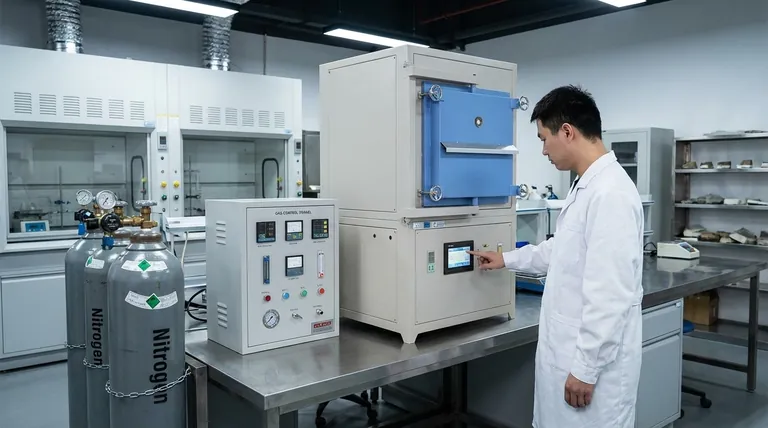
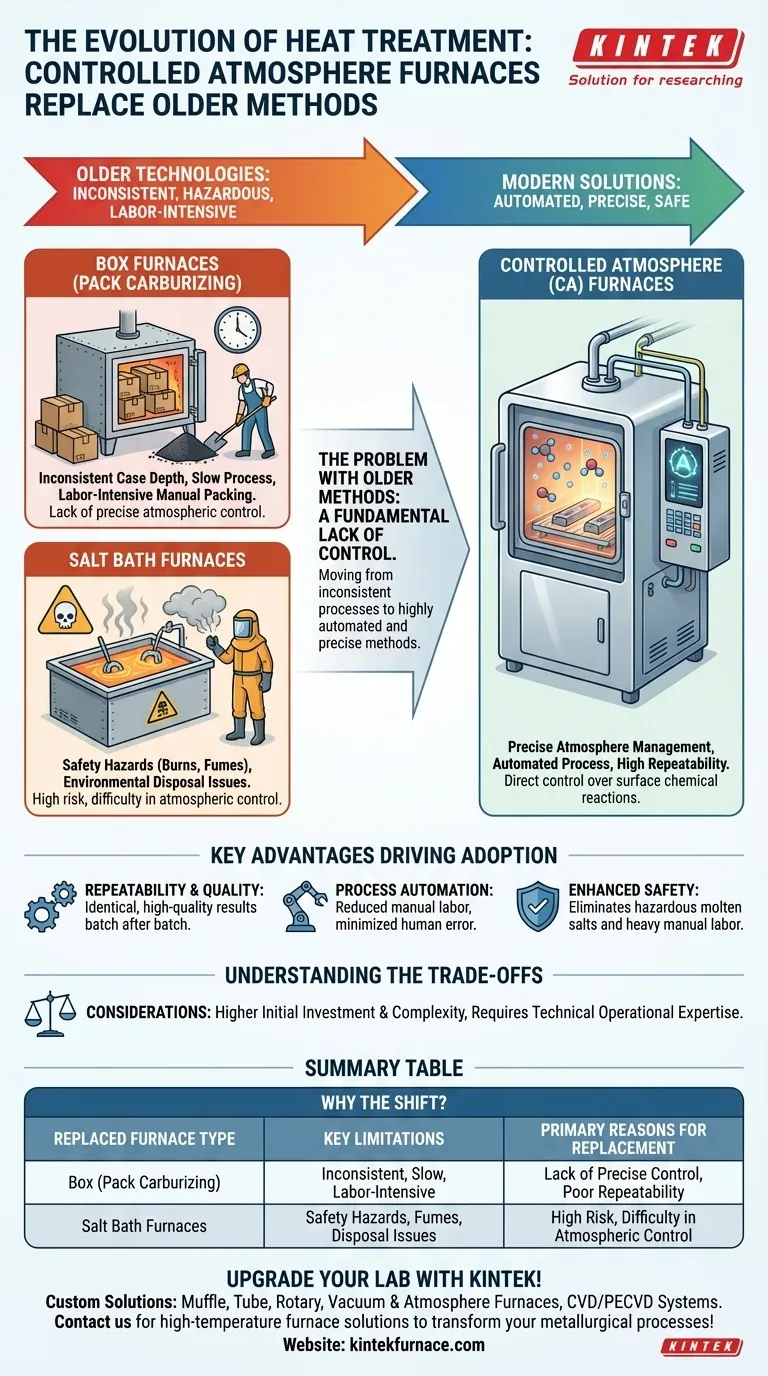
In modern metallurgy, controlled atmosphere (CA) furnaces have almost entirely superseded older, less precise methods of heat treatment. They have largely replaced traditional box furnaces, particularly those used for pack carburizing, and salt bath furnaces due to their superior control, safety, and repeatability.
The core reason for this technological shift is the move from inconsistent, hazardous, and labor-intensive processes to a highly automated and precise method. Controlled atmosphere technology gives engineers direct control over the chemical reactions happening on a part's surface, a capability older methods could never reliably offer.

The Problem with Older Furnace Technologies
To understand why controlled atmosphere furnaces became dominant, it’s essential to recognize the significant drawbacks of the technologies they replaced. These older methods were effective for their time but suffered from a fundamental lack of control.
The Limitations of Box (Pack Carburizing) Furnaces
Pack carburizing involves packing steel parts into a sealed box filled with a solid, carbon-rich compound. The entire box is then heated for a long period, allowing carbon to diffuse into the parts' surface.
This process is notoriously difficult to control. The results were often non-uniform, with inconsistent case depths across a single part and from batch to batch. It was also extremely slow and labor-intensive, requiring manual packing and unpacking of the heavy boxes.
The Hazards and Inconsistencies of Salt Bath Furnaces
Salt bath furnaces involve immersing parts directly into a bath of molten salt heated to a specific temperature. While offering faster heating than pack carburizing, this method presents its own set of challenges.
The primary issue is safety. Molten salts are incredibly hazardous, posing risks of severe burns from splashes. Many salt mixtures also produce toxic fumes. Furthermore, disposing of the used, often contaminated, salt creates a significant environmental and cost burden. While offering better temperature uniformity, precise atmospheric control was still difficult to achieve.
The Rise of Controlled Atmosphere Furnaces
CA furnaces solved the core problems of consistency, safety, and control that plagued earlier methods. Their design is centered around one key principle: precisely managing the gas surrounding the parts during the entire thermal cycle.
Principle of Operation: Precision and Control
A CA furnace is an enclosed, sealed chamber where the internal atmosphere is replaced with a specific mixture of gases. This atmosphere can be tailored to achieve a desired outcome.
For example, an endothermic gas rich in carbon monoxide and hydrogen can be used to add a specific amount of carbon to a steel's surface (carburizing) with incredible precision. A nitrogen-based atmosphere can be used to prevent oxidation and discoloration during annealing, ensuring a bright, clean finish.
Key Advantages Driving Adoption
The shift to CA furnaces was driven by three main advantages:
- Repeatability and Quality: By precisely controlling gas composition, temperature, and time, CA furnaces produce identical, high-quality results batch after batch.
- Process Automation: These systems are easily automated, reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing the potential for human error.
- Enhanced Safety: They eliminate the direct handling of molten salts and the heavy manual labor of pack carburizing, creating a much safer operating environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vastly superior, controlled atmosphere furnaces are not without their own considerations. They represent a more complex and technologically advanced solution.
Initial Investment and Complexity
CA furnaces carry a higher initial capital cost compared to a simple box or salt bath furnace. They require sophisticated control systems, including oxygen probes and gas analyzers, as well as the infrastructure for generating or storing the process gases.
Maintenance and Operational Expertise
Operating a CA furnace effectively requires a higher level of technical skill. Maintaining the integrity of furnace seals, calibrating sensors, and managing the gas supply system are critical for achieving the desired metallurgical results and ensuring safe operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Today, the decision is less about choosing between these technologies and more about understanding why controlled atmosphere processing is the default for high-quality thermal processing.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable production: Controlled atmosphere furnaces are the industry standard for their unmatched consistency and automation capabilities.
- If your primary focus is process precision and surface quality: The ability to finely tune the furnace atmosphere is the only way to guarantee specific case depths and prevent unwanted oxidation.
- If your primary focus is operator safety and environmental compliance: CA furnaces decisively eliminate the acute hazards and waste disposal challenges associated with salt baths and other older methods.
Ultimately, embracing controlled processes is essential for achieving the superior and predictable material properties required by modern engineering.
Summary Table:
| Replaced Furnace Type | Key Limitations | Primary Reasons for Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Box (Pack Carburizing) Furnaces | Inconsistent case depth, slow, labor-intensive | Lack of precise atmospheric control, poor repeatability |
| Salt Bath Furnaces | Safety hazards, toxic fumes, environmental disposal issues | High risk of burns, difficulty in atmospheric control |
Upgrade your lab's heat treatment capabilities with KINTEK's advanced controlled atmosphere furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing safety, repeatability, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can transform your metallurgical processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios



















