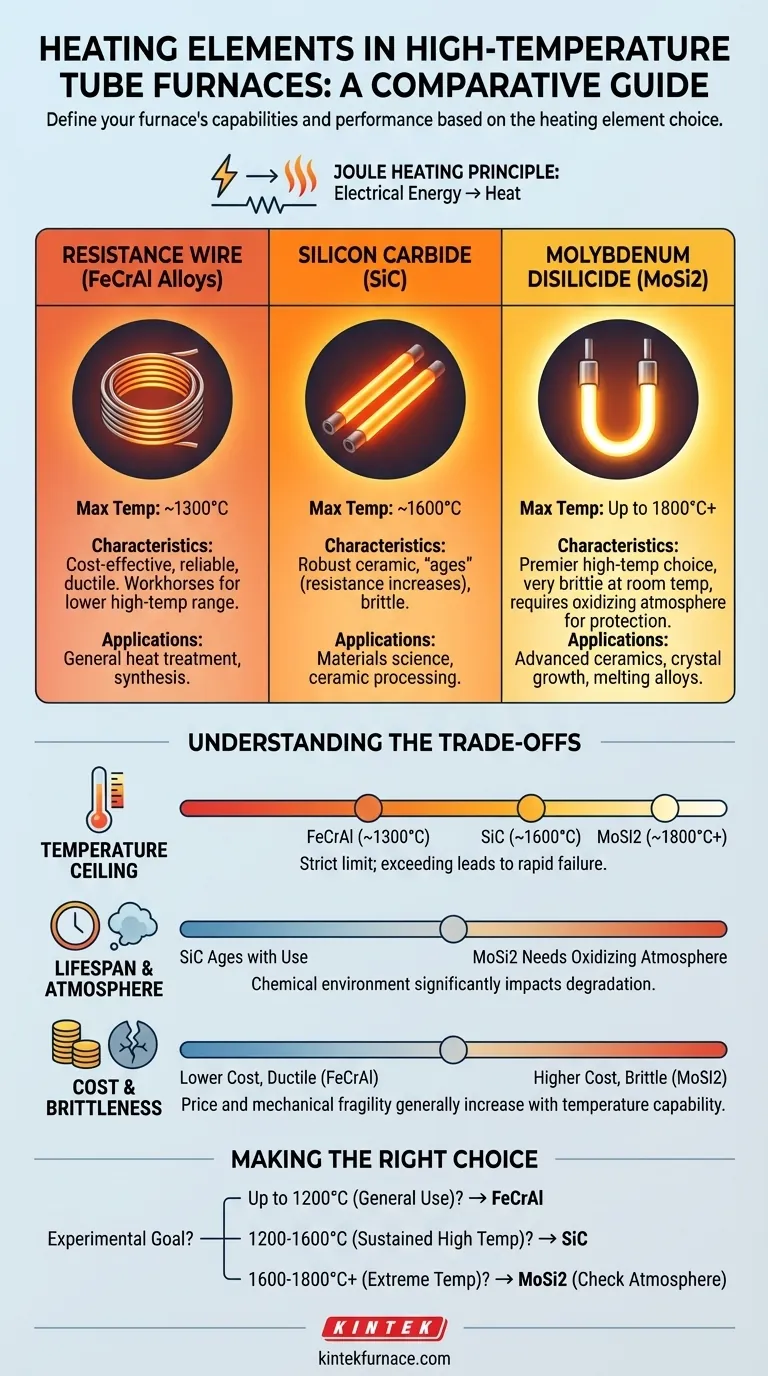
In high-temperature tube furnaces, the primary types of heating elements used are metallic resistance wires, silicon carbide (SiC), and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2). Each material is selected based on its maximum operating temperature and chemical stability, directly defining the furnace's capabilities and intended applications.
The choice of heating element is the single most important factor determining a tube furnace's performance. Your decision hinges on a fundamental trade-off between the maximum temperature you need to achieve, the chemical atmosphere you will use, and the overall cost.
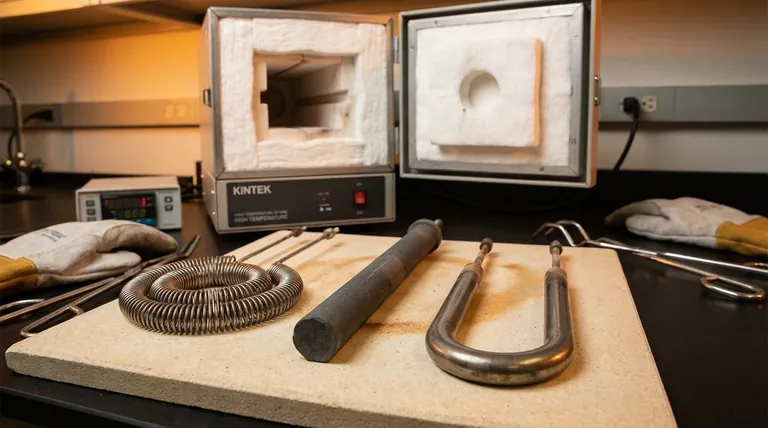

How Resistance Heating Works
All of these elements operate on the simple principle of Joule heating. When an electric current is passed through a material with electrical resistance, the electrical energy is converted into heat.
The key difference between element types is the material's ability to withstand extreme temperatures without melting or degrading, while efficiently radiating that heat to the furnace chamber and your sample.
A Breakdown of High-Temperature Heating Elements
The three main types of elements form a clear hierarchy based on temperature capability.
Resistance Wire (e.g., FeCrAl Alloys)
These are coiled wires, often made from an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy like Kanthal. They are the workhorses for the lower end of the high-temperature spectrum.
These elements are typically used for applications requiring temperatures up to approximately 1200-1300°C. They are known for their reliability and cost-effectiveness in this range.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements
Silicon carbide elements are robust ceramic components, usually formed into rods or spirals. They represent the mid-range solution for higher-temperature processes.
SiC elements are capable of stable operation at temperatures up to 1600°C. They offer a significant step up from metallic wires and are widely used in materials science and ceramic processing.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Elements
These are the premier elements for achieving the highest possible temperatures in a tube furnace. They are cermet materials, combining ceramic and metallic properties, and are often bent into a "U" shape.
MoSi2 elements can operate reliably at extreme temperatures, often up to 1800°C or even higher. They are essential for research involving advanced ceramics, crystal growth, and melting high-temperature alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace isn't just about picking the highest temperature; it's about understanding the compromises involved with each element technology.
The Temperature Ceiling
The maximum operating temperature is the most rigid constraint. Using an element above its recommended limit will lead to rapid failure.
- FeCrAl: Limited to ~1300°C.
- SiC: A strong performer up to 1600°C.
- MoSi2: The only choice for work above 1600°C.
Element Lifespan and Atmosphere
Heating elements degrade over time, and the chemical environment plays a major role.
SiC elements "age" as their electrical resistance gradually increases with use, eventually requiring more voltage to reach the target temperature.
MoSi2 elements rely on an oxidizing atmosphere (like air) to form a protective glassy layer of silica (SiO2). In reducing atmospheres, this protection cannot form, drastically limiting their performance and lifespan.
Cost and Brittleness
Cost and mechanical properties vary significantly. The price of the elements, and therefore the furnace, generally increases with temperature capability.
Resistance wires are ductile and inexpensive. SiC is harder and more brittle. MoSi2 is notoriously brittle at room temperature, requiring careful handling during installation and maintenance, but it becomes ductile at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated by the specific requirements of your experimental or production goals.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment or synthesis up to 1200°C: A furnace with resistance wire elements is the most economical and reliable choice.
- If your work requires sustained temperatures between 1200°C and 1600°C: A furnace with Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements provides the necessary capability and robust performance.
- If your research demands the highest temperatures, from 1600°C to 1800°C: A furnace with Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements is essential, provided your process is compatible with its atmospheric requirements.
By understanding the distinct capabilities of each heating element, you can confidently select the right tool for your specific scientific objective.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element | Max Temperature | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| FeCrAl Alloys | Up to 1300°C | Cost-effective, reliable, ductile | General heat treatment, synthesis |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | Robust, ages with use, brittle | Materials science, ceramic processing |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Up to 1800°C | Brittle at room temp, requires oxidizing atmosphere | Advanced ceramics, crystal growth |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored heating elements can enhance your research and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















