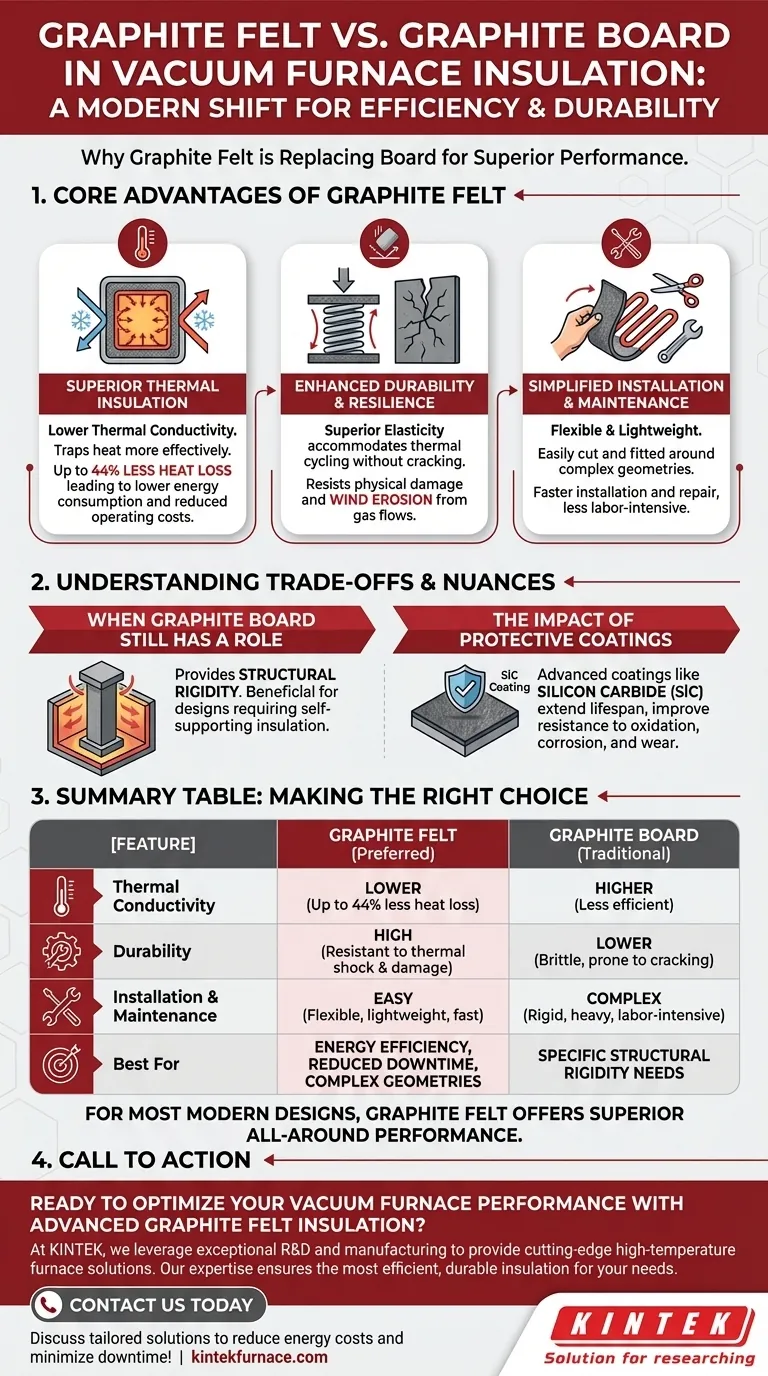
In short, graphite felt is replacing graphite board in modern vacuum furnaces because it offers superior thermal insulation, greater durability, and is significantly easier to install and maintain. This shift results in lower energy consumption, reduced operational downtime, and a longer lifespan for the furnace's thermal insulation system.
The choice between graphite felt and graphite board is not just about insulation material; it's a strategic decision that directly impacts a furnace's long-term energy efficiency, maintenance costs, and operational reliability.

The Core Advantages of Graphite Felt
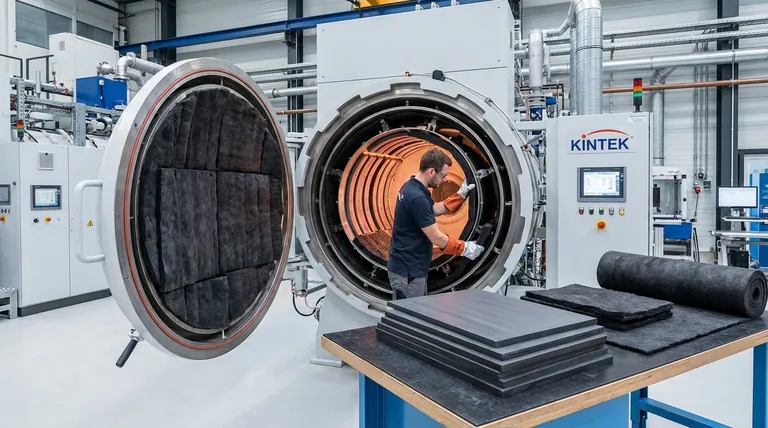
The transition to graphite felt is driven by clear performance benefits that address the demanding environment inside a high-temperature vacuum furnace. While both materials are carbon-based, their physical forms lead to significant differences in performance.
Superior Thermal Insulation
Graphite felt has a significantly lower thermal conductivity than rigid graphite board.
This less-dense, fibrous structure is more effective at trapping heat. As a result, furnaces insulated with felt lose less energy to their surroundings, with some data suggesting heat loss can be reduced by as much as 44%.
This directly translates to lower power consumption to maintain target temperatures, reducing overall operating costs.
Enhanced Durability and Resilience
The furnace environment involves intense thermal cycling, which causes materials to expand and contract.
Graphite felt possesses superior elasticity, allowing it to accommodate these thermal movements without cracking or degradation. Rigid board, being brittle, is more susceptible to developing stress fractures over time.
Furthermore, felt is more resistant to physical damage. If a part falls inside the furnace, the felt's soft surface can absorb the impact. It is also less prone to wind erosion from gas flows during quenching or backfilling cycles, reducing particle contamination.
Simplified Installation and Maintenance
Graphite felt is flexible, lightweight, and can be easily cut and fitted around complex geometries, such as heating elements and gas nozzles. This makes the initial installation and subsequent repairs much faster and simpler.
Graphite board, by contrast, is rigid and heavy. It requires precise cutting and careful handling, making installation more labor-intensive and challenging, especially when replacing a single damaged panel within a larger assembly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While graphite felt is now the preferred choice for most applications, a complete understanding requires acknowledging the role of graphite board and the impact of advanced material treatments.
When Graphite Board Still Has a Role
The primary advantage of graphite board is its structural rigidity. In certain furnace designs, the insulation package may need to be self-supporting.
In these specific cases, the inherent strength of a rigid board can be a design benefit, simplifying the overall hot zone construction. However, for most modern designs, this is outweighed by felt's superior thermal performance and durability.
The Impact of Protective Coatings
The operational lifespan of any graphite component, whether felt or board, can be extended with advanced coatings.
Materials like silicon carbide (SiC) can be applied to the graphite surface. These coatings provide a hard, protective barrier that dramatically improves resistance to oxidation, chemical corrosion, and physical wear.
Applying a coating can mitigate some of the inherent weaknesses of graphite, such as particle shedding, further enhancing the reliability and cleanliness of the furnace environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of insulation material should align directly with your primary operational objectives.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and lower operating costs: Graphite felt is the clear choice due to its superior thermal insulation properties.
- If your primary focus is minimizing downtime and maintenance: Graphite felt's resistance to thermal shock and physical damage makes it more durable and easier to replace.
- If you are designing a furnace with unique structural demands: Carefully evaluate if rigid board offers a necessary structural advantage, but otherwise default to modern graphite felt for better all-around performance.
Ultimately, selecting the right insulation is a critical step in optimizing the long-term performance and total cost of ownership of your vacuum furnace.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Graphite Felt | Graphite Board |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower (up to 44% less heat loss) | Higher |
| Durability | High (resistant to thermal shock & physical damage) | Lower (brittle, prone to cracking) |
| Installation & Maintenance | Easy (flexible, lightweight, easy to cut/fit) | Complex (rigid, heavy, labor-intensive) |
| Best For | Energy efficiency, reduced downtime, complex geometries | Specific structural rigidity needs |
Ready to optimize your vacuum furnace performance with advanced graphite felt insulation?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge high-temperature furnace solutions. Our expertise in materials like graphite felt ensures you get the most efficient, durable, and easy-to-maintain insulation for your specific needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored insulation solutions can reduce your energy costs, minimize downtime, and extend your furnace's lifespan!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness



















