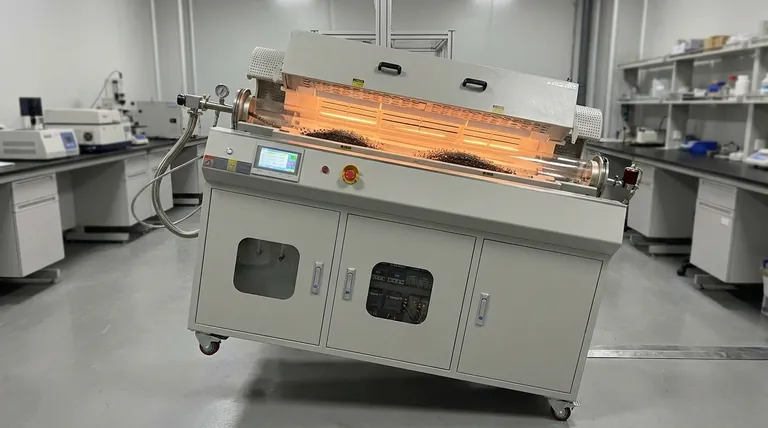
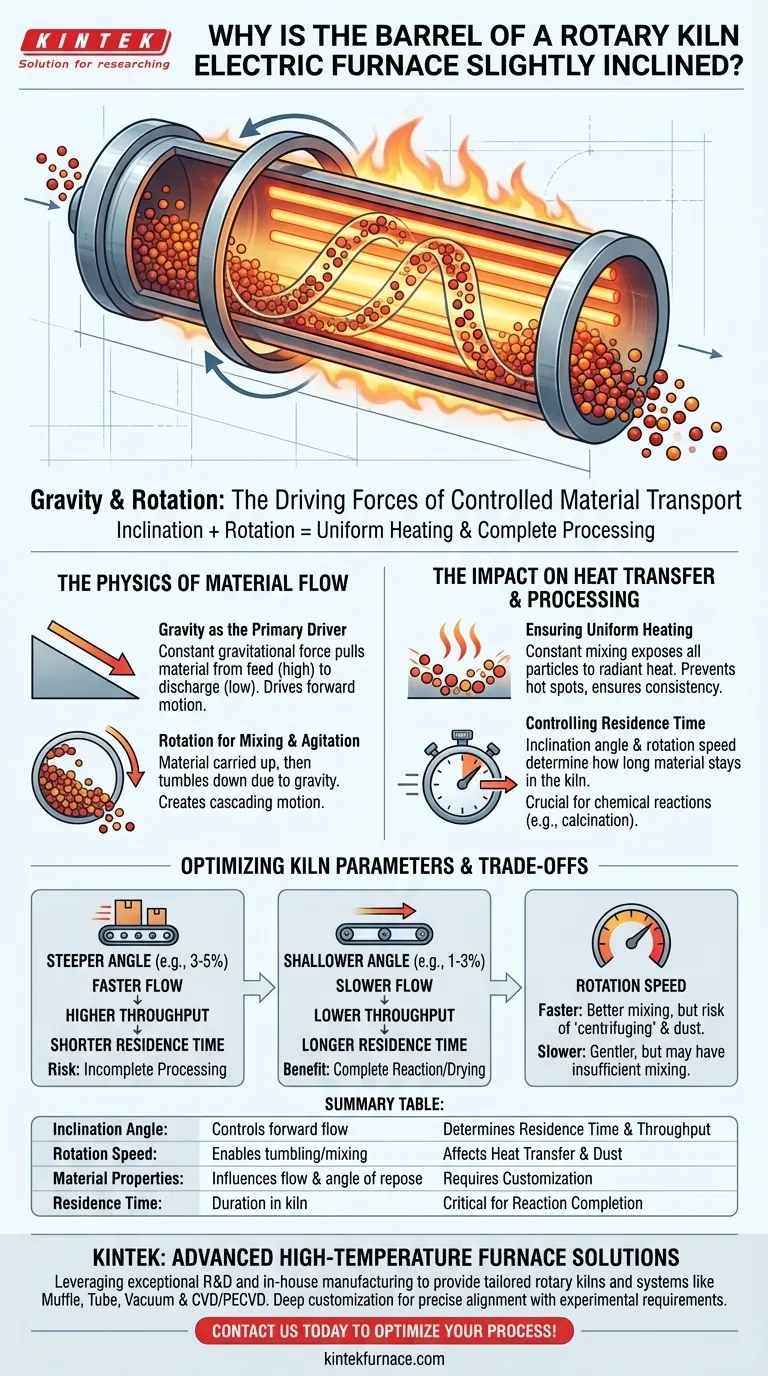
At its core, the barrel of a rotary kiln electric furnace is slightly inclined to leverage gravity for the controlled and continuous transport of material. This deliberate slope works in concert with the kiln's rotation, ensuring that the material tumbles and mixes as it moves from the feed end to the discharge end, which is critical for uniform heating and complete processing.
The inclination of a rotary kiln is not a minor detail; it is the primary mechanism governing the material's journey. This angle, combined with rotation speed, directly controls the residence time—how long the material stays in the furnace—which is the most critical factor in achieving the desired process outcome.

The Physics of Material Flow
Understanding why the inclination is so crucial requires looking at how it interacts with the kiln's rotation. The two forces work together to create a unique and highly effective transport system.
Gravity as the Driving Force
The slight downward slope provides a constant, gentle gravitational force on the material. This is the primary driver of forward motion, pulling the entire bed of material slowly from the higher inlet toward the lower outlet. Without this slope, the material would simply sit in place or move unpredictably.
Rotation for Mixing and Agitation
As the kiln rotates, it carries material up the interior wall. Due to gravity, the material reaches a certain point—its angle of repose—before it tumbles back down to the bottom of the bed. This continuous tumbling action is essential for effective processing.
This "cascading" or "tumbling" motion is the genius of the design. It constantly exposes new particles to the radiant heat from the electric elements and the hot furnace atmosphere, preventing hot spots and ensuring every part of the material is processed.
Combining Slope and Rotation for Controlled Transport
The forward movement from the slope and the cross-sectional mixing from the rotation combine to move the material in a slow, helical (or corkscrew) path down the length of the kiln. The operator can precisely control this journey by adjusting the kiln's parameters.
The Impact on Heat Transfer and Processing
The controlled movement created by the inclination directly enables the kiln's core functions: heating, drying, or inducing chemical reactions. The goal is always uniformity and completeness.
Ensuring Uniform Heating
The constant mixing action is the key to uniform heat transfer. By continuously turning the material over, the kiln ensures that no single portion is over-exposed or under-exposed to the heat source. This is vital for producing a consistent, high-quality final product.
Controlling Residence Time
Residence time is the total time a particle spends inside the kiln. This is arguably the most important operational parameter, and it is primarily controlled by the angle of inclination and the speed of rotation. A steeper angle results in a shorter residence time, while a shallower angle increases it.
Promoting Chemical Reactions
For processes like calcination or reduction, the goal is to drive a chemical reaction to completion. This requires holding the material at a specific temperature for a specific duration. The kiln's inclination allows operators to lock in the exact residence time needed for these reactions to be fully and efficiently realized across the entire batch of material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of inclination angle is a critical design decision based on a series of trade-offs. It is not a one-size-fits-all parameter.
Angle of Inclination vs. Throughput
A steeper angle increases the speed of material flow, leading to higher throughput. However, it also reduces residence time, which may result in incomplete processing. A shallower angle guarantees longer residence time for thorough processing but reduces the overall plant capacity.
Rotation Speed vs. Mixing Efficiency
A higher rotation speed can improve mixing and heat transfer. However, if the speed is too high, centrifugal force can cause the material to stick to the wall ("centrifuging"), stopping the tumbling action altogether. It can also create excessive dust. A slower speed is gentler but may provide insufficient mixing for some materials.
Material Characteristics
The optimal angle and speed are highly dependent on the properties of the material being processed. Factors like particle size, density, moisture content, and angle of repose all influence how the material will behave inside the kiln. The design must be matched to the material.
Optimizing Kiln Parameters for Your Goal
The correct inclination is determined by the primary objective of your industrial process. By adjusting the slope and rotation speed, you can fine-tune the kiln's performance.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: A slightly steeper angle (e.g., 3-5%) and a corresponding rotation speed can be used, as long as the shorter residence time does not compromise product quality.
- If your primary focus is ensuring a complete chemical reaction or drying: A shallower angle (e.g., 1-3%) is necessary to increase residence time and guarantee every particle is uniformly processed.
- If you are processing delicate or dusty materials: A very shallow angle and a slow rotation speed are required to minimize material degradation and prevent fine particles from being carried out with the exhaust gas.
Ultimately, the kiln's inclination is the fundamental design choice that transforms a simple rotating tube into a highly precise and continuous processing machine.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Role in Kiln Operation | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Inclination Angle | Controls forward material flow via gravity | Determines residence time and throughput |
| Rotation Speed | Enables tumbling and mixing of material | Affects heat transfer uniformity and dust generation |
| Material Properties | Influences flow behavior and angle of repose | Requires customization for optimal processing |
| Residence Time | Duration material stays in kiln | Critical for reaction completion and product quality |
Optimize your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored rotary kilns and other systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific needs and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















