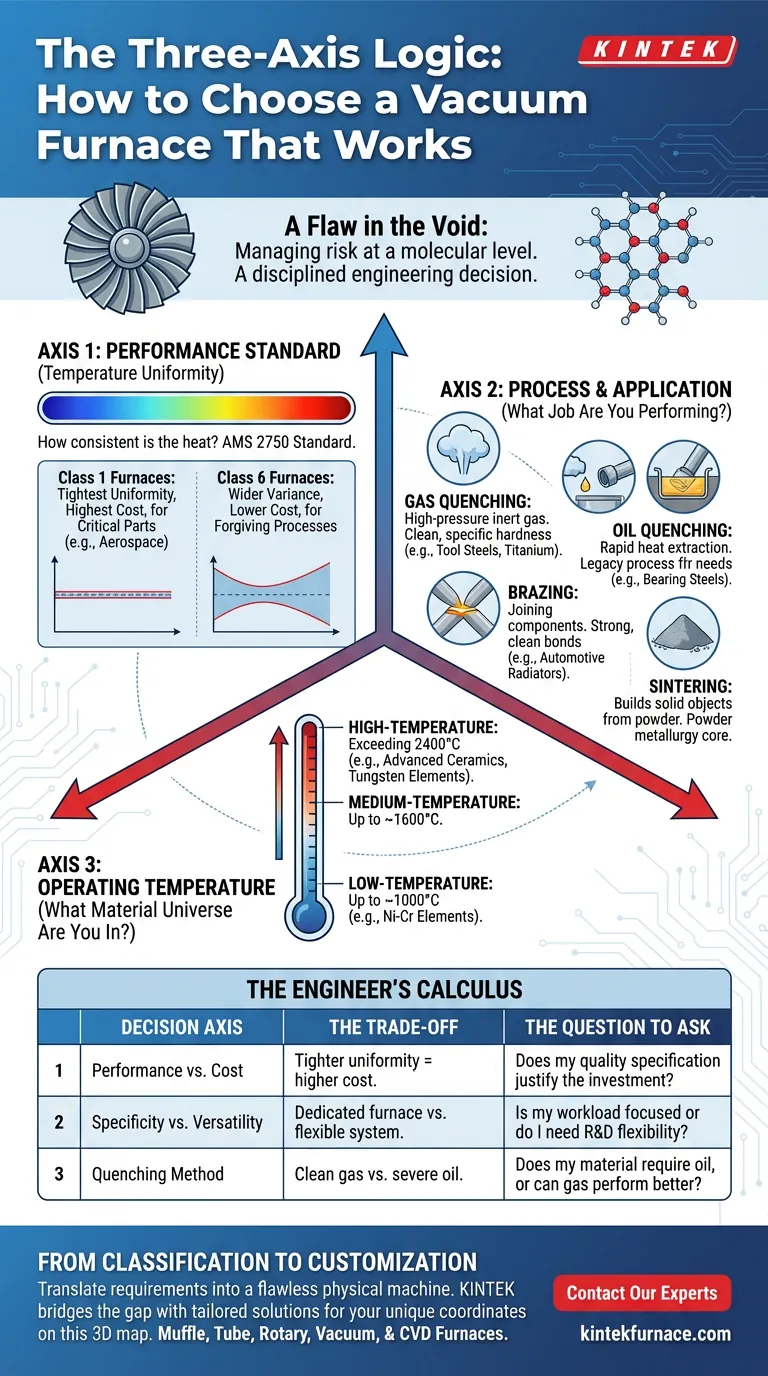
The classification of a vacuum furnace isn't a single label. It’s a three-dimensional map.
Axis 1: How Perfect Must You Be? (Performance Standard)
The first and most formal axis of classification is temperature uniformity. It answers the question: how consistent is the heat across every cubic centimeter of the working zone?
For industries like aerospace or medical device manufacturing, this is non-negotiable. The AMS 2750 standard provides the language for this requirement.
- Class 1 Furnaces: Offer the tightest uniformity, for when a part's structural integrity is paramount and process deviation is unacceptable.
- Class 6 Furnaces: Allow for a wider temperature variance, perfectly suitable for processes or materials that are more forgiving.
The choice is a reflection of your process's required precision. A higher class means more control and higher cost, but it's an investment in repeatability and quality assurance.
Axis 2: What Job Are You Performing? (Process & Application)
A furnace is a tool, and its design should reflect its purpose. This practical classification is based on the specific job the furnace is built to do.
Gas Quenching Furnaces
These are the versatile workhorses of heat treatment. They use high-pressure inert gas to cool parts rapidly and cleanly. This method is ideal for achieving specific hardness in materials like tool steels, high-speed steels, and titanium alloys without surface oxidation or contamination.
Oil Quenching Furnaces
Some materials demand a more aggressive cooling rate than gas can provide. For certain bearing steels or spring steels, the rapid heat extraction of an oil quench is necessary to achieve the required metallurgical properties. It's a legacy process, but one that remains essential for specific applications.
Brazing Furnaces
These are specialized systems for one purpose: joining components. In the vacuum, a filler metal melts and flows between parts, creating a bond that is strong, clean, and free of flux. It's the hidden technology behind complex automotive radiators and high-integrity aerospace assemblies.
Sintering Furnaces
Sintering builds solid objects from powder. In the furnace, compacted metal or ceramic particles are heated below their melting point until they fuse, creating a dense, strong final part. This is the core of powder metallurgy.
Axis 3: What Material Universe Are You In? (Operating Temperature)
The most fundamental classification is the maximum temperature a furnace can safely reach. This number dictates not only the materials you can process but the very construction of the furnace itself.
A furnace’s temperature rating is an engineering commitment.
- Heating Elements: A 1000°C furnace might use nickel-chromium wire. A 2000°C furnace requires robust molybdenum, graphite, or even tungsten elements.
- Insulation: The internal shielding must withstand the environment, evolving from ceramic fiber at lower temperatures to layers of graphite felt in the most extreme high-temperature systems.
This creates natural tiers of capability:
- Low-Temperature: Up to ~1000°C (1832°F)
- Medium-Temperature: Up to ~1600°C (2912°F)
- High-Temperature: Exceeding 2400°C (4352°F) for advanced ceramics and composites.
The Engineer's Calculus
There is no single "best" furnace. There is only the furnace that correctly solves your specific engineering equation. This requires balancing competing variables.
| Decision Axis | The Trade-Off | The Question to Ask |
|---|---|---|
| Performance vs. Cost | Tighter uniformity (e.g., AMS 2750 Class 1) requires more complex systems and is more expensive. | Does my part's quality specification justify the investment in higher precision? |
| Specificity vs. Versatility | A dedicated brazing furnace is optimized for one task. A gas quench furnace can handle many. | Is my workload focused on a single process, or do I need a flexible system for R&D? |
| Quenching Method | High-pressure gas is clean and controllable. Oil is severe and required by some legacy specs. | Does my material require an oil quench, or can I achieve better results with modern gas quenching? |
From Classification to Customization
Understanding this three-axis system—Performance, Process, and Temperature—is how you write the technical specification for the perfect furnace. But a specification on paper is not a solution in your lab.
The real challenge is translating those precise requirements into a physical machine that performs flawlessly, day after day. This is where off-the-shelf solutions often fall short.
At KINTEK, our foundation in R&D and manufacturing is built to bridge this gap. We don't just sell furnaces; we build solutions tailored to your unique coordinates on this three-dimensional map. Our portfolio of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD Furnaces serves as the starting point. Our deep customization capability is how we deliver the exact tool you need—whether it's for a high-uniformity aerospace application or a specialized high-temperature materials research project.
Don't let your process be limited by standard equipment. Let's build the furnace that matches your ambition. Contact Our Experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
Related Articles
- The Physics of Absence: How Vacuum Furnaces Defy the Limits of Heat
- Gravity as an Ally: The Counterintuitive Genius of Vertical Vacuum Furnaces
- Mastering the Void: How Custom Vacuum Furnaces Forge the Future of Materials
- The Physics of Perfection: Deconstructing Temperature Control in a Vacuum Furnace
- The Pursuit of Nothing: How Vacuum Furnace Control Defines Material Destiny




















