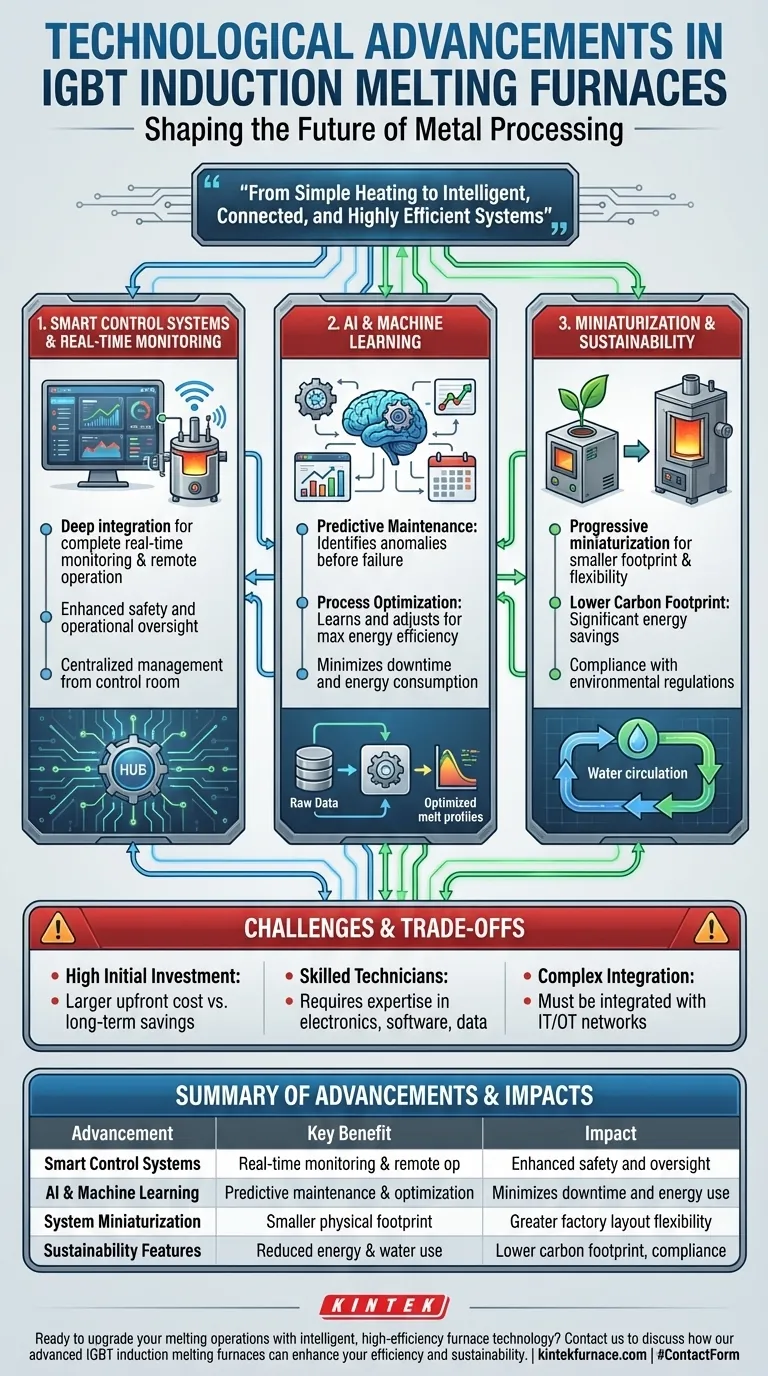
At their core, IGBT induction melting furnaces are being transformed by three key technological advancements: the deep integration of smart control systems for real-time monitoring, the application of artificial intelligence for process optimization, and the progressive miniaturization of the heating systems themselves. These innovations are moving furnaces from simple heating tools to intelligent, data-driven assets that enhance efficiency, predictability, and control over the entire melting process.
The evolution of the IGBT furnace is no longer just about melting metal faster. It is about creating an intelligent, connected, and highly efficient system that minimizes energy waste, predicts failures before they happen, and provides unprecedented operational control.

The Shift from Brute Force to Intelligent Control
Historically, furnace efficiency was a matter of raw power and robust components. Today, the focus has shifted dramatically toward intelligent control systems that optimize every stage of the melting cycle. This new paradigm is built on the foundation of IGBT technology but is being elevated by digital intelligence.
The Core of Modern Furnaces: IGBT Technology
The Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) is the foundational technology enabling these advancements. Unlike older SCR-based systems, IGBT furnaces provide a constant power output regardless of the load or the condition of the furnace lining.
This consistency is crucial for melting materials like stainless steel, copper, and aluminum efficiently. Furthermore, IGBTs produce minimal harmonic pollution, ensuring they don't disrupt the factory's power grid or interfere with other sensitive equipment.
Smart Integration: Real-Time Monitoring and Remote Operation
Modern furnaces now feature all-digital embedded software running on processors like DSP or ARM. These systems provide rich communication interfaces that are the gateway to smart factory integration.
This allows for complete real-time monitoring of every operational parameter. More importantly, it enables full remote control, allowing skilled technicians to manage and troubleshoot furnaces from a central control room, improving both safety and operational oversight.
The Power of AI and Machine Learning
The most transformative advancement is the use of AI and machine learning. By analyzing historical and real-time data, these algorithms can unlock two critical benefits.
First is predictive maintenance. The AI can identify subtle anomalies in performance that indicate a potential component failure, allowing for scheduled maintenance before a catastrophic and costly breakdown occurs.
Second is process optimization. The system can learn the most energy-efficient melting profile for specific metals and loads, automatically adjusting power cycles to minimize energy consumption while achieving faster melting times.
Redefining Physical and Environmental Footprints
Beyond digital intelligence, advancements are also impacting the physical and environmental profile of modern furnaces. The goals are greater flexibility in plant layout and a significant reduction in environmental impact to meet modern sustainability standards.
Miniaturization and Its Practical Impact
A clear trend is the miniaturization of induction heating systems. As components become more efficient and power-dense, the overall footprint of the equipment shrinks.
This provides greater flexibility in factory floor design and can enable new, more localized melting applications that were previously impractical due to space constraints.
Driving Sustainability and Compliance
Sustainability is a primary driver of innovation. The inherent efficiency of IGBT technology already offers significant energy savings and faster processing times compared to older methods.
This is further enhanced by features like closed-loop water circulation systems with heat exchangers, which prevent scale buildup and maintain peak efficiency. These combined efficiencies help companies reduce their carbon footprint and comply with increasingly strict environmental regulations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While these advancements offer profound benefits, adopting them requires a clear understanding of the associated challenges. Objectivity is crucial when considering such a significant investment.
The High Initial Investment
The most significant barrier is the high initial capital cost. Advanced IGBT furnaces integrated with smart technology and AI represent a much larger upfront investment than traditional, less sophisticated systems. This must be weighed against the long-term operational savings in energy, maintenance, and uptime.
The Demand for Skilled Technicians
These are not simple machines. Managing, maintaining, and leveraging the full capability of a smart furnace requires technicians with advanced skills in electronics, software, and data analysis. The need for this specialized talent can be a significant operational hurdle.
The Complexity of Integration
A smart furnace does not exist in a vacuum. To achieve its full potential, it must be integrated into the facility's broader IT and operational technology (OT) network. This can introduce a layer of technological complexity that requires careful planning and expertise to manage effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The decision to invest in a new IGBT furnace depends entirely on your primary operational goals. By clarifying your main driver, you can select the technology that will deliver the most value.
- If your primary focus is maximizing operational efficiency and uptime: Prioritize systems with proven AI-driven predictive maintenance and process optimization features.
- If your primary focus is reducing energy costs and meeting sustainability goals: Focus on the core IGBT efficiency gains, combined with smart monitoring to track and minimize energy consumption per melt.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility or you have space constraints: Investigate the latest generation of miniaturized induction systems to see how they can fit into your workflow.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace technology is about investing in a more predictable, efficient, and sustainable future for your melting operations.
Summary Table:
| Advancement | Key Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Control Systems | Real-time monitoring & remote operation | Enhanced safety and operational oversight |
| AI & Machine Learning | Predictive maintenance & process optimization | Minimizes downtime and energy consumption |
| System Miniaturization | Smaller physical footprint | Greater flexibility in factory layout |
| Sustainability Features | Reduced energy use & water circulation | Lower carbon footprint and regulatory compliance |
Ready to upgrade your melting operations with intelligent, high-efficiency furnace technology? KINTEK's advanced IGBT induction melting furnaces are engineered for labs and industrial facilities that demand precision and reliability. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique requirements. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to discuss how our technology can enhance your efficiency, predictability, and sustainability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















