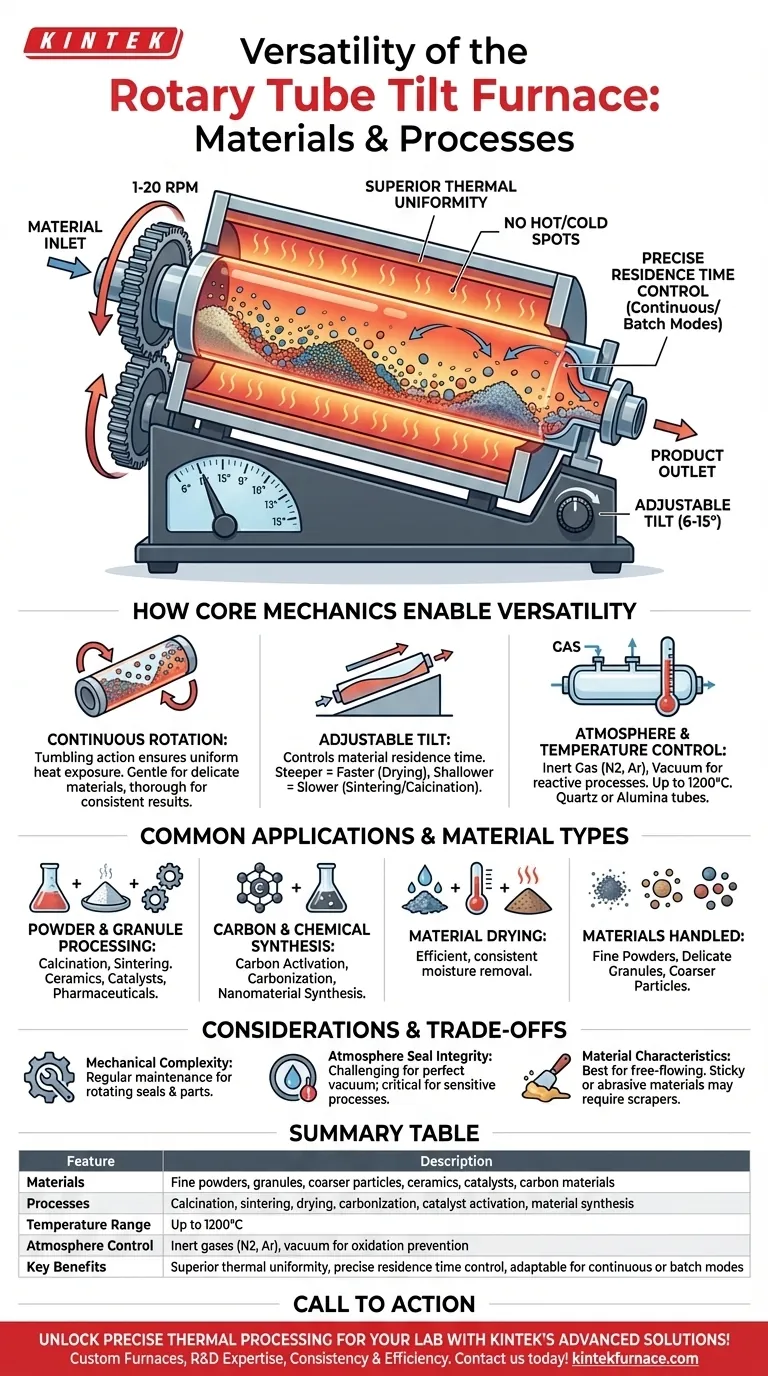
At its core, a Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace is designed for exceptional versatility in thermal processing. It can accommodate a wide spectrum of particulate materials, from fine powders and delicate granules to coarser particles. The furnace is suitable for a range of processes, including calcination, sintering, material drying, carbonization, and both catalyst and carbon activation.
The furnace's true value lies not just in the materials it can handle, but in how it controls the process. By combining slow, continuous rotation with an adjustable tilt angle, it achieves superior thermal uniformity and precise control over material residence time, making it adaptable to a vast range of applications where consistency is critical.

How Core Mechanics Enable Versatility
The furnace's capabilities stem directly from its unique mechanical design. Understanding these principles is key to determining if it fits your specific application.
Continuous Rotation for Thermal Uniformity
The slow, continuous rotation of the process tube is the most critical feature. As the tube turns, it constantly tumbles the material inside.
This action ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source, eliminating the hot and cold spots common in static furnaces. The low speed range (typically 1-20 RPM) is gentle enough for delicate materials while providing the thorough mixing needed for consistent results.
Adjustable Tilt for Flow and Time Control
The ability to tilt the entire furnace assembly (from 6-15 degrees) gives you direct control over the material's residence time—how long it spends in the heated zone.
A steeper angle results in a faster throughput, ideal for continuous drying processes. A shallower angle increases the residence time, which is necessary for processes like sintering or calcination that require prolonged, stable heat. This feature allows for both continuous and batch production modes.
Atmosphere Control for Reactive Processes
These furnaces are designed to operate under specific atmospheric conditions. They can be purged with inert gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation or can operate under a vacuum.
This capability is essential for sensitive applications such as catalyst activation, synthesizing air-sensitive materials, or specific metallurgical processes where the surrounding atmosphere is a critical reaction parameter.
Temperature Range and Material Compatibility
With a typical maximum temperature of 1200°C, the furnace can handle the vast majority of industrial heat treatment applications.
The process tube itself can be made from different materials, such as quartz or alumina, allowing you to select the best option based on your material's reactivity and required processing temperature.
Common Applications and Material Types
The combination of these features makes the furnace a workhorse in many industries.
Powder and Granule Processing
This is the most common use case. The furnace excels at processes like calcination, where materials are heated to drive off volatile substances, and sintering, where fine powders are heated to form a solid, coherent mass. It is widely used for ceramics, catalysts, and pharmaceutical powders.
Carbon and Chemical Synthesis
The precise temperature and atmosphere control are ideal for carbon activation and carbonization. It is also used for the thermal treatment of various chemicals, enabling controlled reactions for material synthesis, including the production of nanomaterials.
Material Drying
The continuous flow and uniform heat exposure make the furnace highly efficient for drying powders and granules. The tilting function facilitates a steady, first-in-first-out flow of material, ensuring consistent final moisture content.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly versatile, this furnace design comes with specific considerations that may influence your decision.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The rotating and tilting mechanisms introduce more moving parts compared to a static box furnace. These components, particularly the rotating seals, require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure reliable, long-term operation.
Atmosphere Seal Integrity
Maintaining a perfect vacuum or a highly pure gas atmosphere can be more challenging with a rotating tube than in a static system. The quality and condition of the rotary seals are paramount for processes that are highly sensitive to atmospheric contamination.
Material Characteristics
While versatile, the furnace works best with free-flowing powders and granules. Materials that are extremely sticky, prone to agglomeration, or highly abrasive can present challenges. Features like internal scraper bars can help manage sticking, but highly abrasive materials may cause premature wear on the process tube.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right equipment requires matching its capabilities to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is process uniformity for powders: The combination of rotation and tilt is ideal for eliminating thermal gradients and ensuring every particle receives identical treatment.
- If your primary focus is R&D or process flexibility: The ability to easily adjust residence time, temperature, and atmosphere makes this furnace an excellent tool for developing and optimizing new thermal processes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, single-product manufacturing: You should carefully evaluate if the furnace's throughput meets your needs compared to a larger, dedicated industrial kiln designed for massive scale.
By matching the furnace's dynamic controls to your specific material and thermal goals, you can unlock highly consistent and efficient processing results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Materials | Fine powders, granules, coarser particles, ceramics, catalysts, carbon materials |
| Processes | Calcination, sintering, drying, carbonization, catalyst activation, material synthesis |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1200°C |
| Atmosphere Control | Inert gases (nitrogen, argon), vacuum for oxidation prevention |
| Key Benefits | Superior thermal uniformity, precise residence time control, adaptable to continuous or batch modes |
Unlock precise thermal processing for your lab with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Rotary Tube Tilt Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental needs are met with consistency and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your material processing and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is the Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace used in the carbon activation process? Achieve Uniform, High-Porosity Activated Carbon
- In what environments are rotary tube furnaces considered indispensable? Essential for Uniform Thermal Processing
- What are the key components of a rotary tube furnace? Essential Parts for Uniform Heating
- What materials are rotary tube furnaces typically constructed from? Choose the Right Tube for Your Process
- What makes rotary tube furnaces user-friendly? Achieve Superior Process Uniformity and Efficiency



















