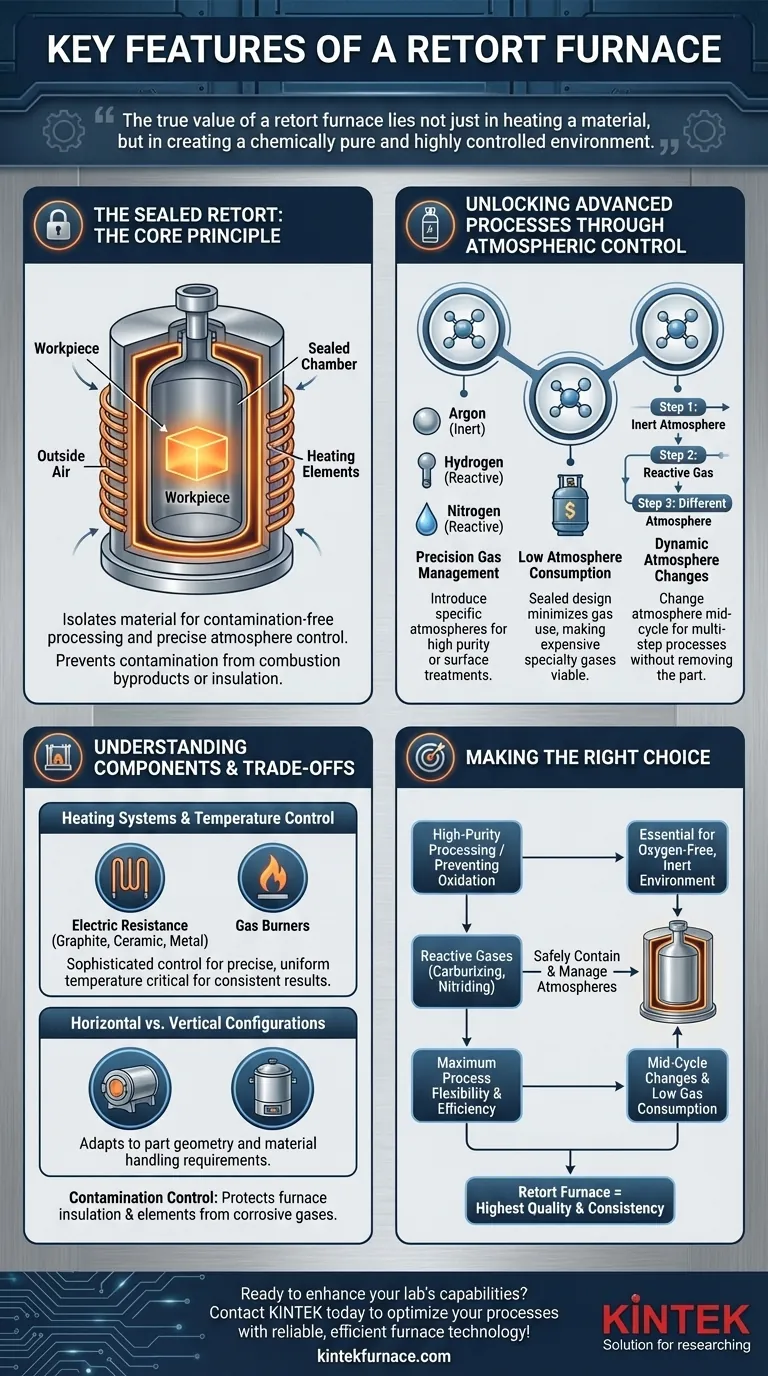
At its core, a retort furnace is defined by its sealed inner chamber, known as the retort. This critical component isolates the material being processed from the furnace's heating elements and the outside air, enabling absolute control over the internal atmosphere. The key features that stem from this design are precise temperature regulation, low consumption of specialized gases, and the flexibility to alter atmospheric conditions during a single process cycle.
The true value of a retort furnace lies not just in heating a material, but in creating a chemically pure and highly controlled environment. This separation is the key to preventing contamination and unlocking advanced material treatments that are impossible in a standard open-air furnace.
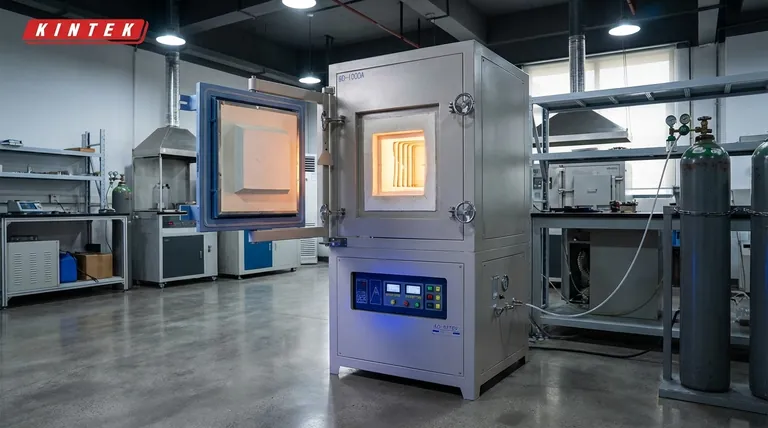

The Defining Principle: The Sealed Retort
A retort furnace's capabilities are built upon the foundation of its central, sealed vessel. Understanding this component is the first step to understanding the furnace's purpose.
What is a Retort?
A retort is a container, often cylindrical and made of high-temperature metal alloys or ceramics, that holds the workpiece. This vessel is sealed and placed inside the main furnace body, which contains the heating system.
Why Separation is Critical
This design physically separates the product from the heat source. This prevents contamination from the byproducts of combustion (in a gas-fired furnace) or from the furnace insulation. Most importantly, it allows for the complete removal of oxygen and the introduction of a specific, controlled atmosphere.
Unlocking Advanced Processes Through Atmospheric Control
The sealed retort is what enables the precise management of the furnace's internal environment. This is where the retort furnace derives its primary industrial value.
Precision Gas Management
Because the retort is a closed system, operators can introduce specific atmospheres required for advanced processes. This can be an inert gas like Argon to prevent oxidation, or a reactive gas like Hydrogen or Nitrogen for processes like nitriding and carburizing.
Low Atmosphere Consumption
A sealed retort has a very low leak rate. This means that once the desired atmosphere is established, very little gas is needed to maintain it. This makes the use of expensive specialty gases economically viable.
Dynamic Atmosphere Changes
One of the most powerful features is the ability to change the atmosphere during a single firing cycle. A part could be heated in an inert atmosphere, then exposed to a carburizing gas, and finally held at temperature in a different atmosphere—all without being removed from the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Core Components
While powerful, a retort furnace is a specialized piece of equipment with specific components and considerations.
Heating Systems and Temperature Control
Retort furnaces can be heated either by electric resistance elements (graphite, ceramic, or metal) or by gas burners. Regardless of the source, they are equipped with sophisticated control systems to ensure precise and uniform temperature, which is critical for consistent results.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Configurations
The furnace can be built in either a horizontal (front-loading) or vertical (top-loading) orientation. The choice depends on the specific application, part geometry, and material handling requirements of the facility.
Potential for Contamination Control
The sealed design not only protects the workpiece but also the furnace itself. Corrosive gases used in some processes are contained within the retort, protecting the furnace's insulation and heating elements from degradation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a furnace requires aligning its capabilities with your processing goals.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or preventing oxidation: A retort furnace is essential for creating the oxygen-free, inert environment required for sensitive materials.
- If your process involves reactive gases like carburizing or nitriding: The retort's ability to safely contain and precisely manage these atmospheres is non-negotiable for achieving desired surface properties.
- If you require maximum process flexibility and efficiency: The ability to alter atmospheres mid-cycle and the low gas consumption make the retort furnace a uniquely powerful and economical tool.
Ultimately, selecting a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize precise atmospheric control to achieve the highest quality and consistency in your final product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Sealed Retort | Isolates material for contamination-free processing and precise atmosphere control. |
| Precise Temperature Regulation | Ensures uniform heating with advanced control systems for consistent results. |
| Low Gas Consumption | Minimizes use of expensive gases due to sealed design, enhancing cost-efficiency. |
| Dynamic Atmosphere Changes | Allows switching atmospheres mid-cycle for flexible, multi-step processes. |
| Horizontal/Vertical Configurations | Adapts to part geometry and handling needs for various industrial setups. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with advanced retort furnaces? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes with reliable, efficient furnace technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation



















