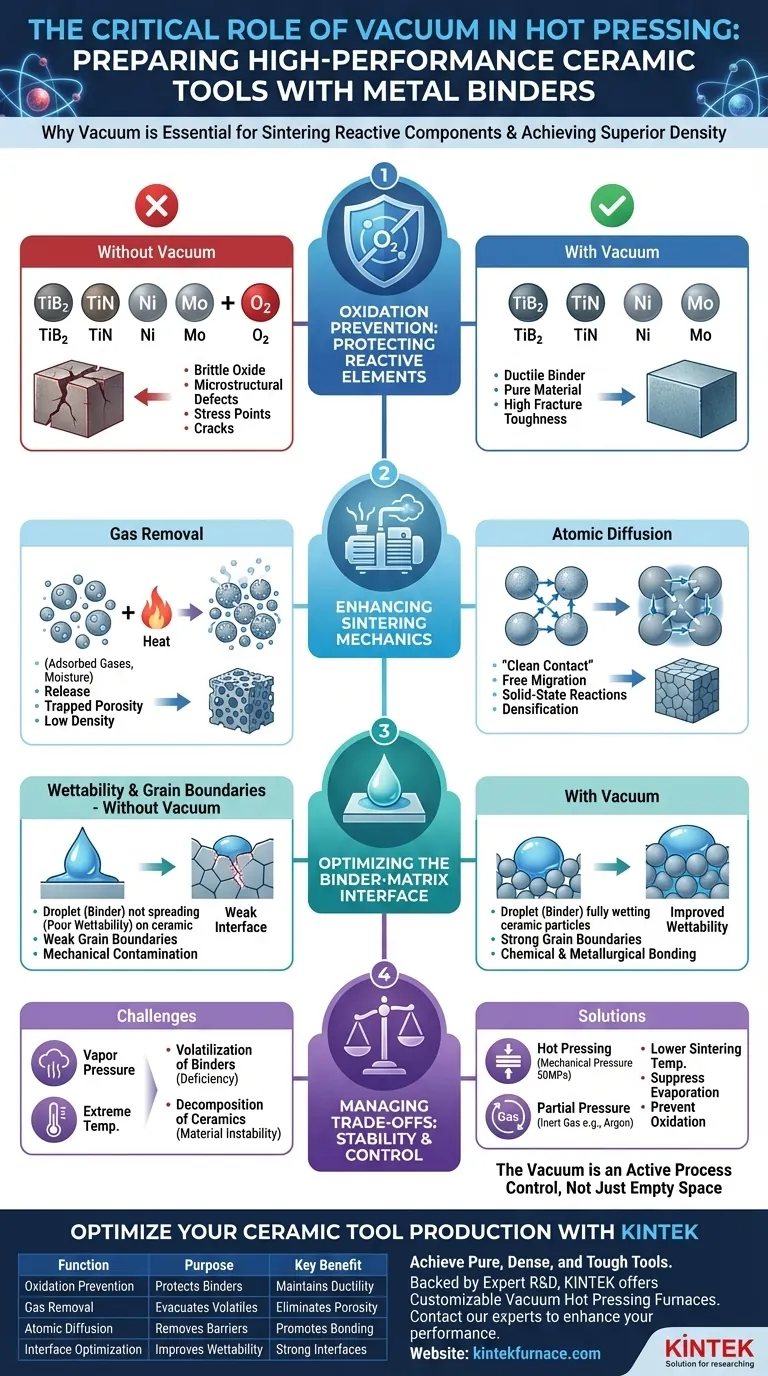
The primary requirement for a vacuum environment in hot pressing ceramic tools with metal binders is to prevent the oxidation of reactive components like Titanium Diboride (TiB2), Titanium Nitride (TiN), Nickel (Ni), and Molybdenum (Mo) at elevated temperatures. Additionally, the vacuum is critical for removing adsorbed gases and volatiles from powder surfaces, which purifies grain boundaries and allows for the atomic diffusion necessary to create a high-density, durable tool.
Core Insight: High-performance sintering is not just about heat and pressure; it is about surface purity. By eliminating oxygen and interstitial gases, a vacuum environment removes the chemical and physical barriers that prevent metal binders and ceramic particles from bonding into a single, cohesive solid.

The Critical Role of Oxidation Prevention
Protecting Reactive Elements
Ceramic tools often utilize metal binders (such as Ni, Mo, or Ti) and non-oxide ceramic phases (such as TiB2 or TiN). These materials are chemically active, particularly as temperatures rise during the sintering process.
Without a vacuum, these elements would react rapidly with atmospheric oxygen. This reaction degrades the metal binder, turning a ductile bonding agent into a brittle oxide that cannot effectively hold the ceramic matrix together.
Avoiding Microstructural Defects
When oxidation occurs, it leads to the formation of oxide inclusions. These inclusions act as contaminants within the material's structure.
In a finished tool, these brittle oxides serve as stress concentration points. Under mechanical load, cracks initiate at these points, significantly reducing the tool's fracture toughness and overall lifespan.
Enhancing Sintering Mechanics
Removing Adsorbed Gases
Powder materials, especially those with high surface areas like nano-powders, naturally adsorb gases and moisture from the air.
As the furnace heats up, these gases are released. A vacuum environment effectively evacuates these volatiles. If these gases were not removed, they would become trapped within the material, leading to porosity (holes) that destroys the density and integrity of the tool.
Promoting Atomic Diffusion
Sintering relies on atomic diffusion—the movement of atoms across particle boundaries to fuse them together.
Oxide layers on particle surfaces act as barriers to this movement. By maintaining a vacuum, you strip away these barriers. This "clean contact" allows atoms to migrate freely, facilitating the solid-state reactions required to form pure intermetallic compounds and densify the material.
Optimizing the Binder-Matrix Interface
Improving Wettability
For a ceramic tool to be strong, the metal binder must effectively "wet" (spread over) the ceramic particles.
Oxidation drastically reduces wettability. A vacuum environment ensures the surfaces remain metallic and reactive, allowing the molten or semi-molten binder to flow smoothly around the ceramic grains.
Strengthening Grain Boundaries
The mechanical strength of a ceramic tool is determined by the strength of its grain boundaries (the interfaces between crystals).
Vacuum processing purifies these interfaces. By preventing chemical contamination, the vacuum ensures that the bonding between the metal binder and the ceramic phase is chemical and metallurgical, rather than merely mechanical.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Vapor Pressure and Decomposition
While a vacuum is essential for purity, it introduces specific challenges regarding material stability that must be managed.
Volatilization of Binders
Some metal binders have high vapor pressures. In an extremely high vacuum at sintering temperatures, these metals may begin to evaporate rather than sinter. This can lead to a deficiency of the binder in the final product, leaving the ceramic matrix unsupported.
Decomposition of Ceramics
Certain ceramics, such as Uranium Nitride (UN) or specific unstable nitrides, can undergo severe decomposition in high vacuum environments at extreme temperatures (e.g., above 1627°C).
In these cases, the "Hot Pressing" aspect becomes vital. The application of mechanical pressure (e.g., 50 MPa) provides an additional driving force for densification. This allows the material to sinter at lower temperatures, avoiding the threshold where vacuum-induced decomposition occurs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your sintering process, you must balance the vacuum level against the volatility of your specific components.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Density: Ensure your vacuum system is capable of removing interstitial gases during the initial heating stage to prevent trapped porosity.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Toughness: Prioritize high vacuum levels to eliminate oxygen, ensuring the metal binder remains metallic and ductile rather than becoming a brittle oxide.
- If you are using High-Vapor-Pressure Binders: You may need to introduce a partial pressure of inert gas (like Argon) after the initial degassing stage to suppress evaporation while still preventing oxidation.
The vacuum environment is not merely an empty space; it is an active process control that clears the path for atomic bonding, transforming loose powder into a high-performance industrial tool.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Prevention | Protects reactive metal binders (Ni, Mo) and ceramics (TiB2, TiN) | Maintains ductility and prevents brittle oxide inclusions |
| Gas & Volatile Removal | Evacuates adsorbed gases and moisture from powder surfaces | Eliminates porosity for maximum density and integrity |
| Enhanced Atomic Diffusion | Removes surface barriers between particles | Promotes strong bonding and solid-state reactions for densification |
| Interface Optimization | Improves wettability and purifies grain boundaries | Creates strong, chemically bonded metal-ceramic interfaces |
Ready to Optimize Your High-Performance Ceramic Tool Production?
Creating a flawless, high-density tool requires precise control over the sintering environment. KINTEK's expertise in high-temperature vacuum furnaces ensures you can:
- Prevent Oxidation: Achieve pure, metallic binders for maximum toughness.
- Eliminate Porosity: Attain superior density and mechanical integrity.
- Customize Your Process: Tailor vacuum levels and temperature profiles for your specific material system, including challenging binders with high vapor pressure.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including specialized Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnaces, all customizable for your unique needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your ceramic tool quality and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why might a vacuum furnace maintain vacuum during cooling? Protect Workpieces from Oxidation and Control Metallurgy
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What are the primary application fields for box furnaces and vacuum furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Process
- Why are some vacuum furnaces backfilled with a partial pressure gas? Prevent Alloy Depletion in High-Temp Processes
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability



















