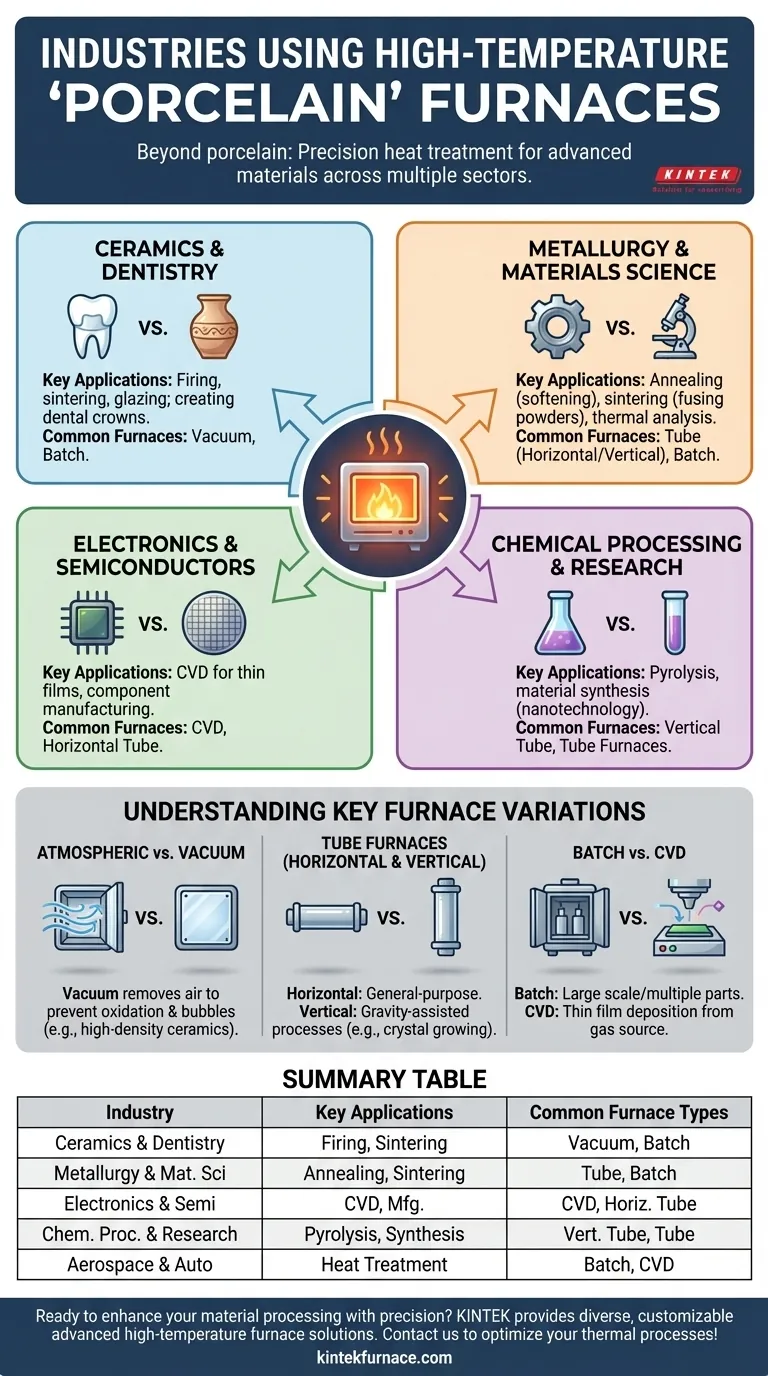
At its core, a porcelain furnace is a high-temperature oven used across any industry that requires precise thermal processing of materials. The most common sectors include ceramics and dentistry, metallurgy, electronics manufacturing, chemical processing, and advanced scientific research.
The term "porcelain furnace" is broader than it suggests. The key isn't the porcelain itself, but the furnace's ability to achieve and precisely control extreme temperatures, which is a fundamental requirement for manufacturing advanced materials across many high-tech industries.
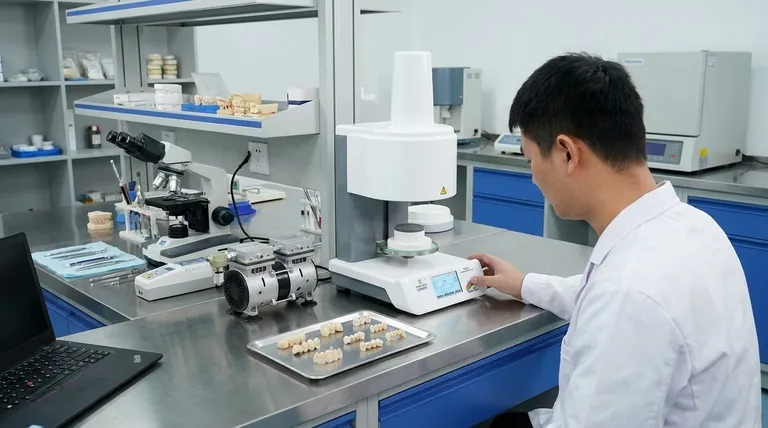

The Core Function: Precision Heat Treatment
The common thread linking all these industries is the need to alter a material's physical or chemical properties through controlled heating and cooling cycles. A furnace provides the environment to execute these critical processes.
Ceramics and Dentistry
This is the most traditional application. Furnaces are used for firing, sintering, and glazing ceramic materials to achieve the desired hardness, density, and finish.
In dentistry, specialized vacuum furnaces are essential for creating crowns and bridges, ensuring the final product is non-porous and strong.
Metallurgy and Materials Science
In metallurgy, furnaces are indispensable for heat-treating metals and alloys to enhance properties like strength and durability.
Processes like annealing (softening a metal), sintering (fusing metal powders together), and thermal analysis are performed in various furnace types, including horizontal tube and batch models.
Electronics and Semiconductors
This sector relies heavily on furnaces for manufacturing components. Horizontal furnaces are common in electronics manufacturing for processes on a larger scale.
Specialized Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnaces are used to grow high-purity thin films on wafers, a foundational step in creating semiconductors and advanced optical coatings.
Chemical Processing and Research
In chemical labs and academic settings, furnaces facilitate controlled chemical reactions at high temperatures.
Vertical tube furnaces are often used for pyrolysis (thermal decomposition in an oxygen-free environment) and synthesizing novel materials in fields like nanotechnology.
Understanding Key Furnace Variations
The specific industry and application dictate the type of furnace required. The design of the furnace is tailored to the process it must perform.
Atmospheric vs. Vacuum Furnaces
Many processes can occur in a standard atmospheric environment.
However, vacuum furnaces are critical when air can interfere with the material. By removing air, they prevent oxidation and eliminate bubbles, which is crucial for creating high-density ceramics or processing reactive metals.
Tube Furnaces (Horizontal and Vertical)
Tube furnaces are extremely common in research and materials science for their versatility.
Horizontal tube furnaces are workhorses for general-purpose heat treatment, annealing, and sintering of samples.
Vertical tube furnaces are advantageous for processes where gravity is helpful, such as growing crystals or ensuring uniform coating in certain CVD applications.
Batch and CVD Furnaces
Batch furnaces are designed for treating larger components or multiple parts simultaneously, making them vital in aerospace, automotive, and tool manufacturing where consistent heat treatment is paramount.
CVD furnaces are highly specialized systems built specifically for depositing thin films from a gas source, essential for the semiconductor and aerospace industries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a furnace depends entirely on the material you are processing and the outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is producing high-density, pure ceramics (like in dentistry): A vacuum furnace is essential to eliminate porosity and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is materials research and development: A versatile horizontal or vertical tube furnace provides a controlled environment for a wide range of thermal experiments.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial heat treatment (e.g., aerospace parts): A batch furnace is engineered to deliver precise, repeatable thermal cycles at scale.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced coatings or semiconductor films: A specialized Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnace is the required tool for the job.
Ultimately, the right furnace is the one engineered to perfectly execute your specific thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Common Furnace Types |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramics & Dentistry | Firing, sintering, glazing; creating dental crowns | Vacuum, Batch |
| Metallurgy & Materials Science | Annealing, sintering, thermal analysis | Tube (Horizontal/Vertical), Batch |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | CVD for thin films, component manufacturing | CVD, Horizontal Tube |
| Chemical Processing & Research | Pyrolysis, material synthesis | Vertical Tube, Tube Furnaces |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Heat treatment of parts | Batch, CVD |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precision? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in ceramics, dentistry, metallurgy, electronics, or research, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how our furnaces can optimize your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What factors determine the quality of sintered zirconia restorations? Master Material, Equipment, and Technique
- How has the sintering process innovated dental zirconia applications? Boost Strength, Precision, and Efficiency
- What are the effects of overloading a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Predictable, High-Quality Zirconia Restorations
- Why is calibration important for dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations and Avoid Costly Failures
- What factors should be considered when choosing a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Quality and Efficiency for Your Lab



















