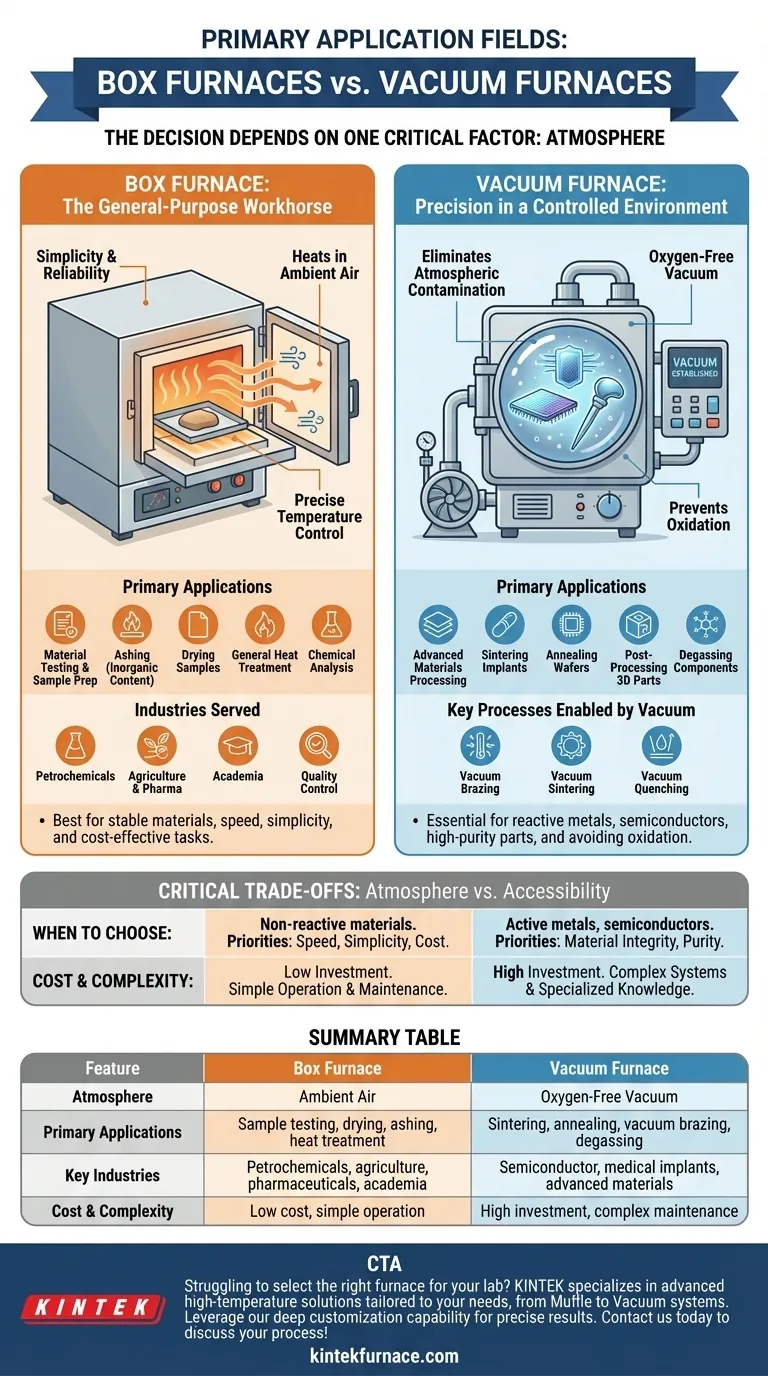
In essence, the choice between a box furnace and a vacuum furnace is determined by one critical factor: atmosphere. A box furnace is a general-purpose tool for heating materials in ambient air, making it ideal for processes like sample testing, drying, or basic heat treatments. A vacuum furnace, however, is a specialized instrument designed for processes that require an oxygen-free environment to prevent oxidation and ensure the chemical purity of the final product.
The decision is not about which furnace is "better," but which environment your process requires. If your material can tolerate being heated in air, a box furnace is the simpler, more economical choice. If air would contaminate or ruin your material, a vacuum furnace is not a luxury—it is a necessity.
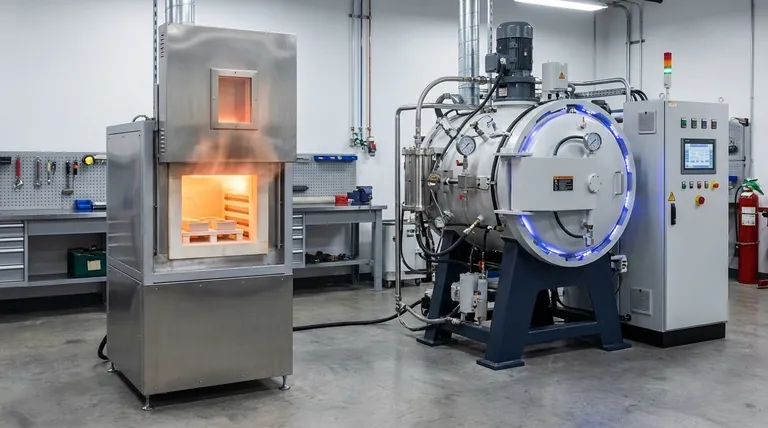

Understanding the Box Furnace: The General-Purpose Workhorse
A box furnace, also known as a muffle furnace, is the most common type of furnace found in laboratories and light industrial settings. Its design prioritizes simplicity, reliability, and ease of use for a wide range of thermal processing tasks.
Core Operating Principle: Simplicity and Reliability
The defining feature of a box furnace is that it heats materials directly within a standard air atmosphere. It is engineered for precise temperature control, rapid heat-up, and consistent performance for repeatable processes.
Its straightforward design makes it easy to operate and maintain, positioning it as a fundamental tool for most thermal applications that do not involve reactive materials.
Primary Applications: Material Testing and Sample Prep
Box furnaces excel in applications where interaction with air is either acceptable or desired. This includes a broad range of preparatory and analytical tasks.
Common uses include ashing to determine inorganic content, drying samples, general-purpose heat treatment, and conducting chemical analysis on materials like coal, cement, and other raw materials.
Industries Served: Broad and Diverse
Due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness, box furnaces are used across nearly every industry.
You will find them in quality control labs for petrochemicals and paper, in agricultural and pharmaceutical research for sample preparation, and in academic settings for general materials science experiments.
Understanding the Vacuum Furnace: Precision in a Controlled Environment
A vacuum furnace is a highly specialized system that performs heat treatment within a chamber where the atmosphere has been evacuated. This removal of air, particularly oxygen, is its primary function and enables processes that are impossible in a box furnace.
Core Operating Principle: Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
By creating a vacuum, this furnace prevents high-temperature oxidation, decarburization, and other chemical reactions that occur when reactive materials are heated in air.
This protection is crucial for maintaining the surface finish, structural integrity, and chemical composition of sensitive components, especially metals and advanced ceramics.
Primary Applications: Advanced Materials and Processing
Vacuum furnaces are indispensable for high-stakes applications where material purity is paramount.
This includes the sintering of biocompatible implants, annealing silicon wafers in semiconductor manufacturing, and the post-processing of 3D-printed metal parts. They are also used for degassing components for vacuum electronics and creating advanced composites.
Key Processes Enabled by Vacuum
Certain industrial processes are defined by their need for a controlled atmosphere, making a vacuum furnace the only viable option.
- Vacuum Brazing: Joining two components using a filler metal. The vacuum prevents oxides from forming, which would otherwise inhibit a strong, clean bond.
- Vacuum Sintering: Fusing powdered materials (like metals or ceramics) into a solid mass. The vacuum ensures the final part has high purity and density.
- Vacuum Quenching: Rapidly cooling a part in the vacuum or with an inert gas. This achieves specific hardness and mechanical properties without surface oxidation.
The Critical Trade-offs: Atmosphere vs. Accessibility
Choosing the wrong furnace type is not just inefficient—it can lead to catastrophic failure of the part or process. The decision must be based on the material's chemistry and the desired outcome.
When to Choose a Box Furnace
A box furnace is the right choice when speed, simplicity, and cost are priorities, and the material is non-reactive. If you are simply testing the thermal properties of a stable ceramic or ashing a biological sample, a box furnace is the efficient tool for the job.
When a Vacuum Furnace is Non-Negotiable
A vacuum furnace is essential if your material is an active metal (like titanium or certain steel alloys), a semiconductor, or an advanced ceramic that would be compromised by oxidation. Processes like brazing, diffusion bonding, and high-purity annealing fundamentally require a vacuum.
Cost, Complexity, and Maintenance
There is a significant difference in investment and operation. Box furnaces are relatively inexpensive, simple to run, and require minimal maintenance.
Vacuum furnaces represent a major investment. They are complex systems involving vacuum pumps, cooling systems, and sophisticated controls, demanding specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance. Using one for a simple drying process is profound overkill in both cost and effort.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your final decision should be guided entirely by the technical requirements of your material and process goal.
- If your primary focus is general lab work, sample prep, or testing stable materials: A box furnace offers the most direct and cost-effective path to achieving your goal.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating reactive metals, advanced brazing, or semiconductor fabrication: A vacuum furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure the integrity and purity of your components.
- If your primary focus is developing novel materials or producing high-purity parts: The precisely controlled environment of a vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for achieving the desired material properties.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is the first step in guaranteeing the success and repeatability of your thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Box Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Ambient Air | Oxygen-Free Vacuum |
| Primary Applications | Sample testing, drying, ashing, heat treatment | Sintering, annealing, vacuum brazing, degassing |
| Key Industries | Petrochemicals, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, academia | Semiconductor, medical implants, advanced materials |
| Cost & Complexity | Low cost, simple operation | High investment, complex maintenance |
Struggling to select the right furnace for your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and results. Don't let furnace choice hold you back—contact us today to discuss how we can support your process with reliable, high-performance equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of the temperature control system in a vacuum furnace? Achieve Precise Material Transformations
- Why might a vacuum furnace maintain vacuum during cooling? Protect Workpieces from Oxidation and Control Metallurgy
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What additional processes can a vacuum heat treatment furnace carry out? Unlock Advanced Material Processing
- Why are some vacuum furnaces backfilled with a partial pressure gas? Prevent Alloy Depletion in High-Temp Processes



















