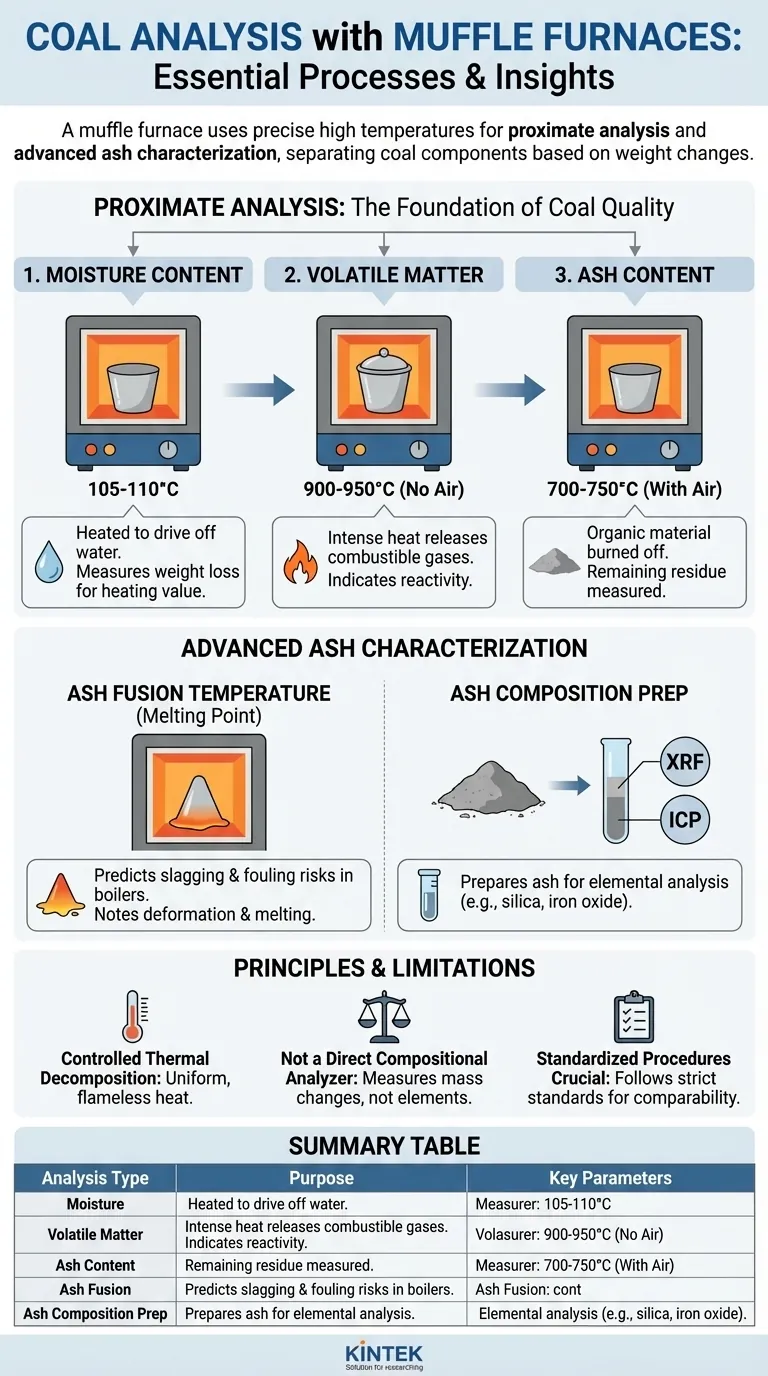
In coal analysis, a muffle furnace is the primary instrument for conducting proximate analysis, which determines the moisture, volatile matter, and ash content of a sample. It is also used to prepare samples for more advanced tests, including analyzing the melting behavior and elemental composition of the resulting ash.
A muffle furnace does not analyze the coal directly. Instead, it uses precise, controlled high temperatures to separate coal into its fundamental components—moisture, volatiles, fixed carbon, and ash—based on the weight changes that occur during heating.
The Foundation of Coal Quality: Proximate Analysis
Proximate analysis is the cornerstone of determining a coal's commercial value and combustion characteristics. The muffle furnace is essential for three of its four components.
Determining Moisture Content
A sample of coal is heated in the furnace to a relatively low temperature, typically around 105-110°C (221-230°F).
This process drives off surface and inherent moisture without burning the coal itself. The resulting weight loss is measured to calculate the moisture percentage, which impacts the coal's heating value and handling properties.
Quantifying Volatile Matter
Next, a sample is heated in a covered crucible to a much higher temperature, around 900-950°C (1650-1740°F), in the absence of air.
This intense heat drives off combustible gases (the volatile matter). The weight loss from this step, after correcting for moisture, reveals the volatile content, which is a key indicator of a coal's reactivity and flame stability.
Isolating Ash Content
The residue left after the volatile matter test is then burned in the furnace in the presence of air at a temperature of 700-750°C (1290-1380°F).
This final combustion removes all organic material, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible residue known as ash. The weight of this final material determines the ash content, a critical factor for boiler design, efficiency, and maintenance.
Advanced Ash Characterization
Once the ash has been produced in the muffle furnace, it becomes the subject of further critical analyses that predict its behavior inside a boiler.
Ash Fusion Temperature (Melting Point)
The ash generated in the furnace is pressed into a small cone and heated again. An observer notes the specific temperatures at which the cone begins to deform, soften, and eventually melt into a fluid.
These ash fusion temperatures are crucial for predicting the likelihood of slagging (molten ash deposits) and fouling (bonded ash deposits) within a boiler, which can severely impact performance and require costly cleaning.
Ash Composition Analysis
The role of the furnace here is sample preparation. The ash produced by complete combustion is collected and then analyzed by other specialized instruments, such as X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) or Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) spectrometers.
This analysis reveals the elemental makeup of the ash (e.g., silica, alumina, iron oxide), which helps predict its abrasiveness, corrosivity, and potential for use in other applications like cement manufacturing.
Understanding the Principles and Limitations
Using a muffle furnace effectively requires understanding what it does and, just as importantly, what it does not do.
The Principle: Controlled Thermal Decomposition
The muffle furnace’s core function is to provide a uniform, controlled thermal environment without the sample coming into direct contact with flames. This allows for the precise separation of components based on their different points of vaporization or combustion.
It Is Not a Direct Compositional Analyzer
A muffle furnace measures changes in mass as a function of temperature. It does not directly identify the chemical elements (like carbon, hydrogen, or sulfur) within the coal. For that, you need dedicated ultimate analysis equipment, though the furnace is used to determine the ash percentage needed for a complete ultimate analysis report.
Importance of Standardized Procedures
Results are only meaningful and comparable if tests are performed according to strict industry standards (such as ASTM or ISO). These standards dictate the exact temperatures, heating rates, time, and atmospheric conditions to ensure reproducibility across different laboratories.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The analyses you prioritize depend entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is basic fuel purchasing and combustion efficiency: Prioritize the full proximate analysis (moisture, volatile matter, ash) to understand the coal's energy content and basic burning characteristics.
- If your primary focus is power plant operations and maintenance: Pay closest attention to the ash fusion temperatures and ash composition, as these predict boiler slagging, fouling, and potential downtime.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance or ash marketing: Concentrate on the ash composition analysis to understand the makeup of the fly ash and bottom ash for proper disposal or commercial reuse.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace serves as a gateway instrument, transforming a raw coal sample into critical data for economic, operational, and environmental decisions.

Summary Table:
| Analysis Type | Purpose | Key Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content | Determines water percentage affecting heating value | 105-110°C, weight loss |
| Volatile Matter | Measures combustible gases for reactivity | 900-950°C, weight loss in absence of air |
| Ash Content | Identifies non-combustible residue for boiler efficiency | 700-750°C, weight of residue |
| Ash Fusion Temperature | Predicts slagging and fouling in boilers | Deformation, softening, melting points |
| Ash Composition Prep | Prepares ash for elemental analysis (e.g., XRF, ICP) | Sample combustion for further testing |
Enhance your coal analysis with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable muffle, tube, rotary, vacuum, atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, whether for proximate analysis, ash testing, or sample preparation. Contact us today to discuss how our products can optimize your lab's efficiency and accuracy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















