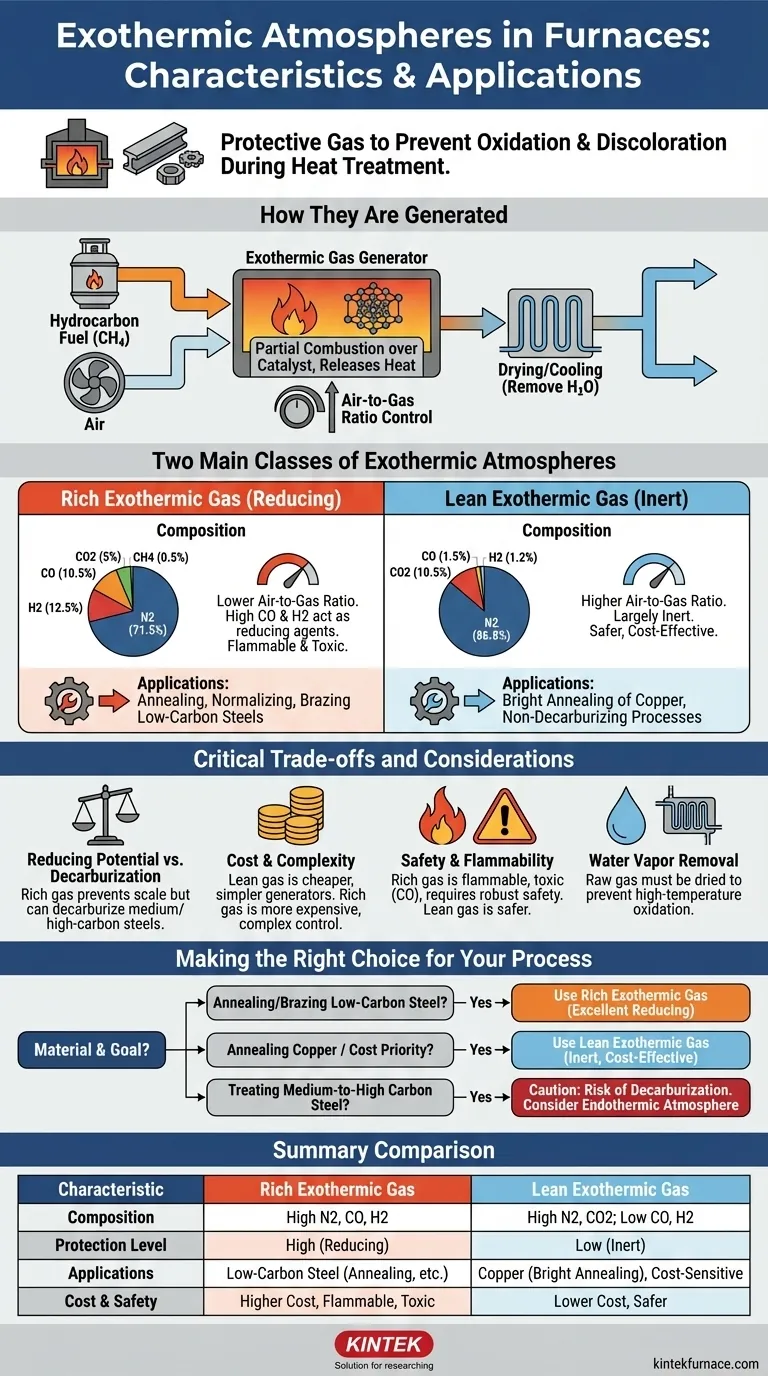
In furnace heat treatment, an exothermic atmosphere is a protective gas generated by the partial combustion of a hydrocarbon fuel. Its primary purpose is to prevent the oxidation and discoloration of metal surfaces during processes like annealing and brazing. These atmospheres are categorized into two main types: "rich" exothermic gas, which is chemically reducing and used for steel, and "lean" exothermic gas, which is more inert and used for metals like copper.
The choice between a rich or lean exothermic atmosphere is a critical decision based on a trade-off. You must balance the required level of chemical protection for the metal against the operational costs, complexity, and safety of the gas generation process.

How Exothermic Atmospheres are Generated
Exothermic atmospheres get their name because the chemical reaction used to create them releases heat. This process occurs within a dedicated piece of equipment called an exothermic gas generator.
The Basic Combustion Reaction
The generator precisely mixes a hydrocarbon fuel, most commonly natural gas (methane, CH4), with air. This mixture is then ignited over a catalyst in a combustion chamber.
The reaction is controlled to be incomplete. Instead of full combustion, which would produce mostly nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O), the partial combustion also yields significant amounts of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2).
Controlling the Air-to-Gas Ratio
The final composition of the gas is determined entirely by the air-to-gas ratio. By adjusting how much air is mixed with the fuel, operators can create either a rich or a lean atmosphere. This ratio is the single most important control variable.
The Two Classes of Exothermic Atmospheres
The specific chemistry of the gas dictates which metals it can protect and what processes it is suitable for.
Rich Exothermic Gas: Maximum Protection
A rich exothermic atmosphere is created using a lower air-to-gas ratio, meaning there is less air for the amount of fuel. This results in a gas that is high in combustible, reducing components.
A typical composition is N2=71.5%, CO=10.5%, H2=12.5%, CO2=5%, and CH4=0.5%.
The high concentrations of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2) make this atmosphere chemically "reducing." These gases actively seek out and react with oxygen, thereby preventing the metal surface from oxidizing. It is ideal for annealing, normalizing, and brazing low-carbon steels.
Lean Exothermic Gas: Cost-Effective and Inert
A lean exothermic atmosphere is produced with a higher air-to-gas ratio, closer to complete combustion. This consumes most of the fuel, leaving a gas that is largely inert.
A typical composition is N2=86.8%, CO2=10.5%, CO=1.5%, and H2=1.2%.
With very low levels of CO and H2, this gas offers minimal reducing potential. It is primarily used for its low cost and for being non-decarburizing to low-carbon steels. Its most common application is the bright annealing of copper, where it is sufficiently protective to prevent gross oxidation without the risks associated with a rich gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an atmosphere is not just about its protective qualities. You must consider its interaction with the specific metal and the operational realities of your facility.
Reducing Potential vs. Decarburization
While the high CO in rich gas prevents scale (oxidation), it can be decarburizing to medium and high-carbon steels. The atmosphere can actually pull carbon atoms out of the steel's surface, softening it. Lean gas is less reducing but also less likely to cause decarburization.
Cost and Complexity
Lean gas is significantly cheaper to produce. It requires more air and less fuel, and the generators are simpler and require less precise control. Rich gas generators are more complex and consume more fuel, increasing operational costs.
Safety and Flammability
This is a critical distinction. Rich exothermic gas is flammable and toxic due to its high CO and H2 content. It requires careful handling, robust ventilation, and safety interlocks. Lean gas, with its very low combustible content, is much safer to handle.
The Hidden Danger: Water Vapor
The raw gas leaving the generator is saturated with water vapor (H2O), which is highly oxidizing to steel at high temperatures. For the atmosphere to be protective, it must first be cooled to condense and remove most of this water vapor. Failing to properly dry the gas is a common cause of failed heat-treating cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your material and your process goal are the ultimate guides for selecting the correct atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is annealing or brazing low-carbon steels: Use a properly dried rich exothermic gas for its excellent reducing properties that prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is annealing non-ferrous metals like copper: Use lean exothermic gas for its excellent balance of cost-effectiveness and sufficient protection.
- If your primary focus is treating medium-to-high carbon steels: Be extremely cautious, as both exothermic atmospheres can be decarburizing. An endothermic atmosphere is often a better, more precisely-controlled choice for these materials.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost and safety risks: Lean exothermic gas is the superior choice, provided its limited protective capability is adequate for your metal.
Ultimately, understanding the specific chemistry of your furnace atmosphere empowers you to achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Rich Exothermic Gas | Lean Exothermic Gas |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | N2=71.5%, CO=10.5%, H2=12.5%, CO2=5%, CH4=0.5% | N2=86.8%, CO2=10.5%, CO=1.5%, H2=1.2% |
| Protection Level | High (reducing) | Low (inert) |
| Applications | Annealing, normalizing, brazing low-carbon steels | Bright annealing of copper, cost-effective processes |
| Cost & Safety | Higher cost, flammable, toxic | Lower cost, safer to handle |
Upgrade your lab's heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, whether you're working with steel, copper, or other metals. Contact us today to discuss how our exothermic atmosphere expertise can enhance your results and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















