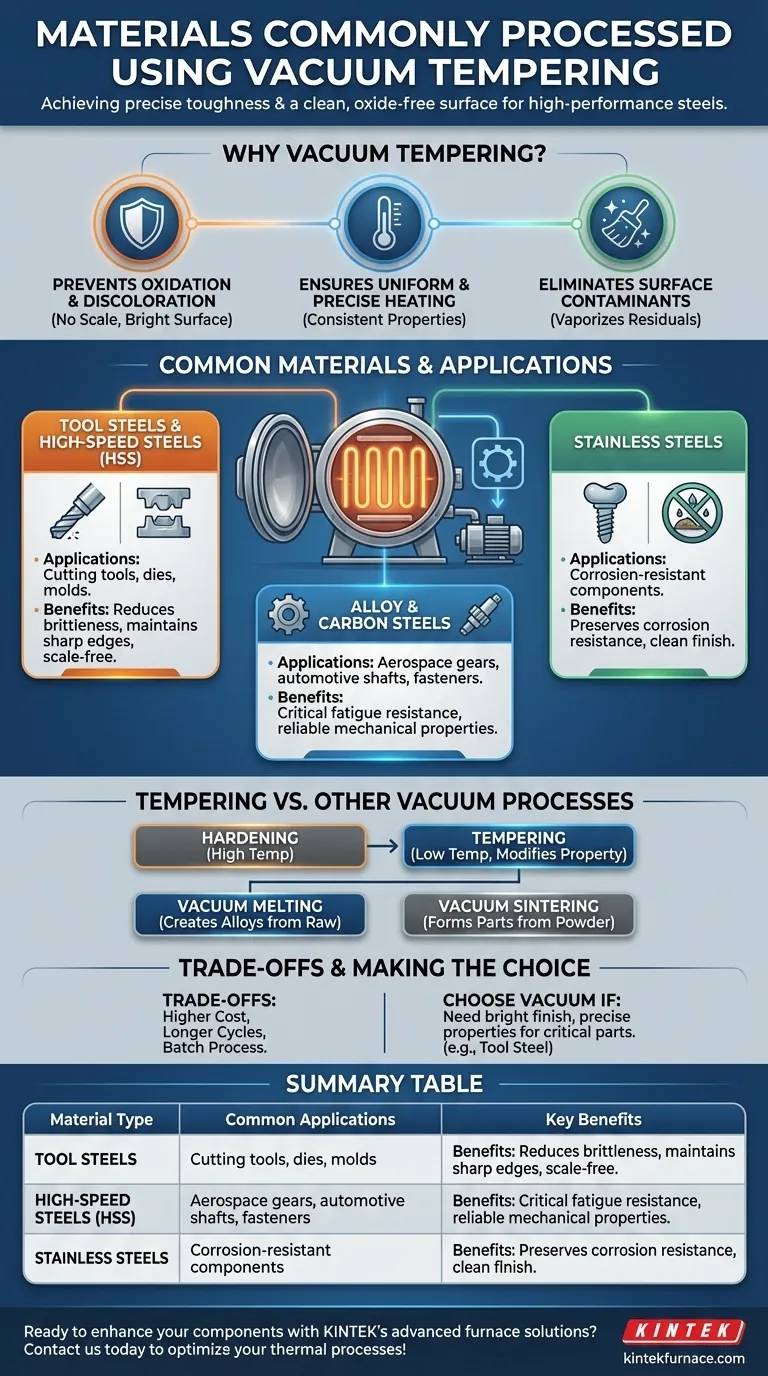
In essence, vacuum tempering is predominantly used for high-performance steels that have already undergone a hardening process. This includes a range of tool steels, high-speed steels (HSS), and specific alloy or carbon steels where surface integrity and precise mechanical properties are critical. The vacuum environment is not just a medium; it is an active part of the process that ensures the final component meets exacting standards.
The core purpose of using a vacuum for tempering is not about the material itself, but about the desired outcome: achieving precise toughness and hardness in a finished part while producing an exceptionally clean, bright, and oxide-free surface.

Why Use a Vacuum for Tempering?
Understanding the "why" behind vacuum tempering reveals its value for high-specification components. The process is chosen for the unique advantages the vacuum environment provides over a traditional atmospheric furnace.
Preventing Oxidation and Discoloration
The primary benefit of a vacuum is the removal of oxygen. In a conventional furnace, oxygen reacts with the hot metal surface to form a layer of oxide, or "scale."
This scale is undesirable as it changes the part's dimensions, dulls its appearance, and often must be removed through costly secondary operations like sandblasting or chemical cleaning. Vacuum tempering prevents this entirely, resulting in a bright, clean surface straight from the furnace.
Ensuring Uniform and Precise Heating
Vacuum furnaces provide extremely uniform heating, typically through convection using an injected inert gas like nitrogen. This uniformity is critical during tempering.
Precise temperature control across the entire part ensures that the desired hardness and toughness are achieved consistently, eliminating weak spots and guaranteeing predictable mechanical performance.
Eliminating Surface Contaminants
The vacuum itself can help purify the workload. The process can begin with a "bake-out" cycle at a low temperature under vacuum.
This helps vaporize and remove residual oils, cleaning fluids, or other surface contaminants left over from manufacturing, a process sometimes called degreasing.
Common Materials and Their Applications
While many metals can be treated in a vacuum, the process is reserved for materials where the benefits justify the cost.
Tool Steels and High-Speed Steels (HSS)
These are the most common materials for vacuum tempering. Parts like cutting tools, dies, and molds are hardened to be extremely hard but are also brittle.
Tempering reduces this brittleness to achieve the required toughness. A clean, scale-free surface is essential for a cutting edge or a molding surface, making the vacuum process ideal.
Alloy and Carbon Steels
High-strength alloy and carbon steels used in critical applications benefit greatly from vacuum tempering.
Components for the aerospace, automotive, or medical industries—such as gears, shafts, and high-strength fasteners—require precise mechanical properties and perfect surface condition to ensure reliability and fatigue resistance.
Stainless Steels
For stainless steel parts, maintaining corrosion resistance is paramount. Traditional tempering can cause unwanted changes to the surface chemistry that degrade this property.
Vacuum tempering protects the surface and ensures the material retains its full "stainless" characteristics after heat treatment.
Tempering vs. Other Vacuum Processes
The term "vacuum furnace" is broad. It is crucial to distinguish tempering from other high-temperature vacuum processes that are used for entirely different purposes.
Tempering vs. Hardening
Tempering is a relatively low-temperature (e.g., 200–650°C) process that follows a high-temperature hardening (austenitizing and quenching) step. Its purpose is to reduce brittleness and increase toughness in a hardened part.
Tempering vs. Vacuum Melting
Vacuum melting is a primary production method, not a secondary heat treatment. It involves melting metals in a vacuum to remove dissolved gases and impurities, creating ultra-pure, high-performance alloys.
Tempering vs. Vacuum Sintering
Sintering is a process used to consolidate and densify powdered materials (like ceramics, composites, or metal powders) into a solid part. It is a material formation process, whereas tempering is a property modification process for an already-solid part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum tempering is not a universal solution. Its selection involves clear trade-offs.
Higher Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to purchase and operate than their atmospheric counterparts. The process cycles are also longer due to the time required to pump the chamber down to the required vacuum level.
Not Necessary for All Applications
For many general-purpose steel parts where a perfect surface finish is not required and slight variations in hardness are acceptable, a conventional air furnace is far more cost-effective. The scale can simply be cleaned off later.
Batch Processing Limitations
Vacuum furnaces are inherently batch-processing systems. This can be less efficient for extremely high-volume, continuous production compared to certain conveyor-style atmospheric furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct process depends entirely on the material and the intended outcome for the final part.
- If your primary focus is a bright, scale-free finish on hardened tool steel parts: Vacuum tempering is the ideal choice to prevent oxidation and eliminate post-processing cleaning.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective heat treatment for non-critical carbon steel components: A conventional atmospheric furnace is likely more than sufficient and far more economical.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid component from metal or ceramic powder: You are looking for a forming process like vacuum sintering or hot pressing, not tempering.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity metal alloys from raw materials: The correct process is vacuum induction melting (VIM) or a similar primary melting technology.
Ultimately, understanding the specific goal of your thermal process—whether modifying properties, forming a part, or purifying a melt—is the key to selecting the correct vacuum technology.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Tool Steels & High-Speed Steels (HSS) | Cutting tools, dies, molds | Scale-free surface, enhanced toughness, precise hardness |
| Alloy & Carbon Steels | Aerospace gears, automotive shafts, medical fasteners | Improved fatigue resistance, reliable mechanical properties |
| Stainless Steels | Corrosion-resistant components | Maintained corrosion resistance, clean surface finish |
Ready to enhance your high-performance components with precise vacuum tempering? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored for industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your thermal processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using a vacuum drying oven? Superior High-Entropy Ceramic Slurry Treatment
- Why is a vacuum drying oven essential for LLTO solid electrolytes? Ensure High-Purity Battery Material Processing
- How does a high-temperature vacuum contact angle system study Al 7075 alloys? Mastering Surface Tension & Oxidation
- What factors are critical for successful vacuum brazing? Master Joint Strength and Clean Bonds
- Why is the vacuum-assisted impregnation process necessary for UHTCMCs? Achieve Superior Composite Density
- Which industries commonly use furnace brazing? Discover Key Applications for High-Strength Joining
- How does high-temperature vacuum processing improve phosphor ceramics? Boost Thermal Stability in High-Power Lasers
- How do vacuum gas quenching furnaces operate? Master Precise Heat Treatment for Superior Materials



















