At its core, the choice between Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is dictated by the material's starting state and the desired final compound. PVD is overwhelmingly used for depositing pure metals and simple dielectrics that start from a solid target. In contrast, CVD is the superior method for creating complex compound films like oxides, nitrides, and carbides from reactive precursor gases.
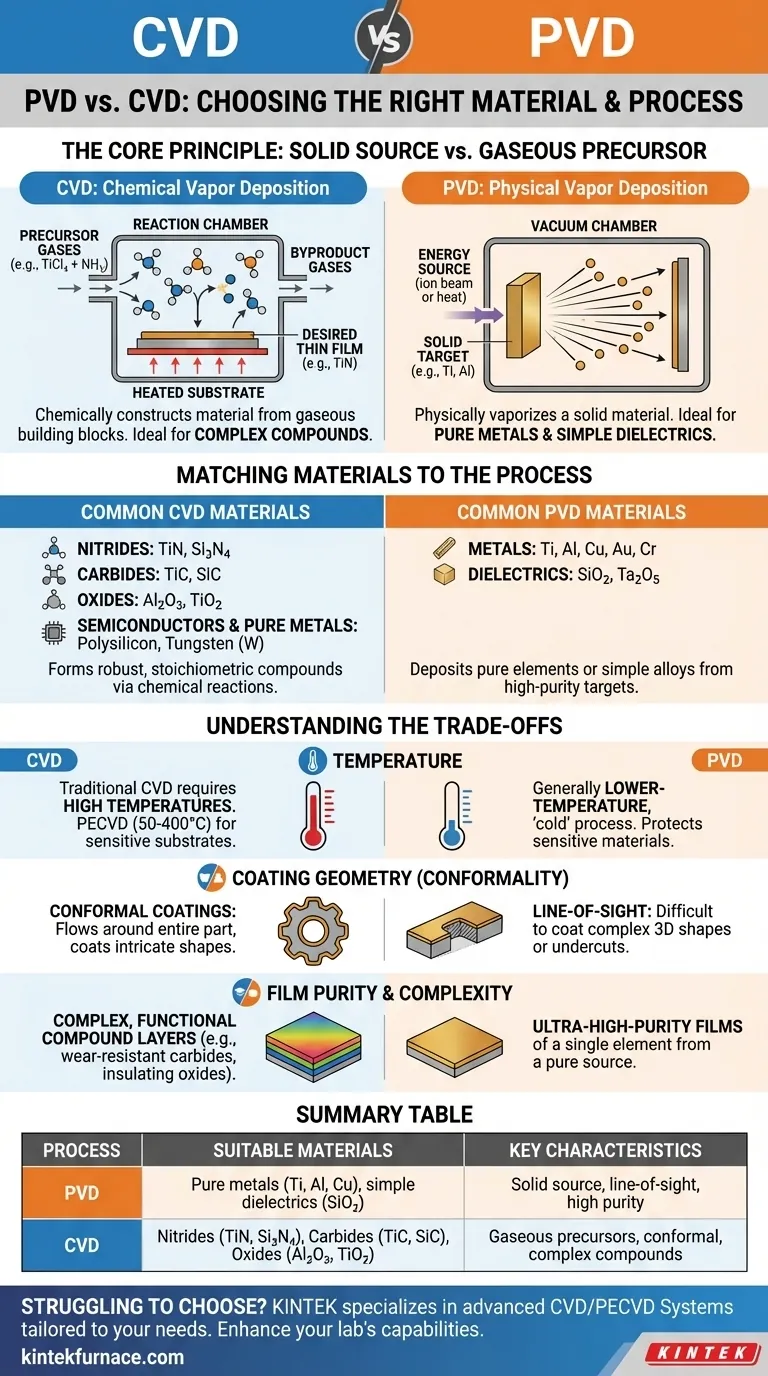
The fundamental difference is not just what you deposit, but how you source it. PVD physically vaporizes a solid material, while CVD chemically constructs a material from gaseous building blocks. This distinction governs which materials are suitable for each process.
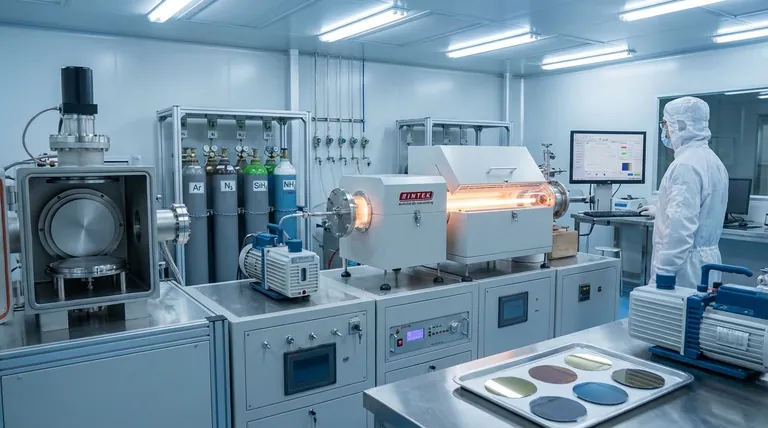

The Core Principle: Solid Source vs. Gaseous Precursor
The suitability of a material for PVD or CVD comes down to the fundamental mechanism of each process. They are not interchangeable; each is designed around a different state of matter.
How PVD Works (Physical Deposition)
In PVD, the material you want to deposit begins as a high-purity solid target. This target is bombarded with energy (e.g., ions in sputtering or heat in evaporation) inside a vacuum chamber.
This energy physically dislodges or "vaporizes" atoms from the solid target, which then travel in a straight line to coat the substrate. This makes PVD ideal for depositing materials that are stable and available in a solid form.
How CVD Works (Chemical Reaction)
CVD, on the other hand, does not use a solid target. Instead, it introduces specific precursor gases into a reaction chamber containing the substrate.
When these gases are heated, they react and decompose on the substrate's surface, forming the desired solid thin film. The byproduct gases are then pumped out. This process allows for the creation of highly specific chemical compounds that may be difficult or impossible to produce as a solid PVD target.
Matching Materials to the Process
Based on this core principle, the list of suitable materials for each technique becomes clear and logical.
Common PVD Materials
PVD is the go-to process for depositing pure elements or simple alloys.
- Metals: Titanium (Ti), Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), Gold (Au), Chromium (Cr)
- Dielectrics: Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂), Tantalum Pentoxide (Ta₂O₅)
These materials work well because they can be manufactured into high-purity solid targets, and their direct deposition preserves that purity in the final film.
Common CVD Materials
CVD's strength is in forming robust, stoichiometric compounds. It is exceptionally versatile due to the wide range of available precursor chemicals.
- Nitrides: Titanium Nitride (TiN), Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
- Carbides: Titanium Carbide (TiC), Silicon Carbide (SiC)
- Oxides: Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂)
- Semiconductors & Pure Metals: Polysilicon, Tungsten (W)
For example, to create a Titanium Nitride (TiN) film with CVD, one might use Titanium Tetrachloride (TiCl₄) and Ammonia (NH₃) as precursor gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a process is about more than just the material; it involves balancing temperature, geometry, and film properties.
Temperature Limitations
Traditional CVD requires very high temperatures to drive the chemical reactions, which can damage sensitive substrates like plastics or certain alloys.
PVD is generally a lower-temperature, "cold" process. For temperature-sensitive applications requiring a CVD-type film, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is an option that uses plasma to enable reactions at much lower temperatures (50°C to 400°C).
Coating Geometry (Conformality)
This is a critical distinction. PVD is a line-of-sight process. The vaporized material travels in a straight line, making it difficult to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or internal surfaces.
CVD excels at conformal coatings. Because the precursor gas flows around the entire part, it can deposit a uniform film on even the most intricate geometries.
Film Purity and Complexity
PVD is unmatched for creating ultra-high-purity films of a single element, as you are directly transferring atoms from a pure source.
CVD is superior for creating specific, complex, and functional compound layers like wear-resistant carbides or insulating oxides, where precise chemical composition is the goal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary technical objective.
- If your primary focus is a high-purity metal film on a simple surface: PVD is the most direct and effective method.
- If your primary focus is a hard, wear-resistant compound coating like a nitride or carbide: CVD is the standard industry choice.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D part with a uniform layer: CVD's excellent conformality makes it the superior technology.
- If your primary focus is depositing on a temperature-sensitive substrate: PVD or a low-temperature variant like PECVD is necessary to prevent damage.
Ultimately, understanding whether your desired film is best built from a solid source or gaseous precursors is the key to selecting the right deposition technology.
Summary Table:
| Process | Suitable Materials | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| PVD | Pure metals (e.g., Ti, Al, Cu), simple dielectrics (e.g., SiO₂) | Solid source, line-of-sight deposition, high purity |
| CVD | Nitrides (e.g., TiN, Si₃N₄), carbides (e.g., TiC, SiC), oxides (e.g., Al₂O₃, TiO₂) | Gaseous precursors, conformal coatings, complex compounds |
Struggling to choose the right deposition process for your materials? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique needs. Our expert R&D and in-house manufacturing ensure precise, efficient coatings for metals, nitrides, carbides, and more. Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities—contact us today to discuss customized solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is plasma-deposited silicon nitride, and what are its properties? Discover Its Role in Solar Cell Efficiency
- What are the drawbacks of CVD compared to PECVD? Key Limitations for Your Lab
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties



















