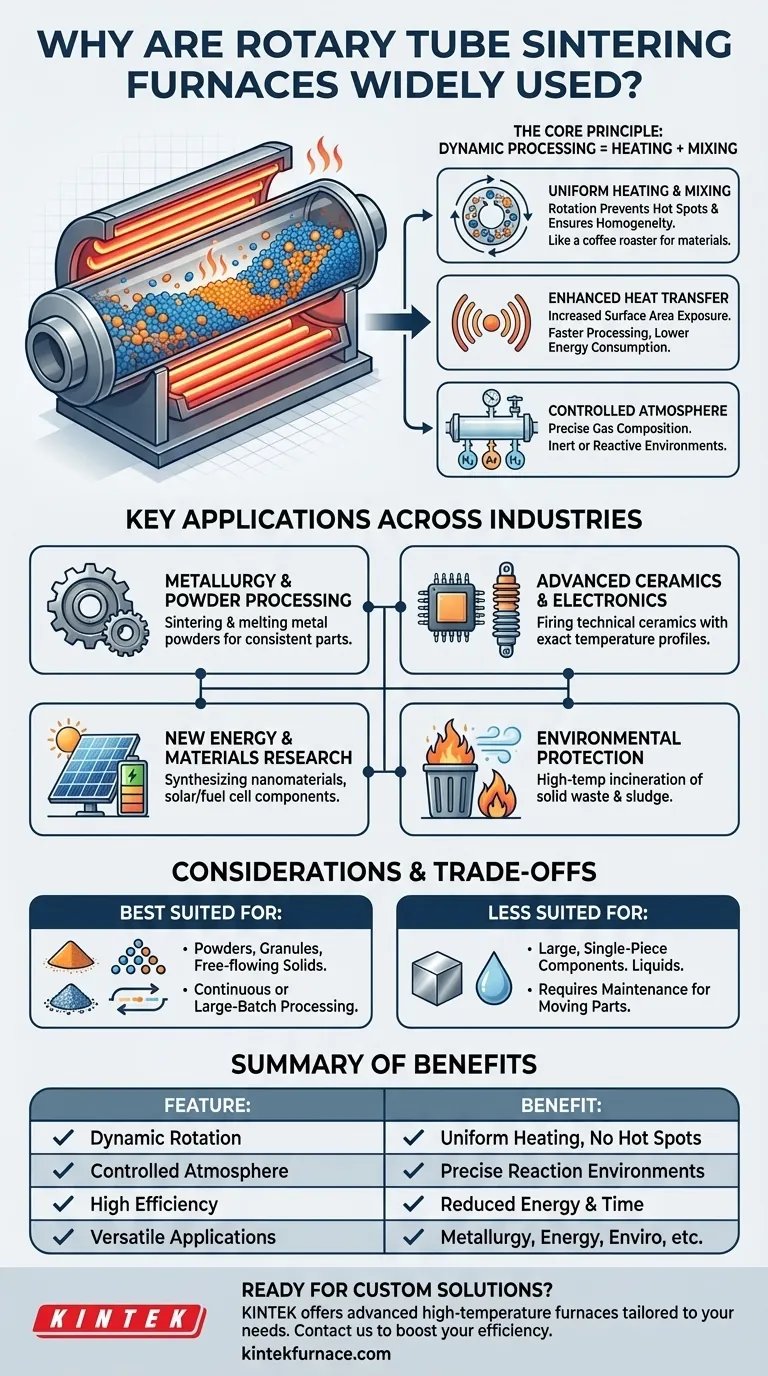
In essence, the rotary tube sintering furnace is widely used because it masterfully combines two critical processes: heating and mixing. Its design ensures that powdered or granular materials are heated with exceptional uniformity in a highly controlled environment. This unique combination of dynamic movement and precise control delivers high efficiency, process flexibility, and consistent results, making it an indispensable tool across a vast range of industrial and research fields.
The core challenge in high-temperature material processing is eliminating inconsistencies. The rotary tube furnace solves this by continuously tumbling the material, which prevents hot spots, ensures uniform heat exposure, and creates a homogenous final product that is difficult to achieve in a static furnace.

The Core Principle: Dynamic Processing
The value of the rotary tube furnace stems from its fundamental design, which turns a static heating process into a dynamic one. This principle is the source of its primary advantages.
How Rotation Ensures Uniform Heating
The defining feature is the slow rotation of the furnace tube. This action constantly tumbles the material inside, ensuring every particle is cyclically exposed to the heat source.
This movement is analogous to a coffee bean roaster, which prevents any single bean from burning by keeping the entire batch in motion. In industrial terms, this eliminates temperature gradients and sample settling, guaranteeing a homogenous thermal treatment.
Enhancing Heat Transfer and Efficiency
By continuously mixing the material, the furnace dramatically increases the effective surface area exposed to heat. This enhances heat transfer efficiency, leading to faster processing times and lower energy consumption.
Modern furnaces pair this mechanical advantage with advanced heating elements and precise temperature control systems. This allows for rapid heating, stable temperature maintenance, and quick, fan-assisted cooling, all of which boost operational efficiency.
Simultaneous Mixing in a Controlled Atmosphere
The furnace does more than just heat; it actively mixes. This is critical when sintering different powders together or when a reaction needs to occur evenly throughout a material.
Furthermore, these systems allow for precise control over the gas composition within the tube. Whether the process requires an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation or a specific reactive gas, the sealed rotating tube provides the perfect environment.
A Breakdown of Key Applications
The combination of uniform heating, mixing, and atmospheric control makes the rotary furnace exceptionally versatile. It is a solution for any process involving heat-treating powders, granules, or other free-flowing solids.
Metallurgy and Powder Processing
In the metallurgical industry, the furnace is essential for sintering and melting metal powders. The uniform heating prevents defects and ensures that the final metal parts have consistent density and structural integrity.
Advanced Ceramics and Electronics
The firing of technical ceramics and the preparation of semiconductor materials demand exact temperature profiles. The rotary furnace's intelligent control systems deliver the precision required to create these high-value products.
New Energy and Materials Research
In the new energy sector, it is used to create materials for solar cells and fuel cells. For researchers, its flexibility in temperature, rotation speed, and atmosphere makes it ideal for synthesizing nanomaterials and studying the high-temperature properties of novel substances.
Environmental Protection
Rotary furnaces are also powerful tools for environmental remediation. They are used for the high-temperature incineration of solid waste and sludge, efficiently transforming hazardous materials into energy or harmless, inert substances.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, the rotary tube furnace is a specialized piece of equipment. Its strengths are most apparent when the material and process are a good fit for its design.
Material Suitability
The furnace is specifically designed for powders, granules, and small, free-flowing solids. It is not suitable for processing very large, single-piece components or liquids, where a static box or batch furnace would be more appropriate.
Complexity and Maintenance
The rotating mechanism, with its seals and drive system, adds a layer of mechanical complexity compared to a simple static furnace. While modern designs are highly durable, these moving parts require a dedicated maintenance schedule to ensure long-term reliability and a properly sealed atmosphere.
Throughput and Scale
Rotary furnaces excel at continuous or large-batch processing, offering high efficiency at scale. For very small, one-off lab experiments, the setup and cleaning time might be less efficient than a simpler, smaller static tube furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing highly uniform powder-based materials at scale: The rotary furnace is the optimal choice due to its superior mixing and temperature consistency.
- If your primary focus is research and development of new materials: Its precise control over temperature, atmosphere, and rotation speed offers the flexibility needed for experimental work.
- If your primary focus is high-volume waste treatment: Its ability to tumble and completely incinerate materials makes it a leading technology for environmental applications.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating large, solid parts or components: A static box or bogie hearth furnace is the correct tool for the job.
Ultimately, the furnace's value lies in its unique ability to transform raw, loose materials into highly consistent, high-value products through controlled, dynamic processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Rotation | Ensures uniform heating and prevents hot spots |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Allows precise gas composition for reactions |
| High Efficiency | Reduces energy use and speeds up processing |
| Versatile Applications | Suitable for metallurgy, ceramics, energy, and environmental uses |
Ready to enhance your material processing with a custom rotary tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and industrial requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can boost your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
People Also Ask
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency



















