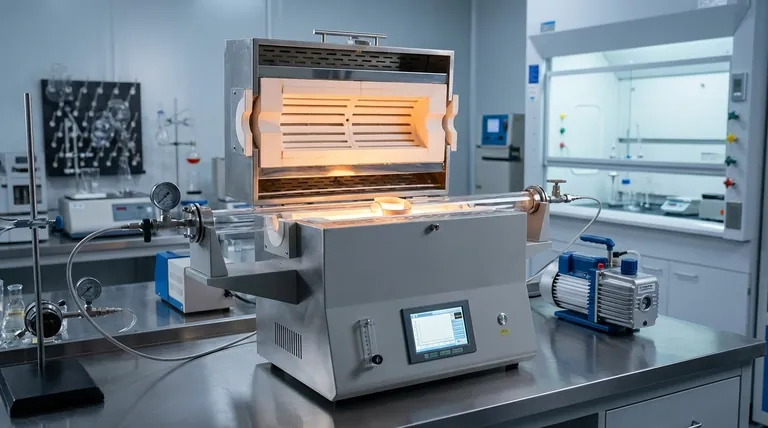
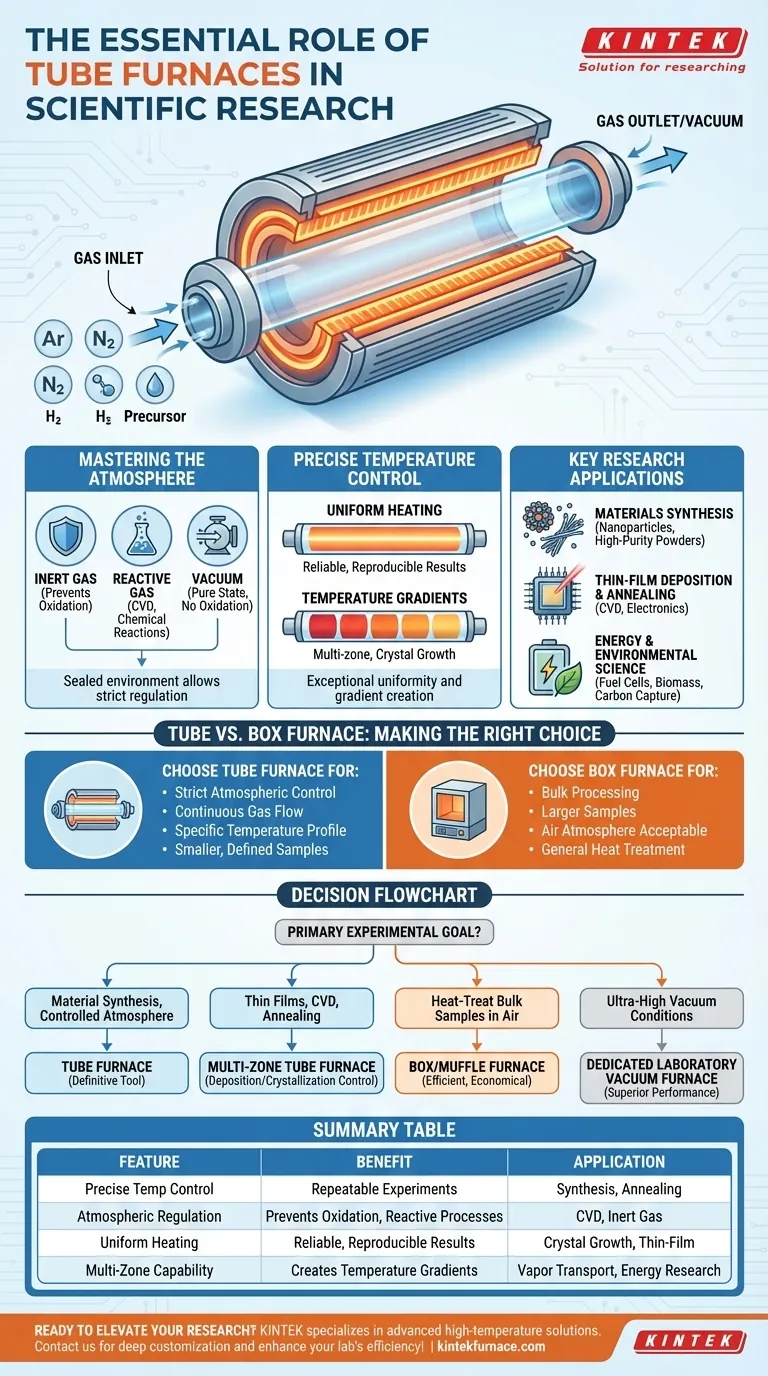
Tube furnaces are essential in scientific research because they offer an unparalleled combination of high-temperature capability, precise temperature control, and the ability to strictly regulate the gaseous atmosphere around a sample. This unique set of features allows researchers to create highly specific, repeatable conditions that are impossible to achieve with other types of laboratory heating equipment.
The true value of a tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its function as a self-contained, highly controllable micro-environment. Its tubular chamber is the key, enabling processes like gas flow, vacuum, and temperature gradients that are fundamental to modern materials science and energy research.

The Core Advantage: A Controlled Processing Environment
A tube furnace's primary function is to provide a controlled environment for thermal processing. Unlike box furnaces, which heat a large chamber, a tube furnace focuses its energy on a narrow, cylindrical space, leading to several distinct advantages.
Uniform Heating in a Confined Space
The cylindrical heating elements surrounding the process tube ensure exceptional temperature uniformity along the length of the sample. This is critical for experiments where every part of the sample must experience the exact same conditions to yield reliable and reproducible results.
Mastering the Atmosphere
The defining feature of a tube furnace is its ability to control the atmosphere. The sealed process tube can be connected to gas lines or vacuum pumps, allowing for experiments under:
- Inert Gas: Using gases like argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation and unwanted reactions.
- Reactive Gas: Introducing specific gases to participate in a chemical reaction, such as in chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
- Vacuum: Removing air entirely to study materials in a pure state or prevent high-temperature oxidation.
Creating Precise Temperature Gradients
Many advanced models are multi-zone tube furnaces, with several independent heating zones along the tube's length. This allows researchers to create a precise temperature gradient, a critical requirement for processes like crystal growth and physical vapor transport.
Key Research Applications Unlocked by Tube Furnaces
The unique capabilities of tube furnaces make them indispensable across a wide range of scientific and industrial R&D fields.
Advanced Materials Synthesis
Tube furnaces are central to creating new materials. They are used for synthesis and processing of nanoparticles, nanowires, and high-purity powders where control over both temperature and atmosphere determines the final material's structure and properties.
Thin-Film Deposition and Annealing
In electronics and optics, creating thin films of material on a substrate is a common task. Tube furnaces are used for chemical vapor deposition (CVD), where precursor gases react at high temperatures to deposit a film, and for annealing, which uses heat to improve the film's crystalline structure and relieve internal stress.
Energy and Environmental Science
These furnaces are vital for developing next-generation energy solutions. They are used to test materials for fuel cells, pyrolyze biomass to create biofuels, and develop novel materials for carbon capture and storage.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Tube vs. Other Furnaces
Choosing the right furnace depends entirely on the experimental requirements. A tube furnace is a specialized tool, and sometimes a simpler device is more appropriate.
When to Choose a Tube Furnace
A tube furnace is the correct choice when your process requires strict atmospheric control, a continuous flow of gas over a sample, or a specific temperature profile along the sample's length. Its geometry is ideal for smaller, well-defined samples.
When a Box or Muffle Furnace is a Better Fit
For bulk processing of larger samples or applications where an air atmosphere is acceptable, a box or muffle furnace is often more practical and cost-effective. These are workhorses for general heat treatment, ashing, and studying material properties in air.
The Limitation of Sample Size
The primary trade-off of a tube furnace is sample throughput. The diameter of the process tube inherently limits the size and quantity of the material you can process at one time. For scaling up production, other furnace designs may be necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
To select the correct equipment, you must first define your primary experimental goal.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis in a controlled atmosphere: A tube furnace is the definitive tool for the job due to its sealing and gas handling capabilities.
- If your primary focus is creating thin films via CVD or annealing: A multi-zone tube furnace is necessary to control deposition and crystallization processes.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating bulk samples in air: A simpler box or muffle furnace is a more efficient and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving ultra-high vacuum conditions: A dedicated laboratory vacuum furnace may offer superior performance over a standard tube furnace setup.
Ultimately, understanding the unique environmental control offered by a tube furnace is the key to unlocking new possibilities in your research.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control | Enables repeatable experiments | Materials synthesis, annealing |
| Atmospheric Regulation | Prevents oxidation, allows reactive processes | CVD, inert gas experiments |
| Uniform Heating | Ensures reliable, reproducible results | Crystal growth, thin-film deposition |
| Multi-Zone Capability | Creates temperature gradients | Physical vapor transport, energy research |
Ready to elevate your research with a tube furnace? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your lab's efficiency and innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















