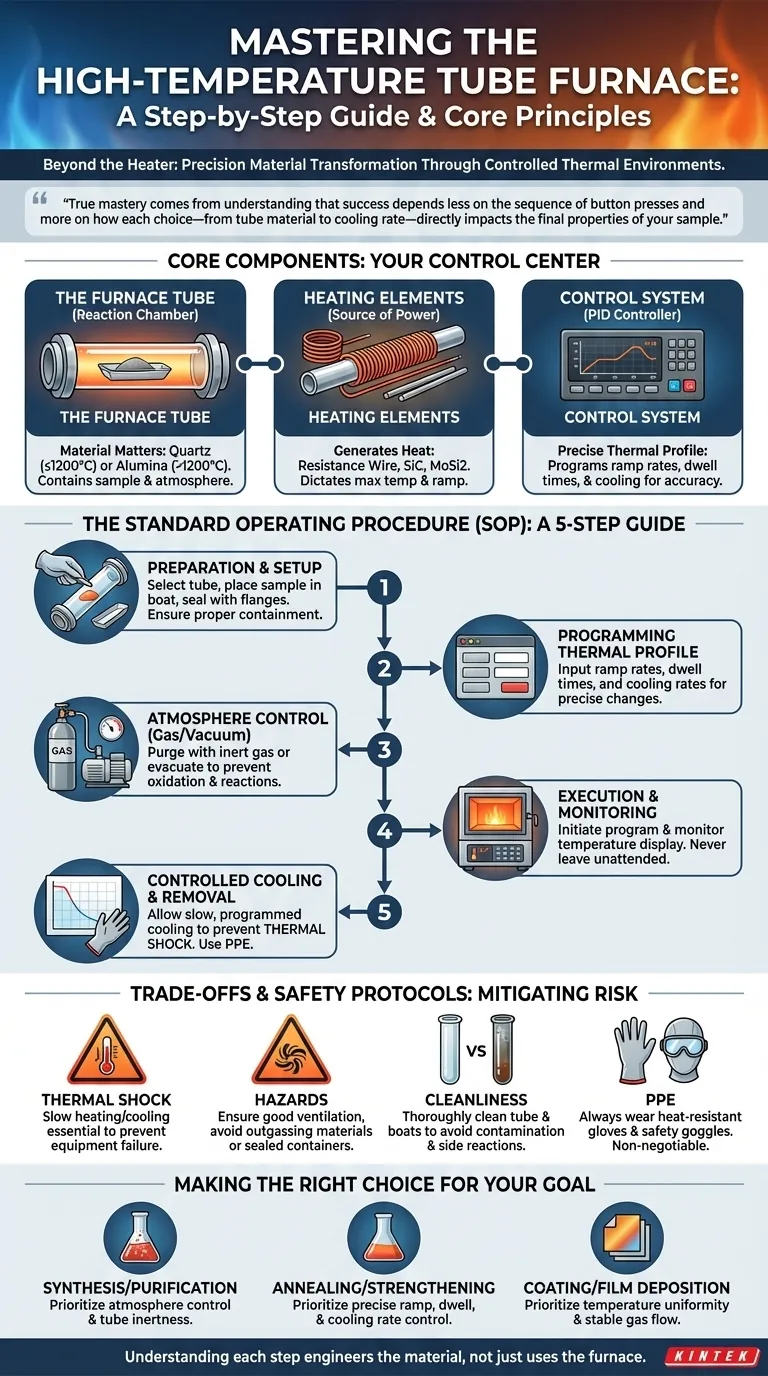
At its core, operating a high-temperature tube furnace involves a sequence of precise steps: preparing the sample and tube, programming a specific heating and cooling profile, controlling the internal atmosphere, and executing the process safely. The goal is to create a perfectly controlled thermal environment to alter or synthesize materials.
A tube furnace is not just a heater; it is a precision instrument for material transformation. True mastery comes from understanding that success depends less on the sequence of button presses and more on how each choice—from tube material to cooling rate—directly impacts the final properties of your sample.
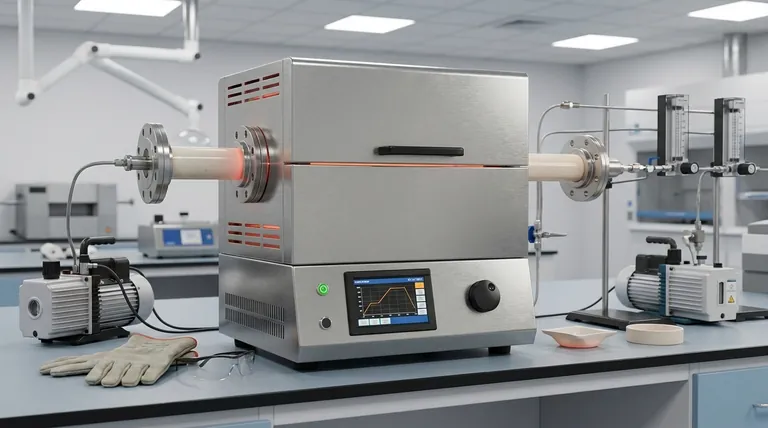

Understanding the Core Components
Before initiating a procedure, it is crucial to understand the function of the furnace's primary components. Your control over these parts determines the outcome of your work.
The Furnace Tube: Your Reaction Chamber
The tube is the heart of the furnace, containing your sample and atmosphere. The material you choose is critical.
Quartz tubes are common due to their high purity and excellent thermal shock resistance but are typically limited to temperatures around 1200°C.
Alumina or other ceramic tubes are required for higher temperatures (up to 1800°C). They are more robust at extreme heat but can be more susceptible to cracking from rapid temperature changes.
The Heating Elements: The Source of Power
These elements surround the tube and generate heat when electricity is applied. Common types include resistance wire for lower temperatures, silicon carbide (SiC) for mid-range temperatures, and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) for the highest temperature applications. Their design dictates the furnace's maximum temperature and ramp rate.
The Control System: Your Command Center
Modern furnaces use a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller for exceptional temperature accuracy. This system allows you to program a precise thermal profile, including ramp rates (how fast it heats up), dwell times (how long it holds a temperature), and cooling rates. Multi-zone furnaces have separate controls for different sections of the tube, enabling highly uniform temperature or creating specific thermal gradients.
The Standard Operating Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
Following a systematic procedure ensures both the safety of the operator and the integrity of the experiment.
Step 1: Preparation and Setup
First, select the appropriate process tube for your temperature and chemical requirements. Inspect it carefully for any cracks or defects.
Place your sample inside the tube, typically in a ceramic or quartz boat. Position the sample in the center of the furnace's heating zone for maximum temperature uniformity.
Securely mount the tube within the furnace, ensuring it is properly supported. Attach end flanges to seal the tube, connecting gas or vacuum lines as needed. A proper seal is critical for atmospheric control.
Step 2: Programming the Thermal Profile
Using the PID controller, input your desired temperature profile. This includes the target temperature, the rate of heating (ramp rate), and the duration at the target temperature (dwell time). Complex processes may involve multiple heating and cooling steps.
Step 3: Controlling the Atmosphere (Gas or Vacuum)
If your process requires an inert atmosphere, purge the tube with a gas like argon or nitrogen to remove oxygen. If a vacuum is needed, connect a vacuum pump and evacuate the tube to the desired pressure. This step prevents unwanted oxidation or reactions.
Step 4: Execution and Monitoring
Initiate the heating program. Monitor the furnace's display to ensure the temperature follows the programmed profile accurately. Never leave a high-temperature furnace completely unattended during operation.
Step 5: Controlled Cooling and Sample Removal
Once the heating cycle is complete, the furnace must cool down. A slow, programmed cooling rate is essential to prevent thermal shock, which can crack the process tube or damage the sample.
Do not open the furnace or remove the sample until it has cooled to a safe temperature, typically well below 200°C. Always wear heat-resistant gloves when handling components that have been in the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Protocols
Operational success is directly tied to mitigating risk. High temperatures and controlled atmospheres introduce hazards that must be respected.
The Dangers of Thermal Shock
The most common cause of tube failure is thermal shock. The trade-off for faster processing is a significantly higher risk of destroying your equipment. Always favor gradual heating and cooling rates, especially when working with ceramic tubes.
Atmospheric and Material Hazards
Ensure your workspace is well-ventilated, especially when working with materials that may outgas volatile compounds or when using process gases. Never heat unknown materials or sealed containers that could build pressure and rupture.
The Importance of Cleanliness
Contamination is the enemy of repeatable results. Any residue left in the process tube from a previous run can become a vapor at high temperatures, contaminating your new sample or reacting with the tube itself. Thoroughly clean the tube and sample boats before every use.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is Non-Negotiable
Always wear safety goggles and heat-resistant gloves when operating the furnace or handling hot components. The risk of severe burns or eye injury is significant.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational focus will change depending on your specific application. Tailor your procedure to achieve your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis or purification: Prioritize atmosphere control and tube inertness to prevent unwanted side reactions.
- If your primary focus is annealing or structural strengthening: Prioritize precise control over the temperature ramp, dwell, and especially the cooling rate, as this governs the final microstructure.
- If your primary focus is coating or film deposition: Prioritize temperature uniformity across the entire heating zone and stable control of gas flow rates.
By understanding how each operational step influences the final product, you move from simply using the furnace to truly engineering a material.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Actions | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation and Setup | Select tube, place sample, seal with flanges | Ensure proper containment and sample positioning |
| 2. Programming Thermal Profile | Input ramp rates, dwell times, cooling rates | Achieve precise temperature control for material changes |
| 3. Atmosphere Control | Purge with inert gas or evacuate with vacuum | Prevent oxidation and unwanted reactions |
| 4. Execution and Monitoring | Initiate program, monitor temperature | Ensure process follows set profile safely |
| 5. Controlled Cooling and Removal | Allow slow cooling, use PPE for handling | Avoid thermal shock and ensure operator safety |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with tailored high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your material transformation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















