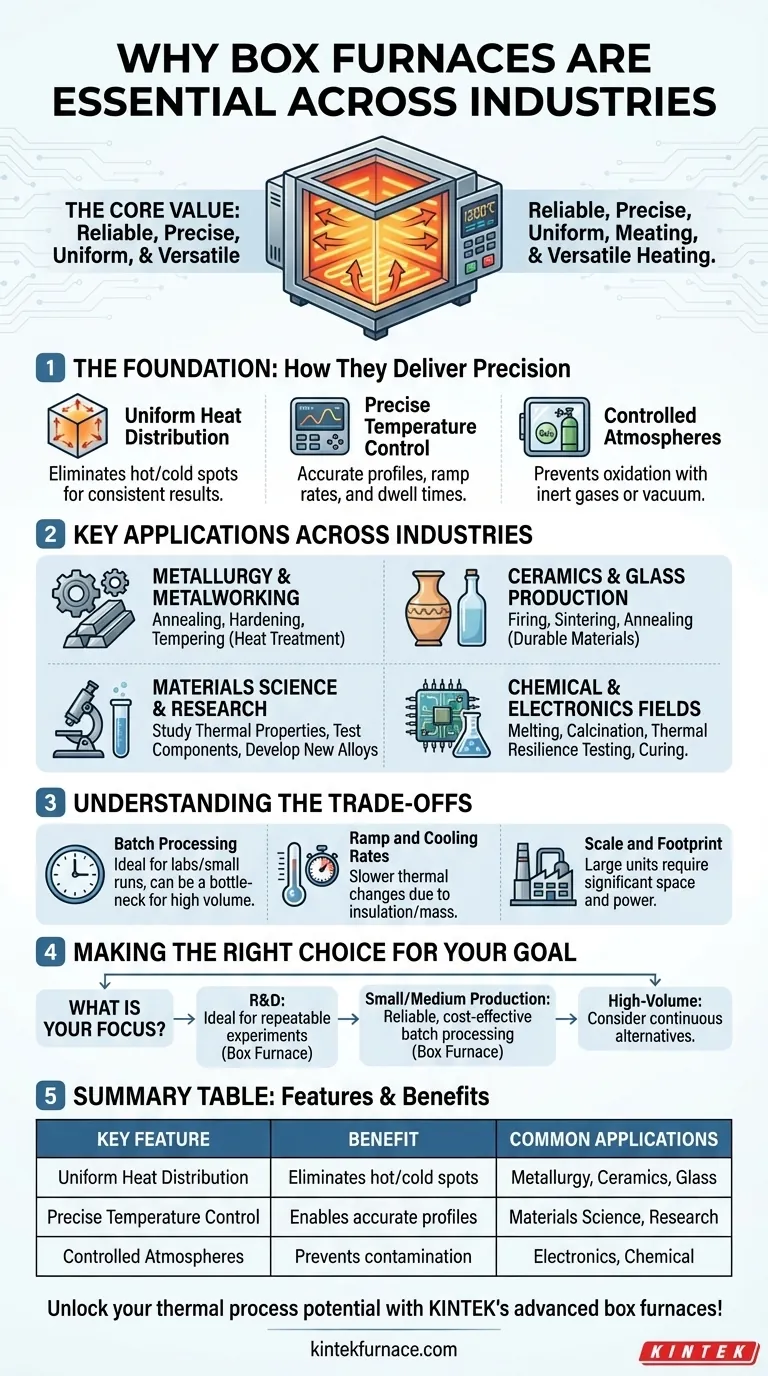
At their core, box furnaces are essential because they provide a highly reliable, precise, and uniform heating environment in an incredibly versatile format. This unique combination makes them indispensable for a vast range of critical processes, from small-scale scientific research in a lab to foundational heat treatments in industrial manufacturing.
The challenge in many advanced fields is not just reaching a high temperature, but holding it with absolute precision and uniformity. Box furnaces solve this by offering a stable, controllable, and adaptable thermal processing environment, making them a cornerstone technology for both innovation and production.

The Foundation: How Box Furnaces Deliver Precision
The value of a box furnace is rooted in its fundamental design, which is engineered for control and consistency. Several key principles work together to achieve this performance.
Uniform Heat Distribution
The enclosed chamber, or "box," design is inherently effective at containing heat. High-quality insulation minimizes thermal loss, allowing heating elements to raise the temperature of the entire internal volume evenly, eliminating hot or cold spots that could ruin a sensitive process.
Precise Temperature Control
Modern box furnaces are equipped with sophisticated digital controllers and thermocouples. These systems continuously monitor the internal temperature and modulate power to the heating elements, allowing users to execute complex heating profiles with specific ramp rates and dwell times to an accuracy of a few degrees.
Controlled Atmospheres
Many critical processes, especially in metallurgy and electronics, are compromised by the presence of oxygen at high temperatures. Advanced box furnaces can be sealed and purged with inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) or operated under a vacuum to create a non-reactive atmosphere, preventing oxidation and contamination.
Key Applications Across Industries
The versatility of the box furnace is demonstrated by its widespread adoption for processes that are fundamental to modern technology and manufacturing.
Metallurgy and Metalworking
This is a primary domain for box furnaces. They are used for heat treatment processes like annealing (softening metal), hardening (increasing strength), and tempering (reducing brittleness). The precise control prevents damage to the metal's grain structure.
Ceramics and Glass Production
Creating durable ceramics requires processes like firing and sintering, where powdered materials are heated to bond together without melting. Box furnaces provide the stable, high-temperature environment needed for these transformations. They are also used to anneal glass, slowly cooling it to remove internal stresses.
Materials Science and Research
In a laboratory setting, a box furnace is an essential tool for discovery. Scientists use it to study the thermal properties of new materials, test the effects of heat on component performance, and develop novel alloys and composites under tightly controlled conditions.
Chemical and Electronics Fields
Box furnaces assist in processes like melting and calcination in the chemical industry. In electronics, they can be used for testing the thermal resilience of components or for specific bonding and curing applications that require a clean, high-temperature environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, the box furnace is not the universal solution for every thermal processing need. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Batch Processing by Design
A box furnace operates on a batch basis: you load it, run a cycle, cool it, and unload it. This is perfect for labs, custom work, or small-to-medium production runs. However, it can become a bottleneck in high-volume manufacturing, where continuous furnaces (like conveyor or tunnel furnaces) are more efficient.
Ramp and Cooling Rates
While precise, the thermal mass of a well-insulated box furnace means it may not heat up or cool down as rapidly as more specialized, smaller-capacity ovens. Processes requiring extreme thermal shocks may necessitate different equipment.
Scale and Footprint
The "box" design is simple and scalable, but large industrial-scale box furnaces require significant floor space and power infrastructure. For extremely large or uniquely shaped parts, a custom-built furnace solution might be more practical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a box furnace should be based on your specific operational needs for precision, volume, and flexibility.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A box furnace's versatility and precise control make it the ideal tool for repeatable scientific experimentation.
- If your primary focus is small-to-medium scale production: A box furnace offers a reliable and cost-effective solution for critical batch heat treatment processes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous manufacturing: You should evaluate whether the box furnace's batch nature is a limitation and explore continuous furnace alternatives.
Ultimately, the box furnace's enduring essentiality comes from providing an accessible and trustworthy method for mastering heat.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Uniform Heat Distribution | Eliminates hot/cold spots for consistent results | Metallurgy, Ceramics, Glass Production |
| Precise Temperature Control | Enables accurate heating profiles with digital systems | Materials Science, Research Labs |
| Controlled Atmospheres | Prevents oxidation and contamination in sensitive processes | Electronics, Chemical Industries |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced box furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our reliable and precise heating solutions can enhance your efficiency and innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace contribute to the thermal treatment process of chalcopyrite ore?
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace used for Ni-BN powder preheating? Achieve defect-free coating density.



















