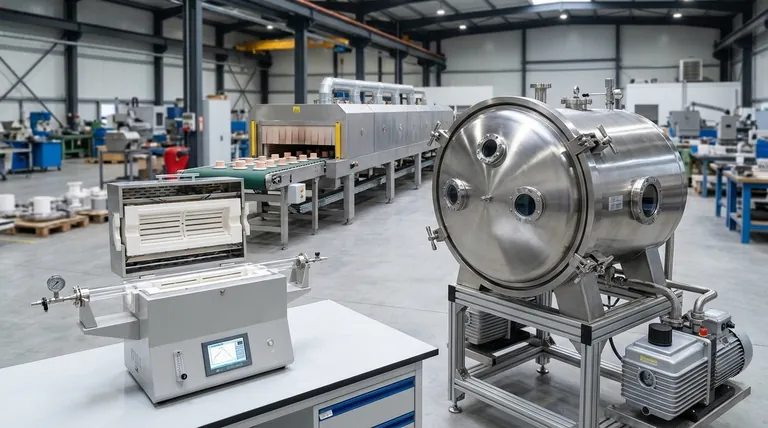
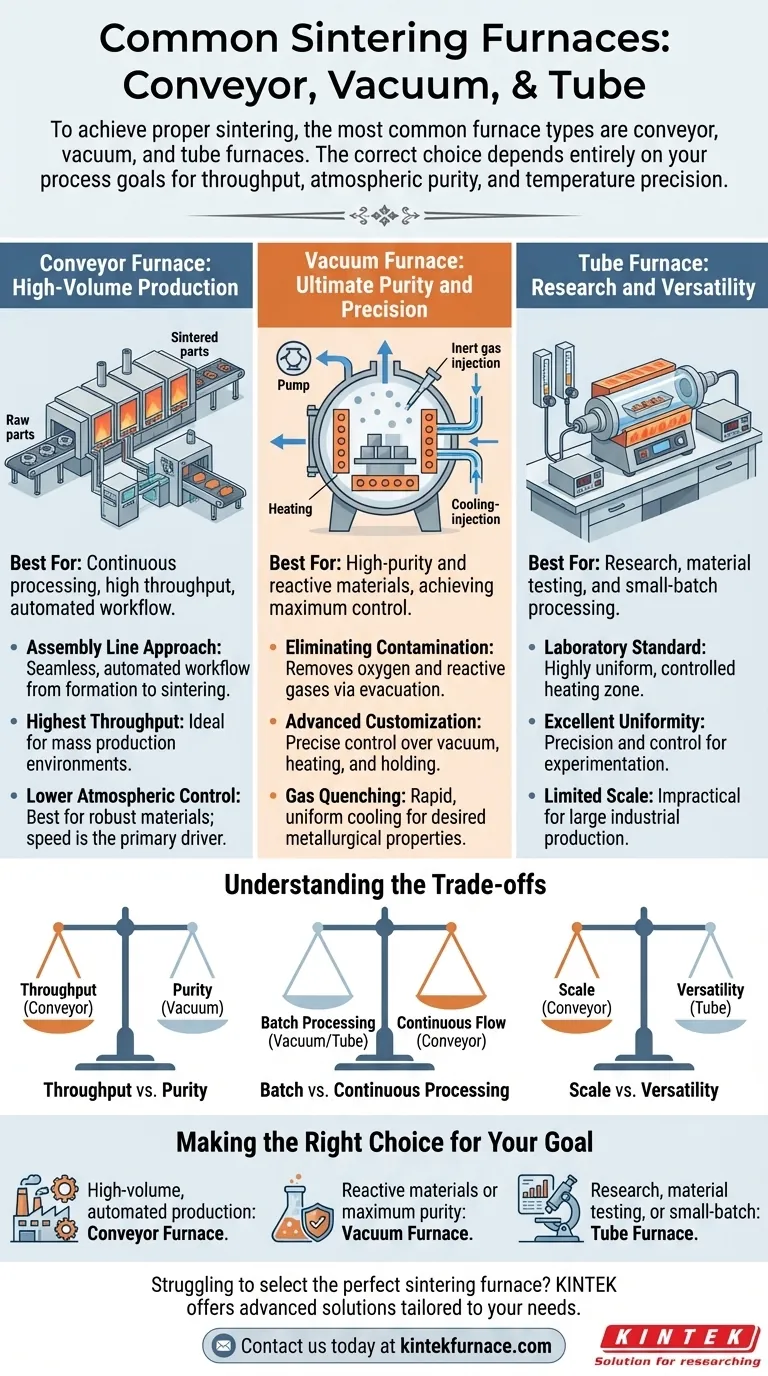
To achieve proper sintering, the most common furnace types are conveyor, vacuum, and tube furnaces. Each is engineered for different operational scales and material requirements, from high-volume industrial production to high-purity laboratory research. The correct choice depends entirely on your process goals for throughput, atmospheric purity, and temperature precision.
The selection of a sintering furnace is not a question of which is "best" overall, but which provides the ideal balance of atmospheric control, production volume, and process flexibility for your specific material and application.

Why Furnace Choice is Critical in Sintering
Sintering is a thermal process that bonds powder particles into a solid, coherent mass below the material's melting point. The furnace's environment—specifically its temperature uniformity and atmospheric composition—directly dictates the final density, strength, and integrity of the sintered part.
The Role of Temperature Control
Precise temperature management is non-negotiable. An advanced control system ensures the material reaches the correct sintering temperature at a controlled rate and is held there uniformly, guaranteeing consistent results from batch to batch.
The Importance of Atmosphere
Many materials are sensitive to oxygen at high temperatures. The furnace atmosphere must be controlled to prevent unwanted oxidation, which can compromise the material's structural and chemical properties.
High-Volume Production: The Conveyor Furnace
For mass production environments, the conveyor furnace is the standard choice. It operates on a principle of continuous processing, moving parts through different temperature zones on a conveyor belt.
The Assembly Line Approach
These furnaces are often placed in line with manufacturing presses, creating a seamless, automated workflow from part formation to final sintering. This integration is key to achieving high throughput and efficiency in an industrial setting.
Ultimate Purity and Precision: The Vacuum Furnace
When working with materials that are highly sensitive to oxidation or require the absolute highest purity, a vacuum furnace is essential. It excels at creating a tightly controlled processing environment.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
By evacuating the chamber, these furnaces remove virtually all oxygen and other reactive gases. A combination of rotary vane and Roots pumps can rapidly achieve a high vacuum, protecting sensitive materials throughout the heating and cooling cycle.
Advanced Process Customization
Modern vacuum furnaces offer exceptional control over all process parameters. Engineers can precisely adjust the vacuum level, heating rates, and holding times to develop a personalized sintering cycle tailored to the specific material's needs.
The Advantage of Gas Quenching
A key feature of many vacuum furnaces is rapid cooling, or gas quenching. After the sintering cycle, an inert gas is introduced to cool the parts quickly and uniformly, which can be critical for achieving desired metallurgical properties.
Research and Versatility: The Tube Furnace
Tube furnaces are the workhorses of research and development labs and small-scale production. They provide a highly uniform and accurately controlled heating zone within a smaller, cylindrical chamber.
The Laboratory Standard
Their smaller size and versatile configurations make them ideal for materials testing, process development, and applications like hydrogen pyrolysis or biomass conversion. They offer precision and control without the scale and expense of a large industrial furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace requires balancing competing priorities. Each type presents a distinct set of advantages and limitations that you must weigh against your project goals.
Throughput vs. Purity
Conveyor furnaces offer the highest throughput but cannot match the atmospheric purity of a sealed vacuum system. They are best for robust materials where speed is the primary driver.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Vacuum furnaces operate in batches, which is inherently slower than the continuous flow of a conveyor furnace. The trade-off for their superior atmospheric control and process flexibility is a lower production rate.
Scale vs. Versatility
Tube furnaces offer excellent temperature uniformity and versatility for experimentation. However, their limited size makes them impractical for anything beyond lab-scale work or very small production runs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by your specific operational needs and material characteristics.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, automated production: A conveyor furnace integrated into your production line is the most efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is sintering reactive materials or achieving maximum purity: A vacuum furnace provides the necessary atmospheric control and process precision.
- If your primary focus is research, material testing, or small-batch processing: A tube furnace offers the ideal combination of accurate temperature control and operational versatility.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's capabilities with your material's requirements and your production goals is the key to a successful sintering operation.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Conveyor Furnace | High-volume industrial production | Continuous processing, high throughput, automated workflow |
| Vacuum Furnace | High-purity and reactive materials | Atmospheric control, precise parameter adjustment, gas quenching |
| Tube Furnace | Research and small-scale processing | Temperature uniformity, versatility, ideal for labs |
Struggling to select the perfect sintering furnace for your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your sintering process with tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















