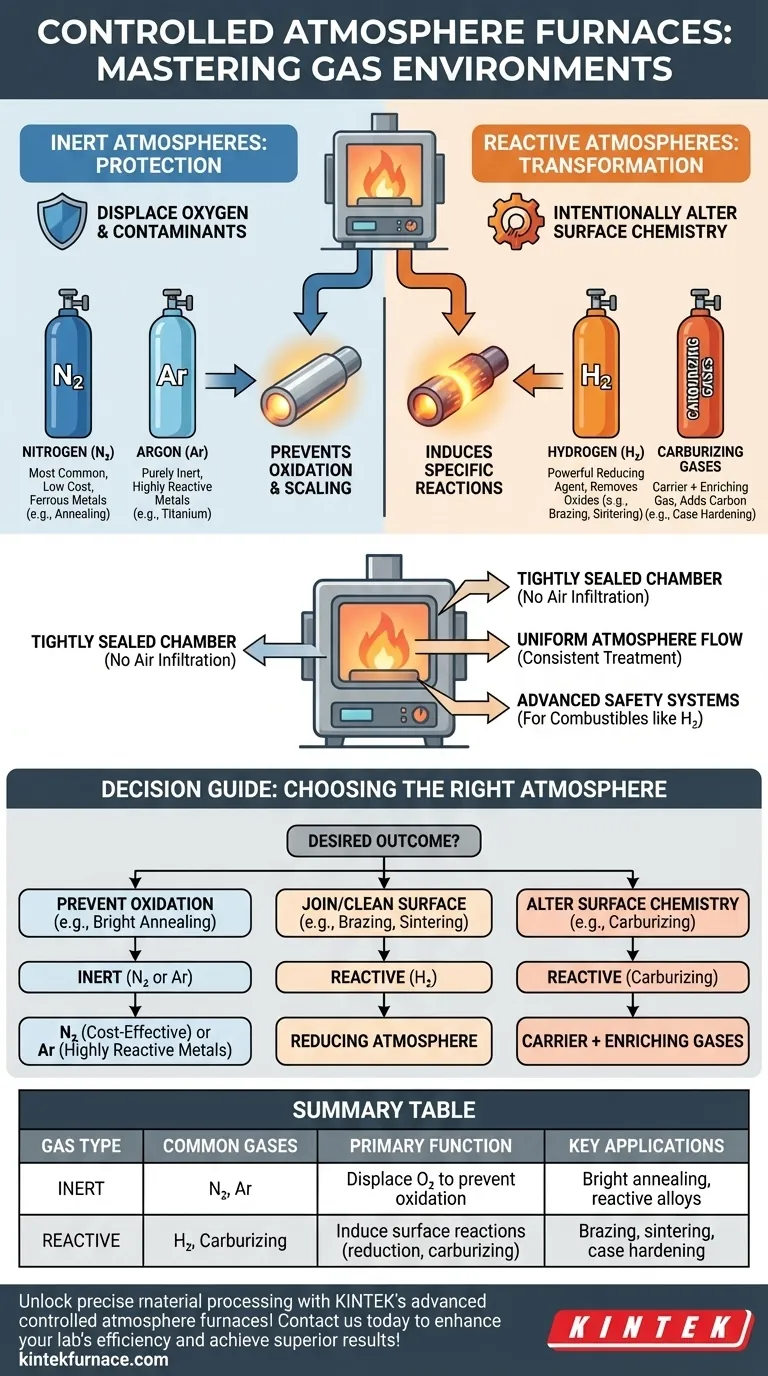
At its core, a controlled atmosphere furnace is engineered to handle two distinct categories of gases: inert and reactive. This allows it to either protect a material from chemical changes or intentionally induce specific reactions on its surface. The most common inert gases are Nitrogen (N₂) and Argon (Ar), while the primary reactive gas used is Hydrogen (H₂).
The purpose of a controlled atmosphere is not just to heat a material, but to actively manage its chemical environment. The gas you choose directly determines whether you are protecting the material from change (inert) or intentionally causing a specific chemical reaction on its surface.

The Role of the Atmosphere: Protection vs. Reaction
The choice of gas is dictated entirely by the desired outcome of the heat-treating process. The atmosphere can be a passive shield or an active participant.
Inert Atmospheres for Protection
An inert atmosphere's primary job is to displace oxygen and other atmospheric contaminants like water vapor. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and scaling during high-temperature processing.
Nitrogen (N₂) is the most widely used inert atmosphere due to its effectiveness and relatively low cost. It is suitable for most ferrous metals in processes like neutral hardening and annealing.
Argon (Ar) is a more purely inert gas than nitrogen. It is used for materials that can react with nitrogen at high temperatures, such as titanium, certain stainless steels, and other highly reactive alloys.
Reactive Atmospheres for Transformation
A reactive atmosphere is used when the goal is to intentionally alter the surface chemistry of the material. These gases actively participate in the process.
Hydrogen (H₂) is a powerful reducing agent. It is used to remove oxides from a material's surface, which is critical for processes like brazing and sintering to ensure clean, strong metallurgical bonds.
Carburizing atmospheres are another common reactive type. These typically use an inert "carrier gas" (like nitrogen) mixed with an "enriching gas" (like natural gas or propane) to precisely add carbon to the surface of steel, a process known as case hardening.
Essential Furnace Design for Gas Control
To handle these gases effectively and safely, a controlled atmosphere furnace must have several key design features.
Ensuring Atmosphere Purity
The furnace chamber must be tightly sealed. Any infiltration of outside air would contaminate the controlled atmosphere, introducing oxygen and compromising the entire process.
Achieving Uniform Treatment
A well-designed furnace provides uniform atmosphere flow. This ensures that every surface of the part is exposed to the same gas concentration, leading to consistent and predictable results across an entire batch.
Handling Hazardous Conditions
Heating elements must be durable and designed to operate in the specific atmosphere without degrading. Most importantly, when using combustible gases like hydrogen, the furnace requires advanced safety systems, including explosion protection devices and gas monitoring, to prevent dangerous situations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a gas is not just a technical decision; it involves balancing cost, safety, and process requirements.
Cost: Nitrogen vs. Argon
Nitrogen is significantly less expensive than argon. For this reason, it is the default choice unless a material specifically reacts with it at process temperatures.
Safety: Inert vs. Hydrogen
Inert gases like nitrogen and argon are relatively safe and easy to handle. Hydrogen, however, is highly flammable and requires specialized storage, delivery systems, and extensive furnace safety features, adding significant cost and complexity.
Process Specificity
The material and the process dictate the gas. You cannot substitute an inert gas when a reducing atmosphere is required for brazing, nor can you use hydrogen when simply trying to prevent oxidation on a standard steel part.
Choosing the Right Atmosphere for Your Process
Your final choice depends entirely on what you need to accomplish with the material.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation and scaling (e.g., bright annealing): An inert atmosphere using Nitrogen is your most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is joining components or removing surface oxides (e.g., brazing, sintering): A reactive, reducing atmosphere containing Hydrogen is necessary to ensure clean, strong bonds.
- If your primary focus is altering the surface chemistry (e.g., carburizing): You need a reactive atmosphere composed of specific carrier and enriching gases to add carbon to the material.
- If you are processing highly reactive metals (e.g., titanium, certain tool steels): A pure inert atmosphere using more expensive Argon is required to prevent unwanted reactions.
Understanding the function of each gas empowers you to select the precise atmospheric conditions needed to achieve your desired material properties.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Common Gases | Primary Function | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | Displace oxygen to prevent oxidation and scaling | Bright annealing, processing reactive alloys |
| Reactive | Hydrogen (H₂), Carburizing gases | Induce surface reactions like reduction or carburizing | Brazing, sintering, case hardening |
Unlock precise material processing with KINTEK's advanced controlled atmosphere furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental requirements are met with high-temperature furnace excellence. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















