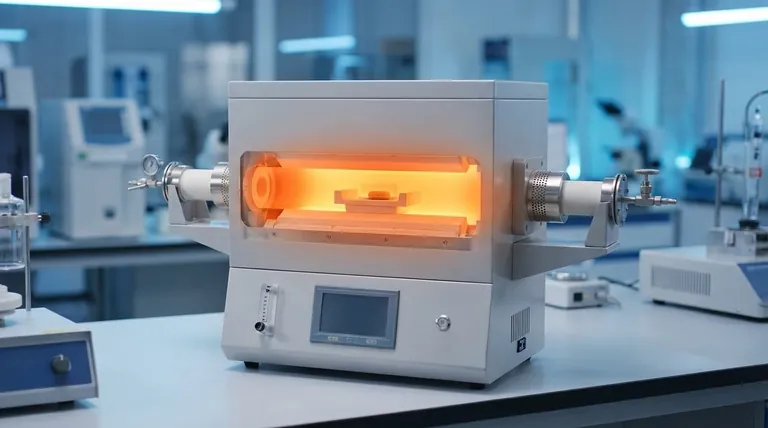
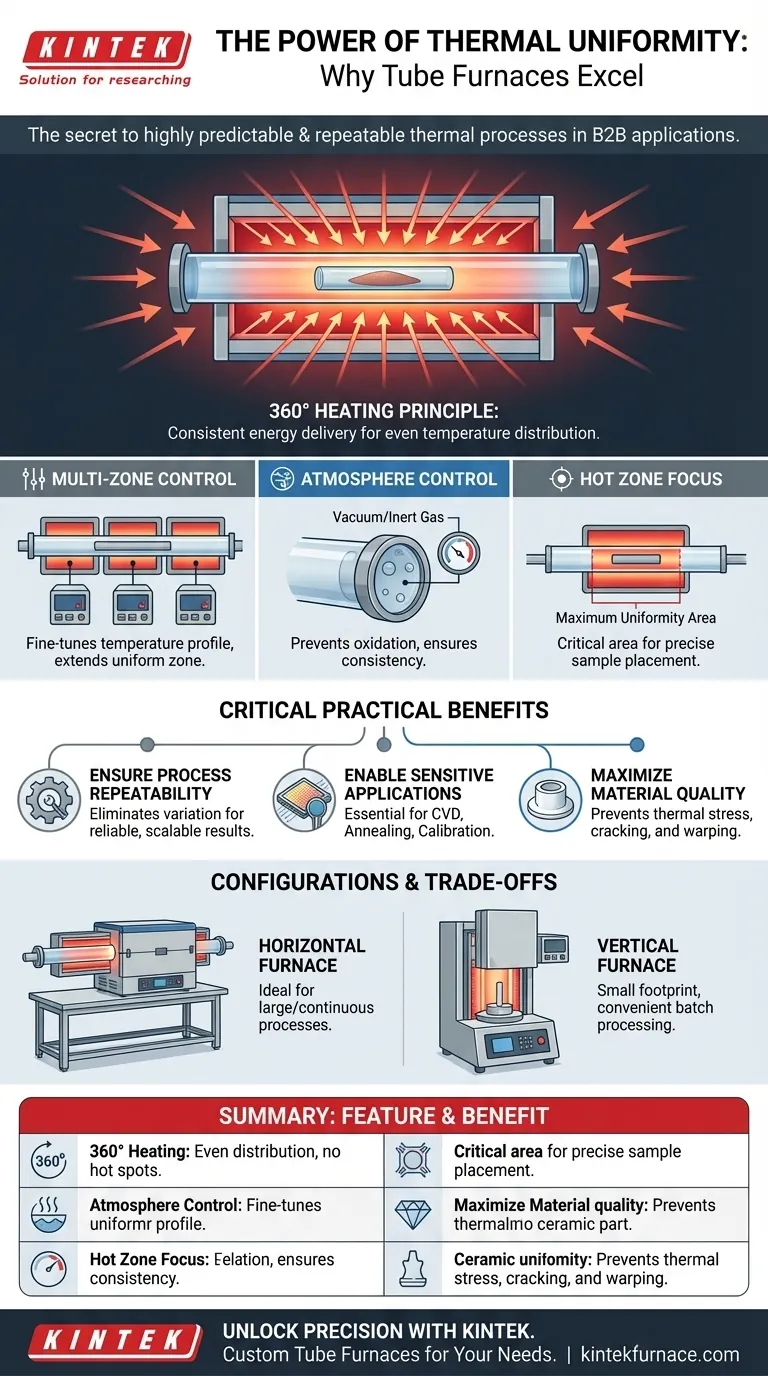
At its core, thermal uniformity is a significant advantage of a tube furnace because its cylindrical design heats the sample from all sides simultaneously. This 360-degree heat exposure ensures that the entire sample experiences a consistent temperature, which is a non-negotiable requirement for sensitive and high-precision thermal processes.
The fundamental value of a tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its ability to create a highly predictable and repeatable thermal environment. This uniformity is the key to achieving reliable outcomes in material science, calibration, and advanced manufacturing.

The Mechanics of Superior Uniformity
To understand why this uniformity is so effective, we need to look at the furnace's fundamental design principles. It’s not a single feature, but a combination of elements working together.
The 360° Heating Principle
A tube furnace's primary heating elements are arranged in a cylinder around a central process tube. This geometry is inherently superior for uniform heating compared to a box furnace, where heat radiates from flat walls.
By surrounding the sample, the furnace delivers consistent energy across its entire circumference, minimizing hot spots and cold spots.
Multi-Zone Control for Precision
Simple tube furnaces have a single heating zone. However, more advanced models feature multi-zone configurations, often with three or more independent heating zones along the length of the tube.
Each zone has its own thermocouple and controller, allowing you to fine-tune the temperature profile. This compensates for heat loss at the ends of the tube, dramatically extending the length of the uniform temperature zone.
Containing the Environment
True uniformity also depends on controlling the atmosphere within the tube. End caps or seals are critical for this.
They prevent heat from escaping and allow for precise control over the internal atmosphere. This can range from a high vacuum (down to 10⁻⁵ torr) to a specific inert gas, preventing unwanted oxidation or reactions that could affect the sample and the thermal environment.
Why Uniformity is Critical in Practice
This precise thermal control isn't just an academic benefit; it has direct, practical consequences for a wide range of applications.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
In both scientific research and industrial production, the ability to get the exact same result every time is paramount.
Thermal uniformity eliminates temperature variation as a variable. This means a process developed in a lab can be reliably scaled or repeated, with the confidence that thermal conditions are not a source of error.
Enabling Sensitive Applications
Many cutting-edge processes are intolerant of temperature fluctuations.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Uniform temperature is essential for depositing a film of consistent thickness and quality.
- Annealing: Evenly heating a material relieves internal stresses and refines its crystal structure without creating new defects.
- Thermocouple Calibration: A highly uniform temperature zone is required to accurately calibrate temperature sensors against a known standard.
Maximizing Material Quality
For thermally sensitive parts, such as advanced ceramics or single-crystal structures, uneven heating can be destructive.
It can induce thermal stress, causing cracks or warping. Uniform heating ensures the entire component undergoes the desired phase transition or treatment consistently, preserving its structural integrity and performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Configurations
While highly advantageous, it's important to understand the practical considerations and different types of tube furnaces.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Furnaces
The orientation of the furnace tube impacts its use.
- Horizontal furnaces offer a larger working volume and are ideal for processing bigger samples or for continuous processes where materials are fed through the tube.
- Vertical furnaces have a smaller footprint and are excellent for batch processing, as samples can be easily lowered into and lifted out of the heat zone. Gravity can also help ensure sample placement and consistency.
The "Hot Zone" Limitation
The specified thermal uniformity (e.g., ±1°C) only applies to a specific region in the center of the furnace, known as the "hot zone."
The temperature will naturally drop off toward the ends of the tube. It is critical to know the length of this uniform hot zone and ensure your sample fits entirely within it for proper processing.
Cost and Complexity
A multi-zone furnace provides superior uniformity over a longer length but is more expensive and complex to operate than a single-zone model. The choice depends on the precision your application demands.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your specific process requirements and priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum uniformity for sensitive research: A multi-zone furnace is the superior choice for creating a highly stable and extended hot zone.
- If your primary focus is processing large or continuous samples: A horizontal tube furnace provides the necessary volume and flexibility.
- If your primary focus is convenient batch processing in a small lab: A vertical tube furnace offers an efficient footprint and simplified sample loading.
- If your primary focus is general heating on a budget: A single-zone furnace is effective, but you must ensure your sample fits completely within its more limited uniform hot zone.
Understanding how a tube furnace achieves thermal uniformity empowers you to select the right tool to deliver consistent, high-quality results for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| 360° Heating | Surrounds sample for even temperature distribution, reducing hot spots |
| Multi-Zone Control | Allows fine-tuning of temperature profiles for extended uniform zones |
| Atmosphere Control | Seals maintain vacuum or inert gas, preventing oxidation and ensuring consistency |
| Hot Zone Focus | Specifies area of maximum uniformity, critical for sample placement |
| Horizontal/Vertical Options | Adapts to large or batch processing needs with optimal space usage |
Unlock Precision in Your Lab with KINTEK's Custom Tube Furnaces
Are you striving for flawless thermal processes in material science, CVD, or annealing? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our tube furnaces can enhance your process repeatability and material quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















