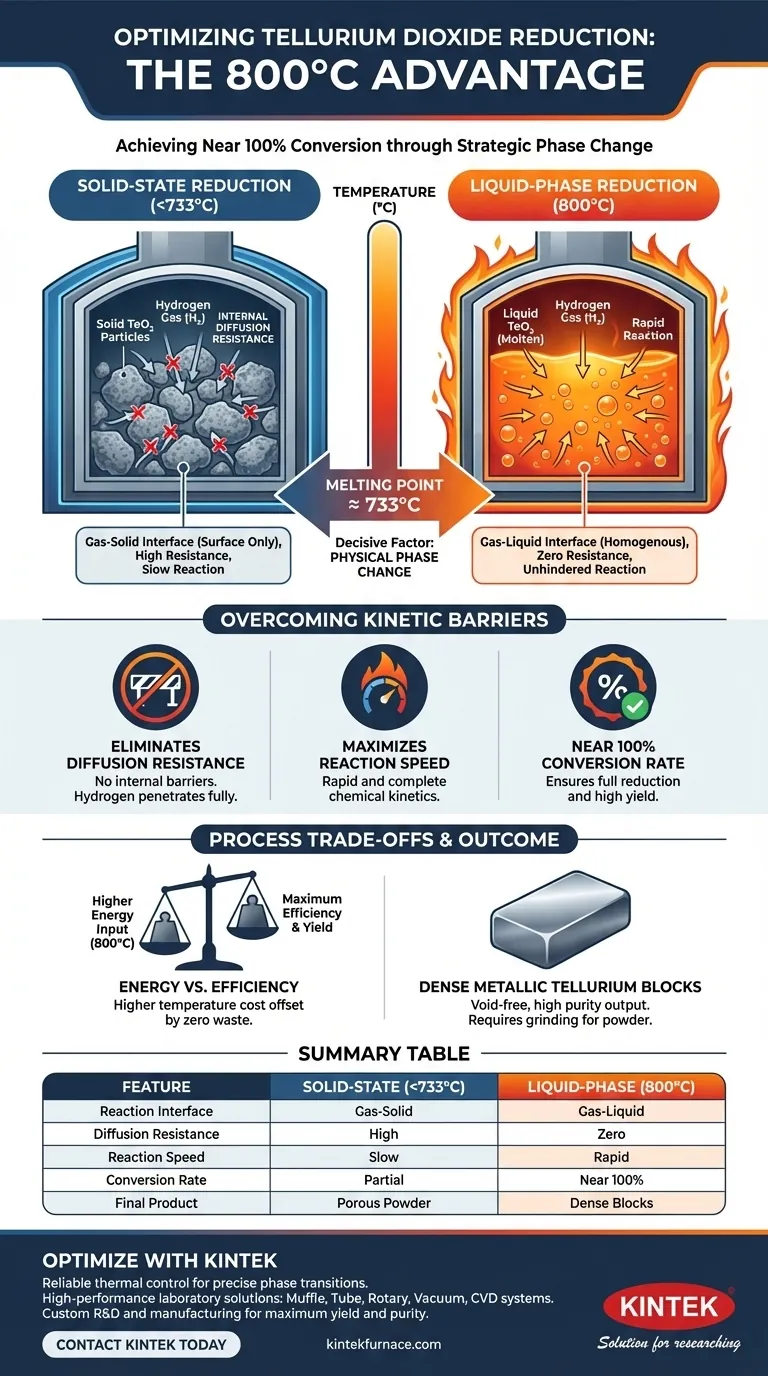
The decisive factor is the physical phase change of the material. A temperature of 800 degrees Celsius is specifically chosen because it exceeds the melting point of tellurium dioxide (approximately 733 degrees Celsius). By converting the solid oxide into a liquid, the process eliminates the internal diffusion resistance that typically slows down gas-solid reactions, allowing the hydrogen to react fully and resulting in near 100 percent conversion.
By operating above the melting point of tellurium dioxide, the reduction process bypasses the kinetic limitations inherent in solid-state reactions. The liquid phase allows hydrogen to react freely without structural barriers, ensuring a rapid, complete conversion into metallic tellurium.

The Mechanics of the Phase Transition
Exceeding the Melting Threshold
The efficiency of this reaction relies on passing a specific thermal milestone. Tellurium dioxide has a melting point of approximately 733 degrees Celsius.
By setting the furnace to 800 degrees Celsius, you ensure the material completely transitions from a solid state to a liquid state. This thermal overhead guarantees that the entire batch remains molten throughout the process.
Shifting the Reaction Interface
At lower temperatures, reduction occurs at a gas-solid interface. This limits the interaction to the surface area of the solid particles.
At 800 degrees Celsius, the dynamic shifts to a gas-liquid interface. The reactants are no longer constrained by the rigid structure of a solid lattice.
Overcoming Kinetic Barriers
Eliminating Diffusion Resistance
The primary obstacle in reducing solid particles is internal diffusion resistance. In a solid, hydrogen gas must struggle to penetrate the particle's outer layer to reach the unreacted core.
When the tellurium dioxide melts, this resistance is effectively eliminated. The liquid state allows for homogenous mixing and prevents the formation of unreacted "cores" often found in solid-state processing.
Maximizing Reaction Speed
With diffusion barriers removed, the chemical kinetics change dramatically. Hydrogen gas can react rapidly and fully with the liquefied oxide.
This unhindered contact is what drives the conversion rate to nearly 100 percent. The result is not just a high yield, but the formation of dense metallic tellurium blocks rather than porous or incomplete products.
Understanding the Process Trade-offs
Energy Intensity vs. Efficiency
Achieving 800 degrees Celsius requires a robust thermal energy input compared to lower-temperature partial reductions.
However, the trade-off is heavily weighted in favor of the higher temperature. The cost of heating is offset by the elimination of wasted, unreacted material and the speed of the reaction.
Product Morphology
It is important to note the physical form of the output. This process produces dense metallic blocks.
If your downstream application requires fine powder, post-processing (grinding) will be necessary. However, if density and purity are the goals, the block form is advantageous as it indicates a void-free, fully reduced material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this high-temperature reduction strategy aligns with your objectives, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is maximum yield: Prioritize operating at 800°C to ensure the material is liquid, guaranteeing near 100% conversion.
- If your primary focus is reaction speed: Use the liquid phase to bypass the slow diffusion rates typical of solid-state reductions.
- If your primary focus is product density: Rely on this method to produce dense metallic blocks rather than loose powders.
Mastering the phase change of tellurium dioxide turns a potentially sluggish reaction into a highly efficient, kinetically optimized process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Solid-State Reduction (<733°C) | Liquid-Phase Reduction (800°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction Interface | Gas-Solid (Surface only) | Gas-Liquid (Homogenous) |
| Diffusion Resistance | High (Limited by solid lattice) | Effectively Zero |
| Reaction Speed | Slow and constrained | Rapid and unhindered |
| Conversion Rate | Partial / Incomplete | Near 100% |
| Final Product Form | Porous/incomplete powder | Dense metallic blocks |
Optimize Your Materials Processing with KINTEK
Achieving precise phase transitions like the 800°C tellurium reduction requires reliable thermal control. KINTEK provides high-performance laboratory solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—specifically designed to meet the rigorous demands of advanced material science.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our furnaces are fully customizable to your unique research or production needs. Ensure maximum yield and purity in your processes by partnering with a leader in high-temp technology.
Ready to elevate your lab's efficiency? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Hanwen Chung, Bernd Friedrich. Hydrogen Reduction of Tellurium Oxide in a Rotary Kiln, Initial Approaches for a Sustainable Process. DOI: 10.3390/cryst15050478
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the overall environmental benefits of using an atmosphere furnace? Reduce Waste and Boost Efficiency
- What are the key features of a retort furnace? Unlock Precise Atmospheric Control for Advanced Processes
- How are atmosphere furnaces utilized in semiconductor manufacturing? Essential for Annealing, Diffusion, and CVD Processes
- What are the considerations for air atmosphere and cooling in Inconel 625 heat treatment? Optimize 3D Part Stability
- How does a heating furnace contribute to the simulated pre-oxidation of alloy powders? Optimize Your Material Research
- What role do atmosphere furnaces play in metal processing? Prevent Oxidation and Enhance Surface Properties
- How does a laboratory electric furnace support the process of evaluating the light-off temperature of Pd/Al2O3 catalysts?
- How does a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace ensure Eu2+ formation? Optimize Your Phosphor Synthesis



















