At its core, the atmosphere tube furnace is a critical tool because it allows for the precise heating of materials within a tightly controlled gaseous environment. This unique combination of high-temperature capability and atmospheric control makes it indispensable for developing and producing new materials, from advanced alloys to semiconductors.
The true importance of a tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot. It is the power to dictate the exact chemical environment a sample experiences during heating, a capability that unlocks material synthesis and process optimization impossible with conventional ovens.
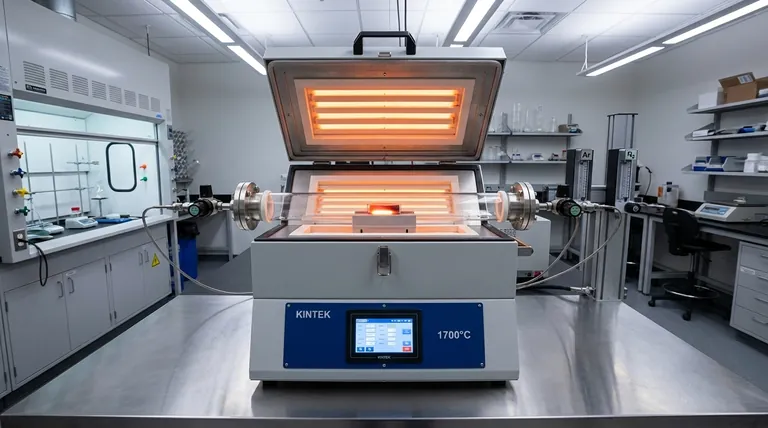

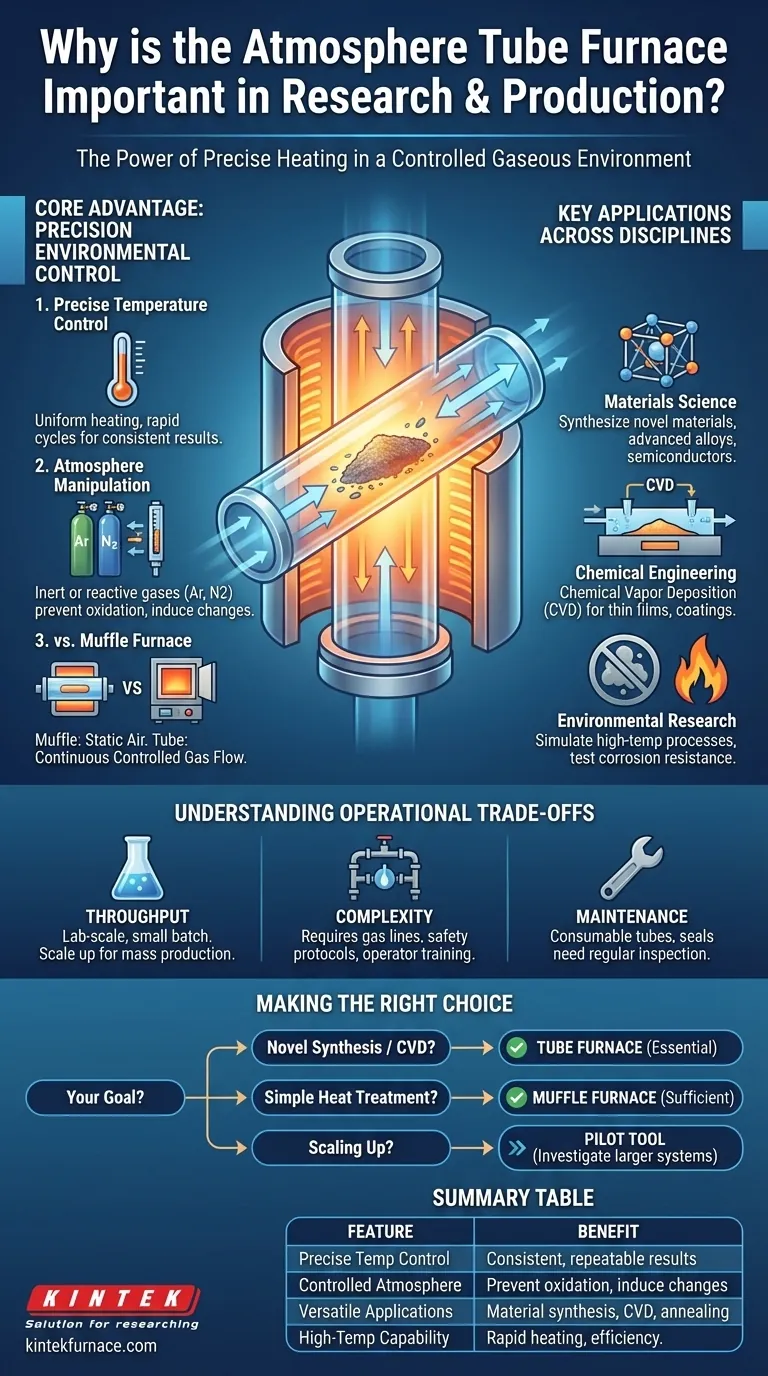
The Core Advantage: Precision Environmental Control
The value of a tube furnace stems from its ability to isolate a sample from the ambient air and create a custom, dynamic environment. This control is the foundation of its utility in both research and industry.
Controlling Temperature with High Accuracy
A laboratory tube furnace is designed for exceptional temperature uniformity along its heating zone. This ensures that the entire sample is subjected to the same thermal conditions, which is critical for consistent and repeatable results.
Advanced heating elements and insulation materials also allow for rapid heating and cooling cycles, enabling researchers to study dynamic processes and improve efficiency.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Manipulation
The defining feature of this furnace is its tubular chamber, which can be sealed and purged with specific gases. This allows for processes to be run in inert atmospheres (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, or in reactive atmospheres to induce a specific chemical change.
This level of atmosphere control is the key to processes like annealing, sintering, and chemical vapor deposition, where the gas composition directly influences the final material's properties.
How It Differs from a Muffle Furnace
While both are high-temperature furnaces, a muffle furnace typically heats samples in ambient air or a static environment. It lacks the ability to have a continuous flow of controlled gas.
A tube furnace, by contrast, is designed for gas to flow through the tube. This makes it the necessary choice for any heat treatment process that requires a specific, non-air atmosphere to achieve the desired outcome.
Key Applications Across Disciplines
The ability to fine-tune both heat and atmosphere makes the tube furnace a versatile workhorse in many scientific and industrial fields.
In Materials Science: Synthesizing the Future
Researchers use tube furnaces to synthesize novel materials with specific crystal structures or properties. By controlling the gas environment, they can prevent unwanted reactions or deliberately introduce elements into a material's structure.
This is fundamental for developing everything from stronger metals to more efficient battery components and semiconductors.
In Chemical Engineering: Enabling Advanced Processes
Processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) rely entirely on the tube furnace design. In CVD, precursor gases are flowed through the heated tube, where they react and deposit a thin solid film onto a substrate.
This technique is essential for manufacturing electronic components, protective coatings, and high-purity materials.
In Environmental Research: Simulating Extreme Conditions
Tube furnaces are used to simulate high-temperature industrial processes, like incineration, to study the breakdown of pollutants.
They also allow scientists to test the corrosion resistance and stability of materials in specific, harsh atmospheric conditions, helping to evaluate their suitability for extreme environments.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While powerful, a tube furnace is a specialized instrument with specific operational considerations that define its best-use cases.
Throughput and Scalability
Tube furnaces are ideal for laboratory-scale research, process development, and small-batch production. Their size, by nature, limits the volume of material that can be processed at one time.
For mass production, the principles discovered in a tube furnace are often scaled up into larger, industrial-grade batch or continuous furnaces.
The Complexity of Gas Handling
Introducing controlled atmospheres adds a layer of complexity and cost. It requires gas lines, flow controllers, and potentially exhaust scrubbers or fume hoods.
Proper safety protocols are also paramount, especially when working with flammable, toxic, or reactive gases. This requires more operator training than a standard air-fired furnace.
Maintenance and Consumables
The quartz or ceramic tube at the heart of the furnace is a consumable item that can degrade over time, especially under harsh chemical conditions or rapid temperature changes. Likewise, seals and gaskets require regular inspection and replacement to ensure atmospheric integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating equipment depends entirely on the specific requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is novel material synthesis or CVD: A tube furnace is essential for the precise atmospheric control you will need.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment in air: A more cost-effective muffle furnace is likely sufficient for your needs.
- If your primary focus is scaling up a developed process: The tube furnace is your pilot tool, but you will need to investigate larger batch or continuous systems for high-volume production.
Ultimately, the atmosphere tube furnace is a foundational tool that empowers innovation by giving scientists and engineers command over the very environment in which materials are born.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control | Ensures uniform heating for consistent, repeatable results in experiments and processes. |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Allows use of inert or reactive gases to prevent oxidation or induce specific chemical changes. |
| Versatile Applications | Supports material synthesis, CVD, annealing, and environmental simulations across various fields. |
| High-Temperature Capability | Enables rapid heating and cooling for dynamic process studies and efficiency improvements. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom high-temperature furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your research and production forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















