At their core, muffle furnaces are critical to research and development because they provide an extremely precise and contaminant-free high-temperature environment. This allows scientists and engineers to reliably test, transform, and analyze materials under controlled conditions, which is fundamental to creating new products and verifying quality.
The true value of a muffle furnace in R&D isn't just its ability to get hot, but its ability to create a pure and repeatable thermal environment. This isolation prevents contamination, ensuring that experimental results are a true reflection of the material's properties, not outside influences.

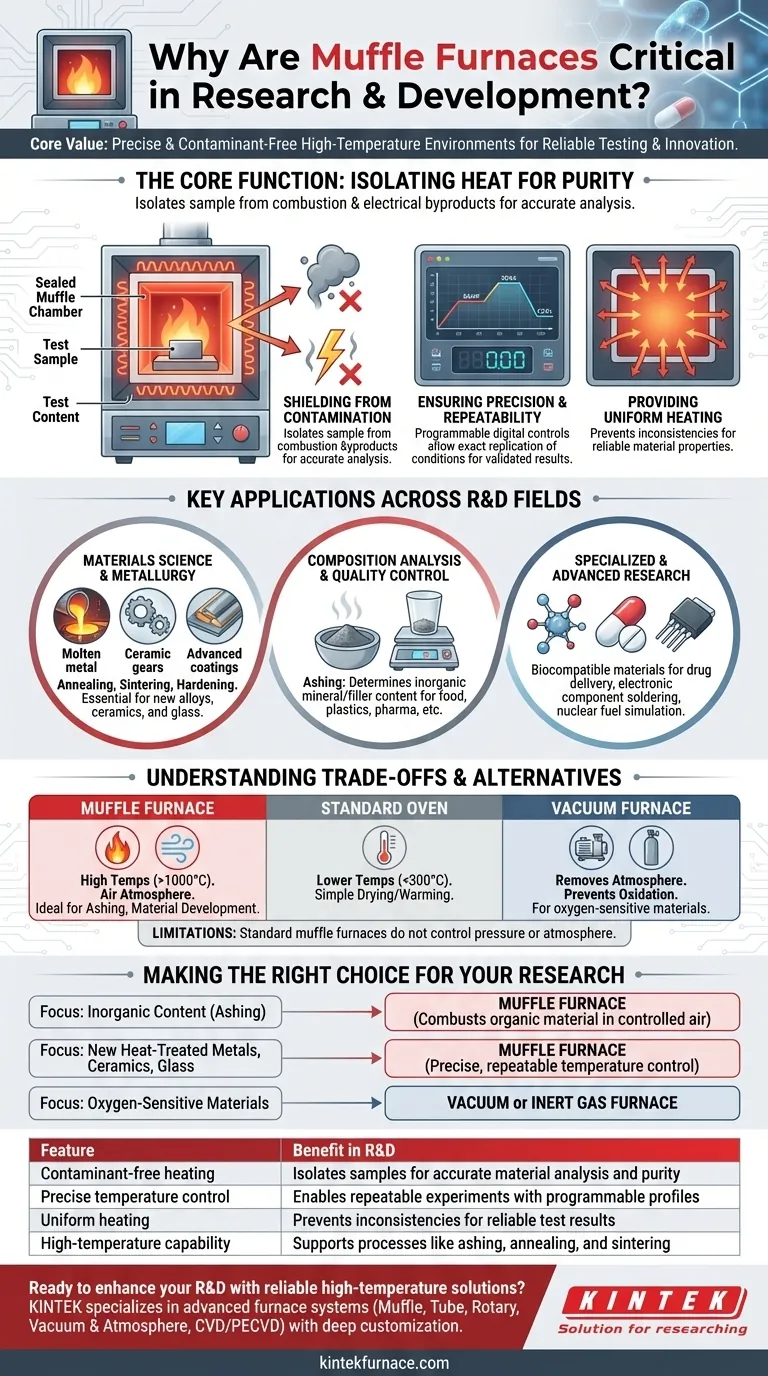
The Core Function: Isolating Heat for Purity
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is the "muffle"—an inner chamber that separates the material sample from the heating elements. This design is the source of its power in a research setting.
Shielding Samples from Contamination
The sealed muffle isolates the sample from any byproducts of combustion or electrical heating. This prevents contaminants from interacting with the sample, which is critical for accurate chemical analysis and materials development.
Without this isolation, it would be impossible to know if changes in the material were caused by the heat itself or by a reaction with gases from the heating source.
Ensuring Precision and Repeatability
Modern muffle furnaces offer programmable digital controls. Researchers can set precise temperature profiles, including ramp rates (how fast it heats up), soak times (how long it holds a temperature), and cooling rates.
This level of control ensures that experiments are repeatable—a cornerstone of the scientific method. The same conditions can be replicated perfectly, validating results and allowing for incremental adjustments in subsequent tests.
Providing Uniform Heating
A well-designed furnace provides uniform heat throughout the chamber. This means the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions, preventing inconsistencies that could skew test results or create defects in a newly formed material.
Key Applications Across R&D Fields
The combination of purity, precision, and high heat makes the muffle furnace an indispensable tool across numerous scientific and industrial sectors.
Materials Science and Metallurgy
This is the most common application. Researchers use muffle furnaces for annealing (softening metals), sintering (fusing powders into a solid mass), and hardening metals.
It is essential for developing new alloys, technical ceramics, glass, and advanced coatings that form the basis of modern technology.
Compositional Analysis and Quality Control
Muffle furnaces are the standard for ashing. This process involves burning a sample at high temperatures to burn off all organic matter, leaving only the inorganic ash.
This allows researchers to determine the exact mineral or filler content of a sample, a critical step in quality control for food, plastics, pharmaceuticals, and environmental testing.
Specialized and Advanced Research
The furnace's reliable environment is used in highly sensitive fields. In pharmaceutical R&D, it aids in creating new biocompatible materials for drug delivery systems.
It is also used in niche applications like simulating conditions for nuclear fuel disposal and creating specialized electronic components through soldering and brazing processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the only thermal processing tool. Understanding its specific role is key to using it effectively.
Muffle Furnace vs. a Standard Oven
A laboratory oven typically operates at much lower temperatures (usually below 300°C) and lacks the sealed muffle. Ovens are for simple drying or warming, while muffle furnaces are for high-temperature material transformations.
Muffle Furnace vs. a Vacuum Furnace
A standard muffle furnace operates in the presence of air. A vacuum furnace removes the atmosphere, creating a vacuum or allowing for the introduction of a specific inert gas (like argon).
This is necessary when studying materials that would oxidize or react with air at high temperatures. The muffle furnace is for processes where an air atmosphere is acceptable or desired.
Limitations to Consider
A standard muffle furnace does not control pressure or atmosphere. If your process is sensitive to oxygen or requires high pressure, you will need a more specialized tool like a vacuum furnace or a hot press furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
Your specific research goal determines whether a muffle furnace is the right instrument.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic content of a sample (ashing): The muffle furnace is the ideal tool due to its ability to completely combust organic material in a controlled air environment.
- If your primary focus is developing new heat-treated metals, ceramics, or glass: The furnace's precise and repeatable temperature control is essential for achieving desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is testing materials that must not be exposed to oxygen: You need a vacuum or inert gas furnace, as a standard muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace enables innovation by providing a reliable and pure environment to explore the very limits of material performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit in R&D |
|---|---|
| Contaminant-free heating | Isolates samples for accurate material analysis and purity |
| Precise temperature control | Enables repeatable experiments with programmable profiles |
| Uniform heating | Prevents inconsistencies for reliable test results |
| High-temperature capability | Supports processes like ashing, annealing, and sintering |
Ready to enhance your R&D with reliable high-temperature solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring precise, contaminant-free processing for materials science, quality control, and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















