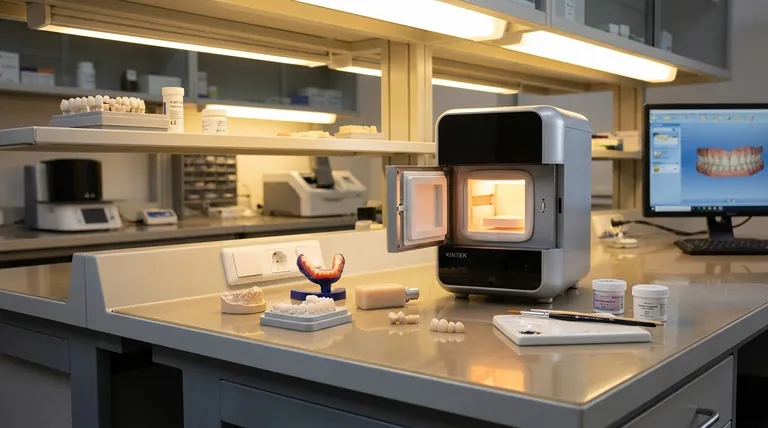
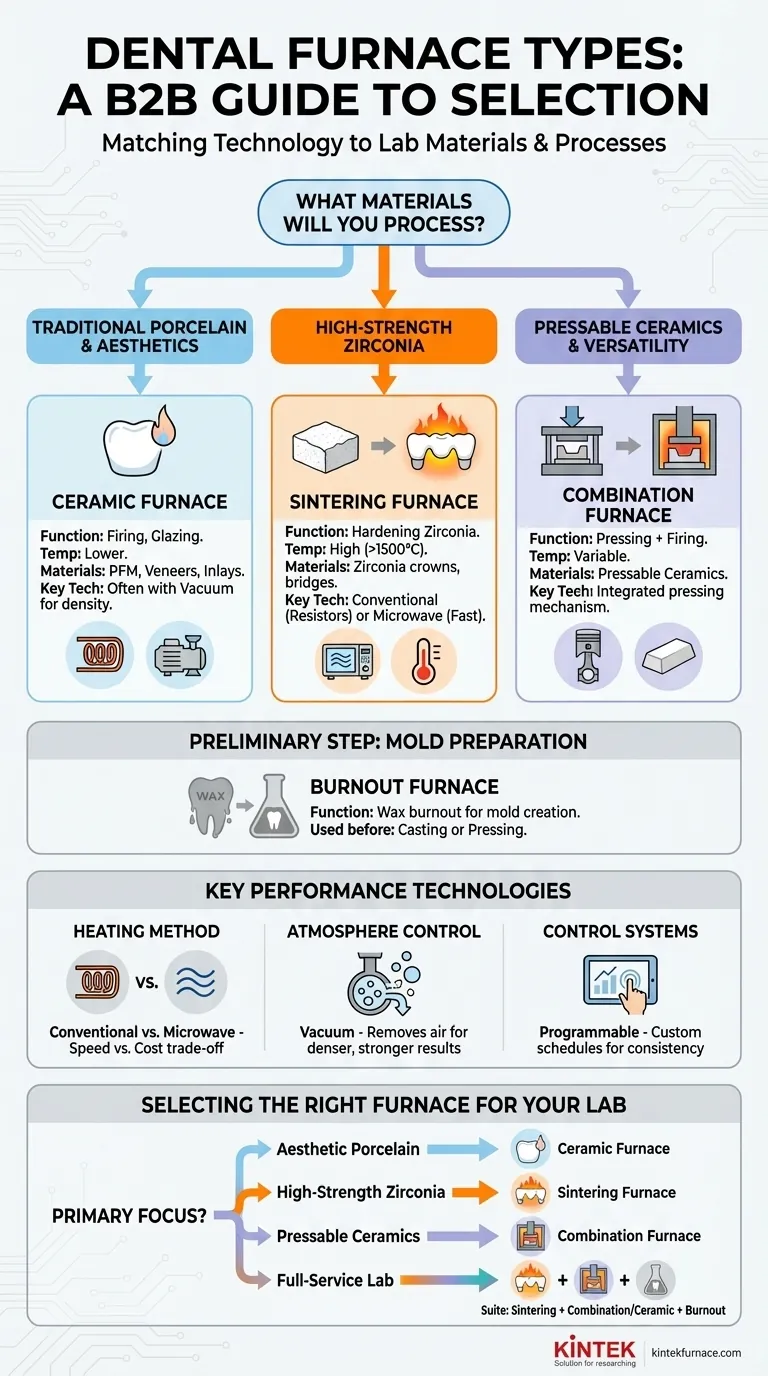
At a foundational level, dental furnaces are categorized by the materials they process and the thermal procedures they perform. The primary types are ceramic furnaces for traditional porcelain work, sintering furnaces for hardening modern materials like zirconia, and combination furnaces that merge firing and pressing functions for specific pressable ceramics. Each is designed for a distinct application within the dental restoration workflow.
The specific type of furnace a dental laboratory needs is not a matter of preference, but a direct consequence of the dental materials it intends to use. The choice between porcelain, zirconia, or pressable ceramics will dictate the required furnace technology.

The Core Furnace Types: A Functional Breakdown
Understanding each furnace begins with its specific role in creating a final dental restoration. The material dictates the necessary temperature, atmosphere, and process.
Ceramic Furnaces: For Porcelain and Aesthetics
A ceramic furnace is the traditional workhorse for firing conventional dental ceramics. These are used for restorations like porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crowns, veneers, and inlays.
They operate at lower temperatures compared to sintering units and use heating elements like Kanthal or Nichrome. Their primary functions are firing (to harden and fuse porcelain layers) and glazing (to create a smooth, glossy surface).
Sintering Furnaces: The Zirconia Powerhouse
Sintering furnaces are high-temperature specialists designed almost exclusively for processing zirconia. Zirconia is milled in a soft, chalk-like "green state" and must be sintered at extremely high temperatures (often above 1500°C) to achieve its final, high-strength form.
These units are essential for any lab producing zirconia crowns, bridges, or frameworks. They are incapable of handling the lower-temperature firing cycles required for conventional porcelains.
Combination Furnaces: Versatility for Pressable Ceramics
A combination furnace integrates the functions of a standard ceramic furnace with a pressing mechanism. This makes it ideal for working with pressable ceramics.
In this process, a wax pattern is replaced by a ceramic ingot that is heated and pressed into a mold. These furnaces can also perform the standard firing and glazing cycles of a regular ceramic furnace, offering valuable versatility in a smaller footprint.
Burnout Furnaces: Preparing the Mold
While sometimes grouped with the others, a burnout furnace serves a distinct preliminary step. Its purpose is to burn away a wax pattern, leaving behind a precise mold cavity in an investment material.
This mold is then used for either casting molten metal or for pressing ceramics in a combination furnace. It is a critical component for labs utilizing casting or pressing techniques.
Key Technologies That Define Performance
Beyond the primary types, specific technologies determine a furnace's efficiency, quality, and capabilities. These are features that differentiate models within a category.
Heating Method: Conventional vs. Microwave
This distinction is most relevant for sintering furnaces. Conventional units use electric resistance heating elements, which are reliable and cost-effective but require longer cycles.
Microwave sintering furnaces use microwave energy to heat the zirconia much faster, significantly reducing processing time. This speed comes at a higher initial equipment cost.
Atmosphere Control: The Role of a Vacuum
Many high-end ceramic and combination furnaces incorporate a vacuum pump. Firing porcelain under a vacuum removes air from between the porcelain particles before they fuse.
This process results in a final restoration that is denser, stronger, and has higher translucency with fewer internal bubbles or voids.
Control Systems: The Power of Programmability
Virtually all modern dental furnaces are programmable. This is not a type of furnace, but a critical feature that allows technicians to create and save custom firing schedules.
Because each dental ceramic and zirconia has a unique, manufacturer-specified temperature and time protocol, programmability is essential for achieving consistent, high-quality results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing cost, speed, and material capabilities. There is no single "best" furnace, only the best fit for a specific laboratory's goals.
Versatility vs. Specialization
A combination furnace offers excellent versatility for a lab focusing on pressable and conventional ceramics. However, a high-volume lab might prefer separate, dedicated furnaces for pressing and firing to run both processes simultaneously and optimize workflow.
Speed vs. Cost
For zirconia sintering, the choice between a conventional and a microwave furnace is a clear trade-off. Microwave units can cut hours from the sintering process, boosting daily output, but require a significantly larger initial investment.
Material Capability vs. Initial Investment
A basic ceramic furnace is the most affordable entry point but limits a lab to PFM and layered ceramic work. Investing in a high-temperature sintering furnace is more expensive but unlocks the ability to produce highly profitable, monolithic zirconia restorations.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Lab
Your decision should be guided by the services you plan to offer. Evaluate your business model and choose the equipment that directly supports it.
- If your primary focus is aesthetic porcelain work (PFM, veneers): A high-quality Ceramic Furnace, ideally with vacuum capability, is your essential tool.
- If your primary focus is high-strength zirconia restorations: A dedicated Sintering Furnace is non-negotiable for your workflow.
- If your primary focus is pressable ceramics with some porcelain layering: A Combination Furnace provides the ideal blend of functionality and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is building a full-service lab: You will ultimately need a suite of equipment, including a Sintering Furnace for zirconia and either a Combination Furnace or separate Ceramic and Burnout Furnaces for other processes.
Understanding these distinct roles empowers you to build a laboratory equipped for precision, efficiency, and growth.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Furnace | Firing porcelain for PFM crowns, veneers | Lower temperatures, firing and glazing, often with vacuum |
| Sintering Furnace | Sintering zirconia to high strength | High temperatures (>1500°C), conventional or microwave heating |
| Combination Furnace | Pressing and firing pressable ceramics | Integrated pressing mechanism, versatile for multiple processes |
| Burnout Furnace | Burning wax patterns for mold creation | Prepares molds for casting or pressing, preliminary step |
Need expert guidance on selecting the perfect dental furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for dental laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Whether you're working with porcelain, zirconia, or pressable ceramics, we can help optimize your workflow for precision, efficiency, and growth. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your dental restorations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns
- What is the importance of dental furnaces in dentistry? Ensure Strong, Precise Dental Restorations
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab
- What aspects of a dental restoration are directly impacted by the choice of a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Fit, Strength & Longevity
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations



















