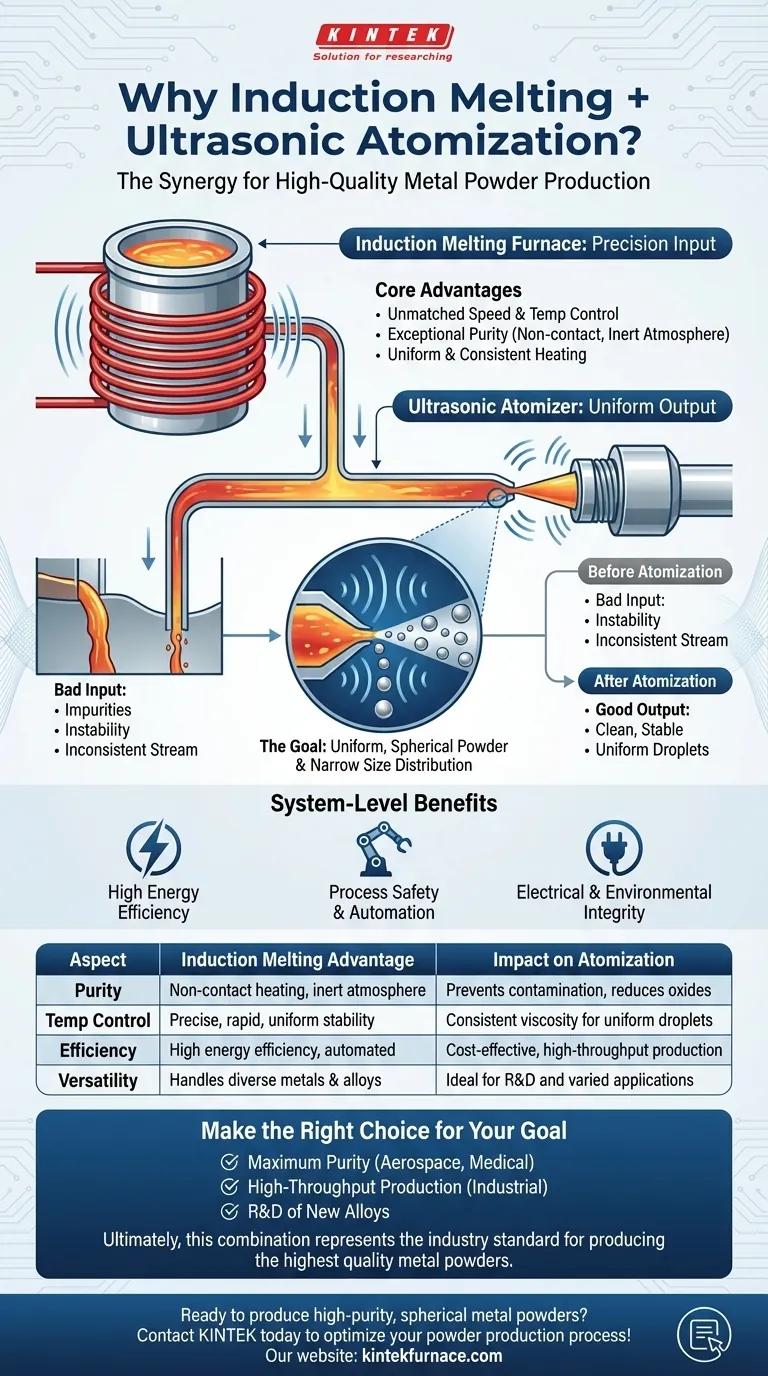
In short, an induction melting furnace is paired with ultrasonic atomization because it delivers an exceptionally clean, stable, and precisely controlled stream of molten metal. This high-quality liquid input is the essential prerequisite for the atomizer to reliably produce the uniform, spherical metal powders required for advanced applications like additive manufacturing.
The core challenge in powder production is controlling quality and consistency. The induction furnace's role is to perfectly prepare the metal by ensuring its purity and thermal stability, creating the ideal conditions for the ultrasonic atomizer to perform its function of creating perfectly uniform droplets.

The Foundation: Why Molten Metal Quality is Paramount
To understand the synergy between these two technologies, we must first appreciate the demands of the atomization process. The final powder quality is a direct reflection of the molten metal's condition just before it is atomized.
The Goal: Uniform, Spherical Powder
Applications like 3D printing, metal injection molding, and thermal sprays depend on powder with very specific characteristics. The particles must be highly spherical to ensure good flowability and packing density, and they must have a narrow size distribution for predictable, repeatable results.
The Challenge: Impurities and Instability
Any instability in the molten metal stream wreaks havoc on this process. Temperature fluctuations change the metal's viscosity and surface tension, leading to inconsistent droplet formation. Likewise, impurities or dissolved gases can cause defects, hollow particles, or "satellites"—smaller particles that cling to larger ones, ruining uniformity.
Core Advantages of Induction Melting for Atomization
An induction furnace is not just a way to melt metal; it is a precision instrument designed to overcome these exact challenges. It is superior to older methods like resistance or flame heating for this specific task.
Unmatched Speed and Temperature Control
Induction heating is incredibly fast, bringing metal to its melting point in minutes rather than hours. More importantly, it offers precise temperature control.
This ensures the molten metal fed to the atomizer is held at a constant temperature, maintaining the ideal viscosity for consistent droplet creation.
Exceptional Purity and Cleanliness
This is the most critical advantage. Induction heating is a non-contact process. An electromagnetic field directly heats the metal inside a crucible, meaning there are no heating elements or flames to introduce contaminants.
Furthermore, the process is easily performed under a vacuum or in an inert gas atmosphere (like argon). This prevents the molten metal from reacting with oxygen, eliminating oxides that would otherwise contaminate the final powder.
Uniform and Consistent Heating
The electromagnetic field induces currents throughout the metal charge, resulting in extremely uniform heating. This eliminates hot or cold spots that could disrupt the laminar flow of molten metal to the atomization nozzle, ensuring a steady, predictable stream.
Material Versatility
Induction systems are highly effective at melting a wide range of metals. This includes materials with high thermal conductivity like copper and silver, or volatile materials like zinc and magnesium, which are difficult to manage with other heating methods.
Understanding the System-Level Benefits
Beyond the direct impact on powder quality, pairing an induction furnace with an atomizer brings significant operational advantages.
High Energy Efficiency
Induction heating is significantly more energy-efficient than traditional furnaces because the heat is generated directly within the material being melted. Very little energy is wasted heating the surrounding environment.
Process Safety and Automation
Because there are no open flames or external heating elements, the process is inherently safer. Modern induction systems are also fully automated, providing repeatable, operator-independent results essential for industrial production.
Electrical and Environmental Integrity
Modern IGBT-based induction power supplies produce very low harmonic distortion. This means they do not "pollute" the facility's power grid or interfere with other sensitive electronic equipment—a crucial factor in a high-tech lab or production environment. The lack of combustion also means no harmful emissions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use this technology pairing is driven by the strict requirements of your final application.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for critical applications (aerospace, medical): The non-contact heating and inert atmosphere capabilities of an induction furnace are non-negotiable to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production (industrial soldering, coatings): The speed, precise automation, and energy efficiency of induction melting ensure a cost-effective and highly repeatable process.
- If your primary focus is research and development of new alloys: The process control and versatility to handle diverse materials make this pairing the ideal platform for experimentation.
Ultimately, the combination of an induction furnace and an ultrasonic atomizer represents the industry standard for producing the highest quality metal powders.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Melting Advantage | Impact on Atomization |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | Non-contact heating, inert atmosphere capability | Prevents contamination, reduces oxides for defect-free powder |
| Temperature Control | Precise, rapid heating with uniform thermal stability | Consistent viscosity for uniform droplet formation |
| Efficiency | High energy efficiency with automated operation | Cost-effective, high-throughput production |
| Versatility | Handles a wide range of metals, including high-conductivity and volatile alloys | Ideal for R&D and diverse industrial applications |
Ready to produce high-purity, spherical metal powders for additive manufacturing or industrial applications? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our induction melting systems can optimize your powder production process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















