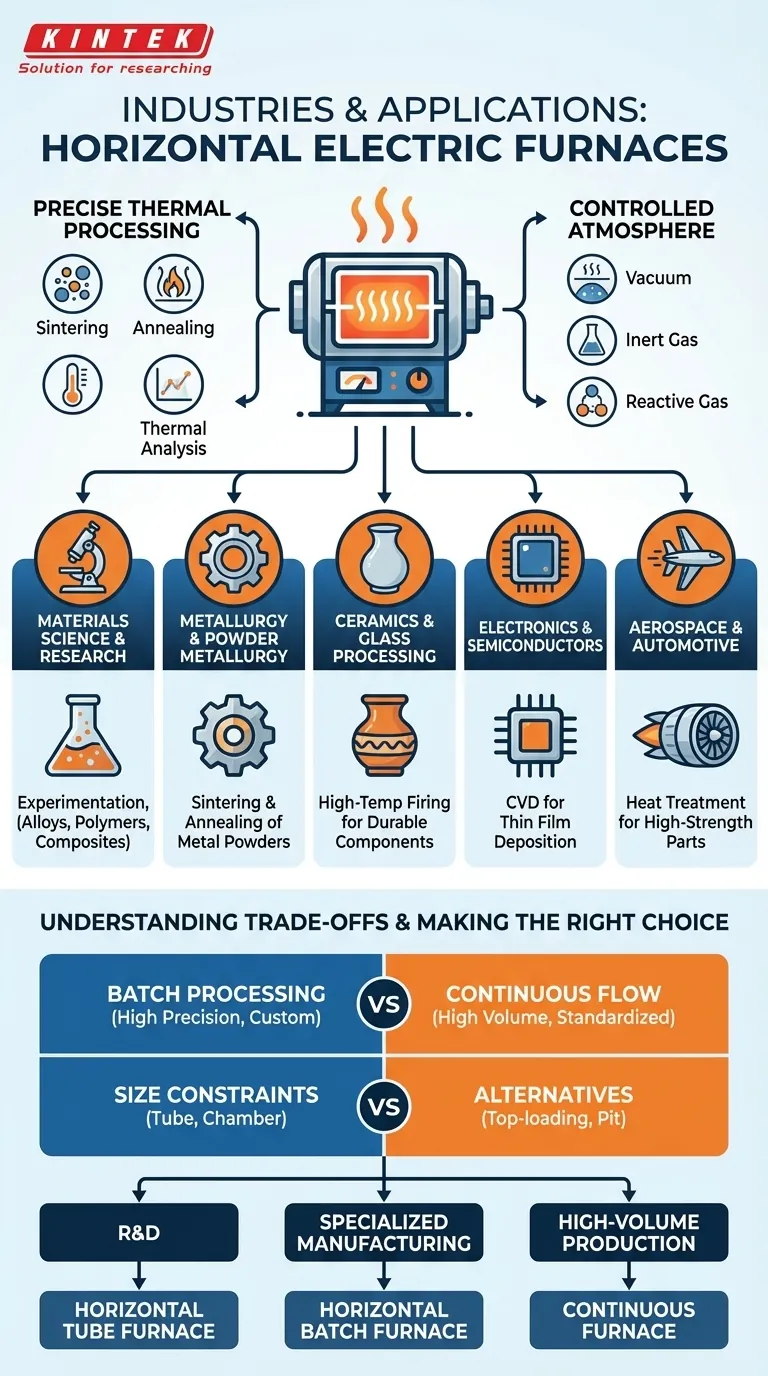
In short, horizontal electric furnaces are foundational tools in industries that develop and manufacture advanced materials. They are widely used in materials science, metallurgy (especially powder metallurgy), ceramics, aerospace, automotive, and electronics manufacturing for their precision and process control.
The core reason these industries rely on horizontal electric furnaces is their ability to create highly controlled, repeatable high-temperature environments. This precision is not just a feature—it is the essential requirement for processes like sintering, annealing, and creating advanced coatings.

The Core Function: Precise Thermal Processing
A horizontal electric furnace is designed for one primary purpose: to apply heat to a material in a meticulously controlled manner. This is not simply about making something hot; it's about executing a precise thermal profile over time.
Why Precision Is Paramount
The physical and chemical properties of advanced materials are often defined by their heat treatment history. Processes like sintering, annealing, and thermal analysis depend on exact temperatures and durations to achieve the desired outcome.
Electric heating elements provide this level of precision, offering uniform heat and rapid response that is difficult to achieve with fuel-fired alternatives.
Controlling the Process Atmosphere
Many heat treatment processes must occur in a specific atmosphere to prevent oxidation or to introduce reactive elements. Horizontal tube furnaces, a common variant, are exceptionally well-suited for creating a vacuum or introducing inert or reactive gases.
This capability is critical for creating pure metals, advanced ceramics, and specialized coatings used in high-tech applications.
A Closer Look at Key Industrial Applications
The versatility of horizontal furnaces makes them a staple across several advanced sectors. Each industry leverages the furnace's core capabilities for specific, high-value applications.
Materials Science & Research
For researchers developing new alloys, polymers, or composites, the horizontal furnace is an indispensable tool for experimentation. It allows them to test how different thermal cycles affect a material's properties on a small, controlled scale.
Metallurgy and Powder Metallurgy
In this field, furnaces are used for annealing (softening metals to improve workability) and sintering. Sintering involves heating compressed metal powders just below their melting point to bond them into a solid, high-strength part.
Ceramics and Glass Processing
Manufacturing technical ceramics and specialized glass requires extremely high and uniform temperatures. Horizontal batch furnaces provide the stable environment needed to create durable, defect-free components for everything from dental implants to aerospace parts.
Electronics and Semiconductors
The production of semiconductors and electronic components demands pristine, particle-free environments. Specialized Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) furnaces, often in a horizontal configuration, are used to deposit microscopically thin films onto substrates to create integrated circuits.
Aerospace and Automotive
These industries rely on heat-treated metals and alloys for high-strength, lightweight components. Horizontal furnaces are used for the precise heat treatment of critical parts like turbine blades, engine components, and structural fasteners to ensure they meet stringent safety and performance standards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, horizontal electric furnaces are not the universal solution for every heating application. Their design comes with inherent limitations.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
Most horizontal furnaces are batch furnaces, meaning parts are loaded, processed, and then unloaded in discrete groups. This is ideal for high-precision work, custom parts, or moderate production volumes.
However, for mass production of standardized items, a continuous or conveyor furnace may be far more efficient, as it processes parts on an assembly line without interruption.
Size and Geometry Constraints
The horizontal chamber, especially in tube furnaces, can limit the size and shape of the parts being processed. Very large, heavy, or awkwardly shaped components may be better suited for top-loading or pit furnace designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the specific process requirements and production goals.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A horizontal tube furnace offers the greatest process flexibility, precision, and atmospheric control for experimentation.
- If your primary focus is specialized component manufacturing: A horizontal batch furnace provides the process repeatability and quality control needed for aerospace, medical, or ceramic parts.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: You should evaluate if a continuous conveyor-style furnace would provide better throughput and efficiency than a batch process.
Ultimately, the right furnace is the one that reliably and repeatably achieves the material properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Materials Science & Research | Experimentation with alloys, polymers, composites |
| Metallurgy & Powder Metallurgy | Sintering, annealing of metal powders |
| Ceramics & Glass Processing | High-temperature firing for durable components |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | CVD for thin film deposition |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Heat treatment of high-strength parts |
Leverage KINTEK's exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing for advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior material properties!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















