Argon and Hydrogen are utilized together to create a balanced thermal environment that maximizes coating quality while protecting the material. Argon serves as the primary stabilizing gas to maintain the plasma arc, while Hydrogen acts as a high-energy auxiliary gas that boosts the flame's heat and conductivity to ensure the AlCoCrFeNi powder melts completely.
The combination of Argon and Hydrogen provides a high-enthalpy, inert environment essential for processing complex alloys. While Argon creates a stable plasma core, Hydrogen acts as a thermal amplifier, delivering the intense energy required to fully melt AlCoCrFeNi particles without causing detrimental oxidation.
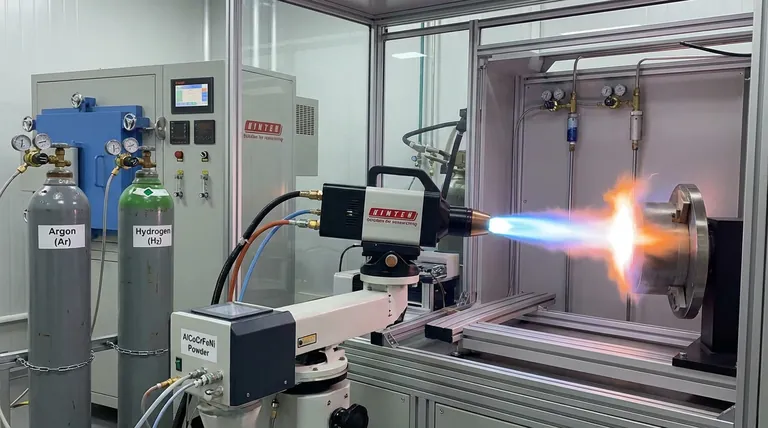
The Mechanics of the Gas Mixture
The Foundation: Argon (Ar)
Argon acts as the primary working gas in the plasma spray process. Its fundamental role is to provide a stable plasma arc.
Because Argon is chemically inert, it sustains the electric arc without reacting with the internal components of the plasma gun. This stability is the baseline requirement for a consistent, controllable spray process.
The Energy Booster: Hydrogen (H2)
Hydrogen is introduced as an auxiliary gas to radically alter the properties of the plasma flame. Its primary function is to increase the enthalpy (heat content) and thermal conductivity of the plasma.
While Argon creates the arc, it has relatively low heat capacity. Adding Hydrogen allows the plasma plume to carry significantly more energy and transfer that heat more efficiently to the powder particles injected into the stream.
Why AlCoCrFeNi Requires This Specific Blend
Ensuring Complete Melting
AlCoCrFeNi is a complex high-entropy alloy that requires substantial thermal energy to transition from a solid powder to a liquid state during its short flight time.
The Argon-Hydrogen mixture ensures complete melting of the powder. Without the added thermal conductivity provided by Hydrogen, the particles might remain semi-molten, leading to a porous or weakly bonded coating.
Controlling Spray Power
The ratio of Hydrogen to Argon gives the operator direct control over the spraying power.
By adjusting the Hydrogen content, you can fine-tune the voltage and total energy output of the plasma gun. This capability allows for precise manipulation of the process to suit the specific particle size and melting point of the AlCoCrFeNi alloy.
Preventing Oxidation
Maintaining material purity is critical for high-entropy alloys. The Argon-Hydrogen atmosphere creates a protective shield around the molten particles.
This mixture creates a reducing environment that minimizes accidental oxidation of the coating during application. It ensures that the chemical composition of the deposited coating closely matches the original powder, preserving the alloy's intended properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Balancing Energy and Stability
While Hydrogen provides necessary heat, it adds complexity to the process control. The mixture must be carefully balanced; relying solely on Argon would provide stability but insufficient heat for this alloy.
Conversely, an aggressive Hydrogen-rich mixture increases thermal intensity. You must balance the need for high enthalpy (to melt the powder) against the need to maintain a stable, non-turbulent arc that deposits the material uniformly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Optimizing your process atmosphere is about balancing thermal energy with arc stability.
- If your primary focus is coating density: Prioritize a mixture with sufficient Hydrogen to ensure high thermal conductivity and complete particle melting, which reduces porosity.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Ensure the gas flow rates are calibrated to maintain a strict inert/reducing atmosphere, minimizing any risk of oxidation during the particle flight.
By leveraging Argon for stability and Hydrogen for energy, you ensure a robust, oxidation-free AlCoCrFeNi coating that performs reliably in demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Gas Component | Primary Role | Impact on AlCoCrFeNi Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Argon (Ar) | Primary working gas | Sustains a stable plasma arc and protects against oxidation. |
| Hydrogen (H2) | Auxiliary energy booster | Increases enthalpy and thermal conductivity for complete powder melting. |
| Mixture (Ar+H2) | Balanced atmosphere | Creates a high-energy, reducing environment for dense, low-porosity coatings. |
Elevate Your Coating Precision with KINTEK
Precision in thermal processing is the key to achieving high-performance AlCoCrFeNi coatings. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides the advanced thermal solutions necessary to master your plasma spray applications.
Whether you need specialized CVD systems, high-temperature lab furnaces, or customizable vacuum solutions, our equipment is designed to meet the rigorous demands of high-entropy alloy processing. Ensure complete material purity and optimal density with technology tailored to your unique research and production needs.
Ready to optimize your thermal processes? Contact our experts today to discover how KINTEK’s customizable systems can drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
References
- Rong Chen, Peng Song. Initial Oxidation Behavior of AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Coating Produced by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying in the Range of 650 °C to 1000 °C. DOI: 10.3390/ma17030550
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do temperature control systems work in atmosphere furnaces? Achieve Precise Thermal Management for Superior Results
- What is the role of a laboratory annealing furnace in memristor fabrication? Enhance Interface & Stability
- Why is an inert atmosphere necessary for SPAN carbonization? Achieve High-Quality Synthesis with Precise Control
- What function does a flow-gas furnace serve in iron ore reduction? Mastering Lab Gas Delivery and Thermal Sync
- What are the characteristics and applications of exothermic atmospheres in furnaces? Optimize Metal Heat Treatment
- What industries commonly use retort furnaces and for what purposes? Unlock High-Purity Thermal Processing
- What kind of atmosphere is typically used in low vacuum atmosphere furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment with Inert Gases
- What features make the experimental box type atmosphere furnace easy to operate? Discover Intuitive Controls and Automation









