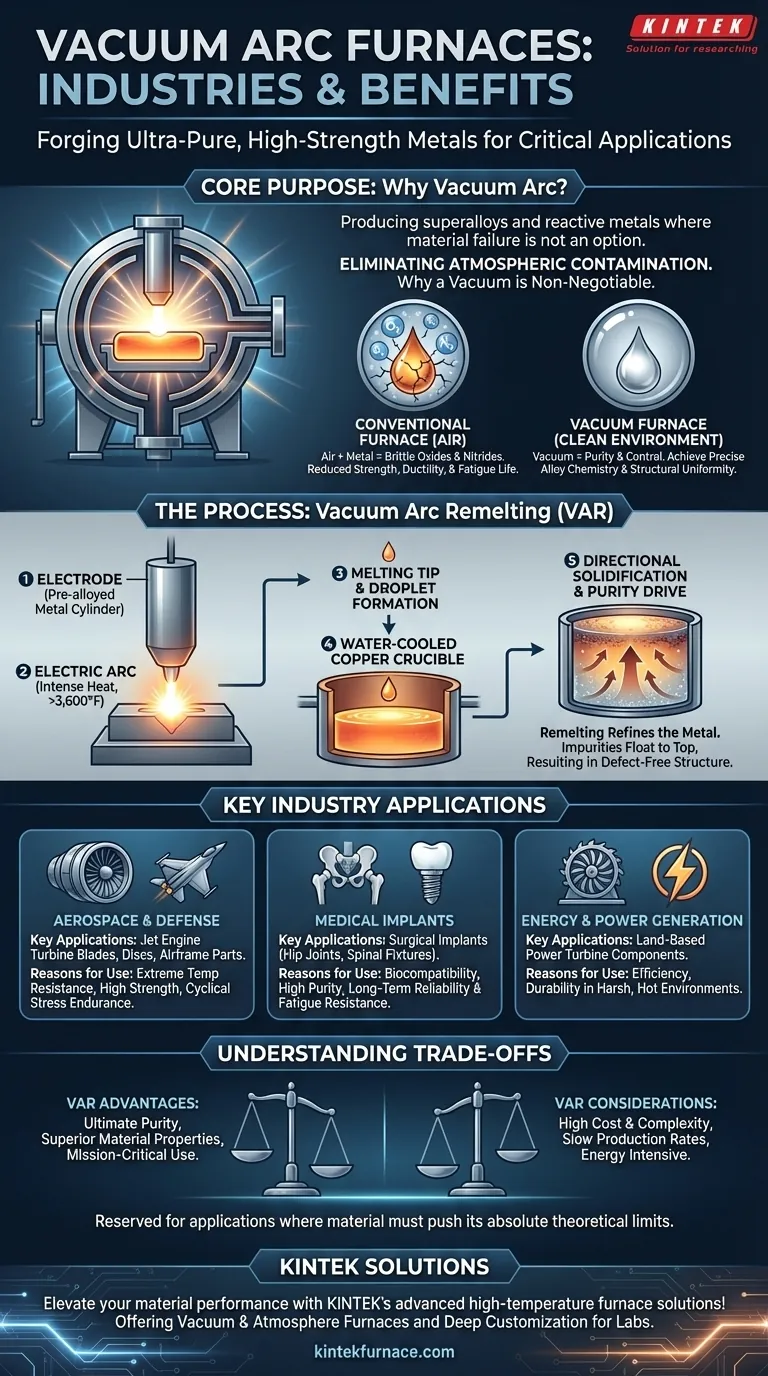
At its core, the industries that rely on vacuum arc furnaces are those where material failure is not an option. Aerospace, medical, and energy sectors are the primary users because this technology is uniquely capable of producing the ultra-pure, high-strength superalloys and reactive metals required for their most demanding applications. The vacuum environment is essential for eliminating atmospheric impurities that would otherwise compromise the metal's structural integrity, while the arc provides the intense, controlled heat needed for melting and refining.
The central challenge in high-performance metallurgy is preventing contamination. Vacuum arc furnaces solve this by removing the air, which contains reactive gases like oxygen and nitrogen. This allows for the creation of exceptionally pure and structurally uniform metals that are impossible to produce with conventional methods.
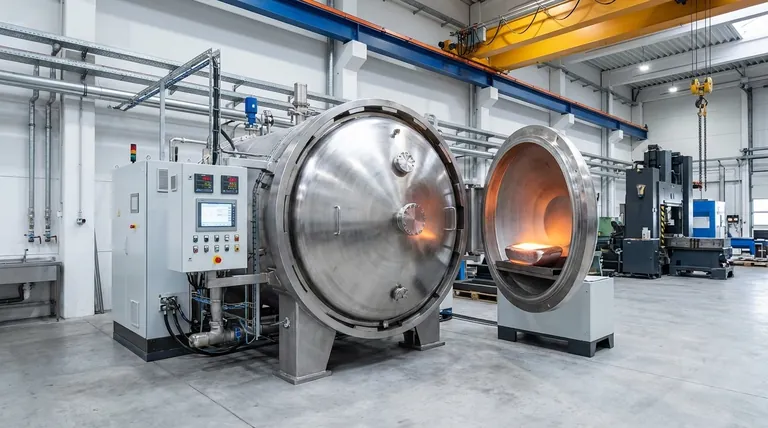

Why a Vacuum is Non-Negotiable
A furnace's atmosphere is a critical ingredient in the final metal. For high-performance alloys, the presence of air is a catastrophic contaminant.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
At the extreme temperatures required for melting metals like titanium or nickel, the metal becomes highly reactive. It will aggressively bond with oxygen and nitrogen from the air.
These reactions form oxides and nitrides, which are microscopic, brittle impurities within the metal's structure. These impurities act as weak points, dramatically reducing the material's strength, ductility, and fatigue life.
A vacuum furnace solves this by physically removing the air, creating a clean environment where the pure metal can be melted without these harmful reactions occurring.
Achieving Precise Alloy Chemistry
Creating a superalloy is like following a precise recipe. Elements like aluminum, chromium, or molybdenum are added in exact, often tiny, percentages to achieve specific properties.
In a conventional furnace, these sensitive alloying elements can be lost to oxidation. In a vacuum, metallurgists have complete control, ensuring the final chemical composition is exactly as designed for peak performance.
The Role of the Electric Arc in Refining
While the vacuum provides a clean environment, the electric arc provides the means for melting and, crucially, for refining the metal. This process is most often called Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR).
The Remelting Process (VAR)
The VAR process does not start with raw ore. It begins with a solid, pre-alloyed cylinder of metal, called an electrode, which was typically created in a different vacuum furnace.
This electrode is suspended inside the VAR furnace. A powerful electric arc is struck between the bottom of the electrode and a shallow, water-cooled copper base. The intense heat of the arc, often exceeding 3,600°F (2,000°C), progressively melts the tip of the electrode.
How Remelting Drives Purity
As the electrode's tip melts, droplets of liquid metal fall into the water-cooled copper crucible below. The metal cools and solidifies in a highly controlled, directional way, from the bottom up.
This directional solidification acts as a powerful refining process. Any remaining non-metallic impurities are less dense and have lower melting points, so they are pushed ahead of the solidifying front and float to the top.
The final result is a new, remelted ingot with exceptional chemical purity and a highly uniform, defect-free internal grain structure. This ingot is then ready for forging into a critical component.
Key Industry Applications
The demand for VAR-processed metals comes from sectors where performance and reliability are absolute requirements.
Aerospace and Defense
This is the largest user of VAR technology. Components like jet engine turbine blades, discs, and critical structural airframe parts are made from titanium alloys and nickel-based superalloys. These materials must withstand extreme temperatures and cyclical stress without failing.
Medical Implants
The human body is a harsh environment. Surgical implants like hip joints, spinal fixtures, and dental implants are made from VAR-processed titanium and specialty steels. The high purity ensures biocompatibility (preventing rejection by the body) and the fatigue resistance needed to last a lifetime.
Energy and Power Generation
Components in land-based power generation turbines face similar conditions to jet engines. VAR-processed superalloys are used for blades and other parts in the hottest sections of these turbines to ensure efficiency and long-term operational reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the VAR process produces superior materials, it is not a universal solution. It involves significant compromises that limit its use to only the most critical applications.
High Cost and Complexity
Vacuum arc furnaces are expensive to build, maintain, and operate. The process is highly energy-intensive, and the required vacuum systems and controls add significant complexity and cost.
Slow Production Rates
VAR is a deliberate, slow, and precise batch process. It cannot compete with the high-volume output of conventional air-melt steel mills. This low throughput contributes to the high cost of its products.
Not for Every Application
For the vast majority of metal applications, such as automotive body panels, structural steel beams, or standard tools, the extreme purity of a VAR-processed metal is unnecessary overkill. More economical methods like air-melting or low-vacuum heat treatments are perfectly sufficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum arc furnace is driven entirely by the performance demands of the final component.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material purity and fatigue life: A vacuum arc remelting (VAR) furnace is the definitive choice for mission-critical superalloys and reactive metals where failure is catastrophic.
- If your primary focus is bulk heat treatment or brazing: A standard vacuum furnace (without an arc) is the correct tool for preventing surface oxidation on a wide range of parts.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: For materials where some level of impurity is acceptable, a conventional air-melt or induction furnace is the more practical and economical solution.
Ultimately, vacuum arc furnaces are reserved for applications where you must push a material to its absolute theoretical limits.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Reasons for Use |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Jet engine turbine blades, structural parts | Extreme temperature resistance, high strength, fatigue life |
| Medical | Surgical implants (e.g., hip joints, spinal fixtures) | Biocompatibility, purity, long-term reliability |
| Energy | Power generation turbine components | Efficiency, durability under harsh conditions |
Elevate your material performance with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge equipment like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your aerospace, medical, or energy applications with ultra-pure, high-strength metals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















