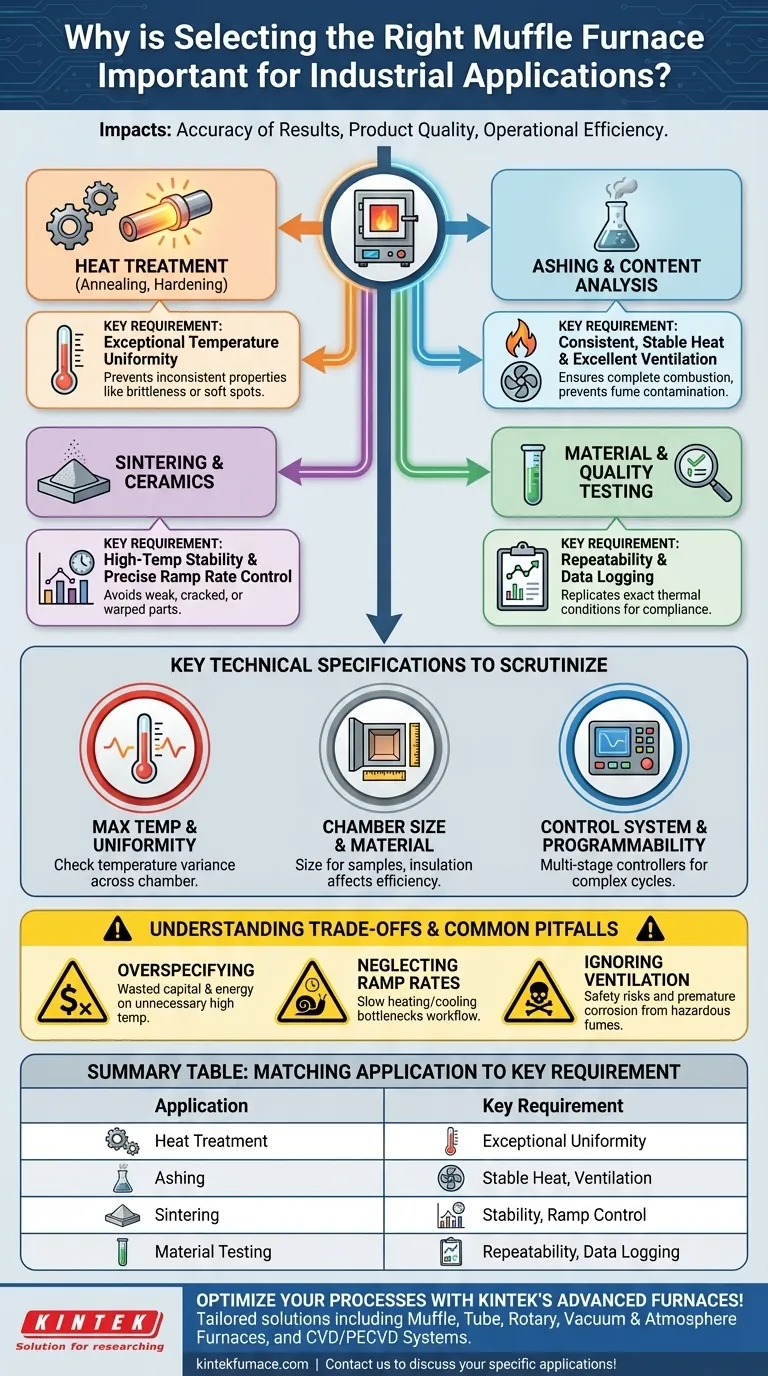
In industrial and laboratory settings, selecting the right muffle furnace is a critical decision that directly impacts the accuracy of your results, the quality of your product, and the efficiency of your operation. A furnace that is poorly matched to its intended application can lead to inconsistent heat treatment, inaccurate material analysis, and failed quality tests, compromising your entire process.
The core challenge is not finding the single "best" furnace, but aligning the furnace's specific technical capabilities—temperature range, uniformity, and control—with the precise demands of your scientific or industrial process. The application must dictate the choice of equipment.

The Core Function: Matching Furnace to Process
A muffle furnace provides a controlled, high-temperature environment. However, different applications place vastly different demands on that environment. The success of your work depends on how well the furnace meets the unique needs of your process.
For Heat Treatment (Annealing, Hardening)
Heat treatment processes in metallurgy fundamentally alter a material's molecular structure to change its physical properties, like hardness or ductility.
This requires exceptional temperature uniformity throughout the chamber. Any hot or cold spots can result in inconsistent material properties, leading to brittleness or soft spots in the final product.
For Ashing and Content Analysis
Ashing involves burning off organic substances to isolate and quantify the non-combustible inorganic residue. This is common in pharmaceutical, environmental, and food quality control.
The key here is consistent, stable heat and excellent ventilation. The furnace must maintain a precise temperature to ensure complete combustion without volatilizing the target minerals. Proper venting is crucial to remove fumes and prevent contamination.
For Sintering and Ceramics
Sintering fuses powdered materials, like ceramics or metals, into a solid mass using heat below the material's melting point.
This application demands high-temperature stability and precise ramp rate control (the speed of heating and cooling). A furnace that cannot hold a steady temperature or control its thermal cycle will produce weak, cracked, or warped ceramic parts.
For Material and Quality Testing
When testing material properties like flame retardancy or durability under extreme heat, the primary requirement is repeatability.
The furnace must be able to replicate the exact same thermal conditions test after test. This requires a reliable control system and often includes data logging capabilities to prove compliance with industry standards.
Key Technical Specifications to Scrutinize
Once you understand your process requirements, you can evaluate a furnace based on its technical specifications.
Maximum Temperature and Uniformity
The maximum temperature is the most obvious specification, but temperature uniformity is often more important. Ask for data on the temperature variance across the furnace chamber at your target operating temperature.
Chamber Size and Material
The chamber must be large enough to accommodate your samples without restricting airflow. The insulation material (e.g., ceramic fiber vs. firebrick) affects heating/cooling rates and energy efficiency.
Control System and Programmability
A simple setpoint controller maintains a single temperature. For complex processes like annealing or sintering, you need a multi-stage programmable controller that can execute specific heating, soaking, and cooling cycles automatically.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance, cost, and safety. Being aware of common mistakes can prevent a costly purchasing error.
The Mistake of Overspecifying
Buying a 1700°C furnace for a process that only requires 900°C is a waste of capital and energy. Higher-temperature furnaces use more expensive heating elements and insulation, leading to higher upfront and operational costs.
Neglecting Ramp Rates
The speed at which a furnace heats and cools can be as critical as its maximum temperature. A furnace with slow ramp rates can bottleneck your workflow or fail to meet the requirements of a specific thermal profile.
Ignoring Ventilation and Fumes
Ashing or processing polymers can release corrosive or hazardous fumes. A standard furnace without adequate ventilation can pose a safety risk to operators and cause premature corrosion of the furnace components, including the heating elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, your selection should be a direct reflection of your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control and ashing: Prioritize a furnace with excellent temperature stability and robust ventilation over an extremely high temperature range.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical heat treatment: Scrutinize the furnace's temperature uniformity and the sophistication of its programmable controller for precise thermal cycles.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or ceramics: Investigate high-temperature capabilities, ramp rate control, and options for specialized atmosphere control.
By aligning the furnace's technical capabilities with the specific demands of your process, you ensure accuracy, repeatability, and the long-term integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Requirements |
|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Exceptional temperature uniformity, precise control |
| Ashing | Stable heat, excellent ventilation |
| Sintering | High-temperature stability, ramp rate control |
| Material Testing | Repeatability, data logging |
Optimize your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















