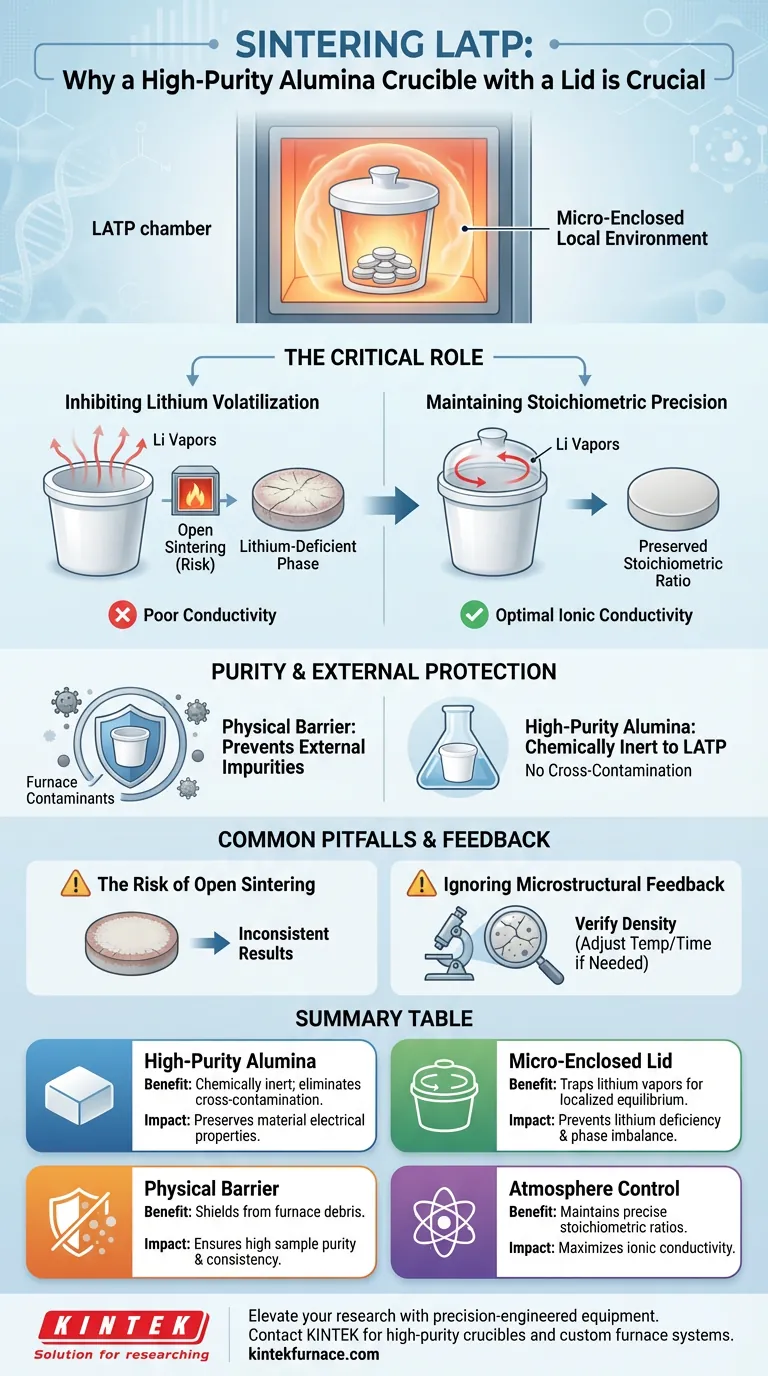
The recommendation to use a high-purity alumina crucible with a lid focuses on creating a stable, micro-enclosed local environment around the LATP pellets during high-temperature processing. This setup is critical for suppressing the volatilization of lithium components and shielding the sample from external contaminants.
The enclosed environment of a covered alumina crucible prevents lithium loss during sintering, preserving the material's precise stoichiometric ratio. This chemical stability is essential for achieving the high electrochemical performance required of LATP solid electrolytes.

The Critical Role of the Micro-Enclosed Environment
Inhibiting Lithium Volatilization
The most significant challenge in sintering Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 is the tendency of lithium (Li) to evaporate at high temperatures.
Unchecked volatilization leads to a deficiency of lithium in the final ceramic.
By placing a lid on the crucible, you trap lithium vapors within a small volume. This creates a localized equilibrium that effectively inhibits further evaporation from the pellet surface.
Maintaining Stoichiometric Precision
The electrochemical performance of LATP is directly tied to its specific chemical formula.
Any deviation from the intended stoichiometric ratio—caused by the loss of lithium—compromises the material's stability.
The covered crucible ensures that the final product retains the exact chemical composition necessary for optimal ionic conductivity.
Purity and External Protection
Preventing External Contamination
High-temperature furnaces contain heating elements and insulation that can release particulate matter or vapors.
A covered system acts as a physical barrier, preventing these external impurities from infiltrating the LATP sample.
The Importance of "High-Purity" Alumina
The choice of crucible material is just as vital as the lid.
High-purity alumina is chemically inert regarding LATP under standard sintering conditions.
Using lower-grade crucibles risks introducing contaminants that could diffuse into the ceramic, altering its electrical properties.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of Open Sintering
Sintering LATP without a lid allows lithium vapor to escape continuously into the larger furnace chamber.
This results in a lithium-deficient phase on the surface or throughout the bulk of the pellet.
Such deficiencies often lead to poor conductivity and inconsistent experimental results.
Ignoring Microstructural Feedback
While the crucible preserves chemistry, it does not automatically guarantee perfect density.
As noted in supplementary findings, researchers must still verify results through microstructural observation.
If micro-cracks or residual pores appear, the sintering temperature and holding time must be adjusted, even if the stoichiometry was successfully preserved by the crucible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your LATP ceramics, align your equipment usage with your specific technical objectives.
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Performance: Use a tightly covered crucible to prioritize the retention of lithium and maintain the exact stoichiometric ratio.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Ensure the alumina crucible is of certified high purity to eliminate any risk of cross-contamination during the heating phase.
By strictly controlling the local atmosphere around the sample, you ensure the chemical stability required for high-performance solid electrolytes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for LATP Sintering | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Alumina | Chemically inert; eliminates cross-contamination. | Preserves material electrical properties. |
| Micro-Enclosed Lid | Traps lithium vapors to create localized equilibrium. | Prevents lithium deficiency and phase imbalance. |
| Physical Barrier | Shields pellets from furnace heating element debris. | Ensures high sample purity and consistency. |
| Atmosphere Control | Maintains precise stoichiometric ratios. | Maximizes ionic conductivity for electrolytes. |
Elevate your material research with precision-engineered equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-purity crucibles alongside Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum systems—all customizable for your unique lab requirements. Ensure the chemical integrity of your LATP ceramics by choosing tools designed for high-performance outcomes. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your furnace and accessory needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Q.Z. Zeng, Zhongmin Wang. Influence of Zr Addition on the Microstructure and Hydrogenation Kinetics of Ti50−xV25Cr25Zrx (x = 0, 5, 7, and 9) Alloys. DOI: 10.3390/ma17061366
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Ultra High Vacuum Stainless Steel KF ISO CF Flange Pipe Straight Pipe Tee Cross Fitting
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Ultra High Vacuum Observation Window KF Flange 304 Stainless Steel High Borosilicate Glass Sight Glass
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using an infrared thermograph over traditional thermocouples in Plasma Flash Sintering (PFS)?
- Are customization options available for alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Tailor Them for Your Lab's Needs
- Why is a copper getter chamber integrated into heating systems? Ensure Ultra-Pure Alloy Processing
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in Al-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mn-Ni alloy prep? Master Mechanical Alloying Efficiency
- Why are high-purity alumina (Al2O3) crucibles used for melting aluminum alloys at 950°C? Ensure Pure Metal Integrity
- Why is a stainless steel closed-end tube required for controlled atmospheric experiments? Ensure Precise Material Purity
- Why are laboratory vacuum pumps and pressure gauges essential for aluminum foams? Ensure High-Quality Sintering Results
- How do 15x80mm technical openings and seals boost electric furnace efficiency? Maximize Thermal Performance Today









